MITHRAMYCIN A
Synonym(s):Aureolic acid;Mithramycin A - CAS 18378-89-7 - Calbiochem;Plicamycin;Plicamycin, Mithramycin
- CAS NO.:18378-89-7
- Empirical Formula: C52H76O24
- Molecular Weight: 1085.15
- MDL number: MFCD00135618
- EINECS: 634-048-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 15:53:33
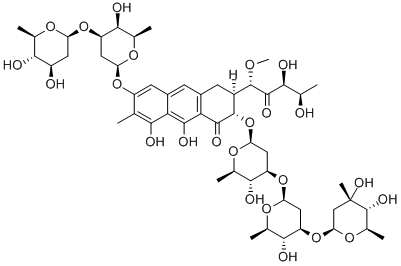
What is MITHRAMYCIN A?
Toxicity
The most important form of toxicity associated with the use of plicamycin consists of a dose-related bleeding syndrome which usually begins with an episode of epistaxis. Plicamycin crosses the blood-brain barrier; the concentration found in brain tissue is low but it persists longer than in other tissues.
Description
Mithramycin is an antineoplastic antibiotic produced by Streptomyces plicatus. It is well known as the aureolic acid antitumor antibiotic that inhibits both cancer growth and bone resorption by cross-linking GC-rich DNA, thus blocking binding of Sp-family transcription factors to gene regulatory elements. Transcription of c-Src, a gene implicated in many human cancers and required for osteoclast-dependent bone resorption, is regulated by the binding of Sp factors to specific elements in its promoter. Therefore, this gene represents an important anticancer target and a potential lead target through which mithramycin displays action against osteoclastic bone resorption via an unknown mechanism. Hazards of handling this drug by the health-care personnel arise from a combination of factors: (1) its inherent toxicity and (2) the extent to which workers are exposed to the drug in the course of carrying out their duties. This exposure may be through inadvertent ingestion of the drug on foodstuffs (e.g., workers’ lunches), inhalation of drug dusts or droplets, or direct skin contact. Mithramycin has been used to decrease bone resorption in patients with humoral hypercalcemia and Paget’s disease.
Chemical properties
yellow powder
The Uses of MITHRAMYCIN A
Mithramycin was the first of the aureolic acid class of antitumour antibiotics, isolated from Streptomyces. Mithramycin inhibits transcription and protein synthesis by non-covalent binding with G-C-rich duplex DNA in the presence of magnesium and zinc ions. Mithramycin also induces differentiation of leukemic cells accompanied by an early decrease in c-myc expression, and selectively inhibits collagen-1 gene expression in human fibroblasts.
The Uses of MITHRAMYCIN A
Transcription inhibitor
The Uses of MITHRAMYCIN A
Mithramycin A was the first of the aureolic acid class of antitumor antibiotics, isolated from Streptomyces. Mithramycin inhibits transcription and protein synthesis by non-covalent binding with G-C-rich duplex DNA in the presence of magnesium and zinc ions. Mithramycin also induces differentiation of leukemic cells accompanied by an early decrease in c-myc expression, and selectively inhibits collagen-1 gene expression in human fibroblasts.
Background
Plicamycin is an antineoplastic antibiotic produced by Streptomyces plicatus. It has been used in the treatment of testicular cancer, Paget's disease of bone, and, rarely, the management of hypercalcemia. The manufacturer discontinued plicamycin in 2000.
Indications
For the treatment of testicular cancer, as well as hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria associated with a variety of advanced forms of cancer.
What are the applications of Application
Mithramycin A is a polymerase inhibitor that binds to GC rich sequences located in the minor groove of DNA
Indications
Plicamycin (mithramycin, Mithracin) is one of the chromomycin group of antibiotics produced by Streptomyces tanashiensis. Plicamycin binds to DNA and inhibits transcription. It also inhibits resorption of bone by osteoblasts, thus lowering serum calcium levels.Very little is known about its distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Because of its severe toxicity, plicamycin has limited clinical utility.The major indication for plicamycin therapy is in the treatment of life-threatening hypercalcemia associated with malignancy. Plicamycin also can be used in the palliative therapy of metastatic testicular carcinoma when all other known active drugs have failed.
Definition
ChEBI: Mithramycin is a carbohydrate-containing antibiotic, an anthracycline antibiotic, an aureolic acid and a secondary alpha-hydroxy ketone. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent, an EC 2.7.7.6 (RNA polymerase) inhibitor and a metabolite.
What are the applications of Application
Mithramycin, recently renamed plicamycin, was found in the culture broth of Streptomyces argillaceus and S. tanashiensis by Abbott Laboratories in 1952. It is structurally related to chromomycin A3. Mithramycin shows strong inhibitory activity against malignant cells of human origin. It acts by inhibition of the DNA-directed RNA synthesis through binding with DNA. Mithramycin is used intravenously to treat cancers of the embryonal cells, seminoma, choriocarcinoma, etc.
brand name
Mithracin (Pfizer) [Name previously used: Mithramycin.].
General Description
Chemical structure: aureolic acid
Biological Activity
Anticancer antibiotic that selectively binds to G-C-rich DNA in the presence of Mg 2+ or Zn 2+ , inhibiting RNA and DNA polymerase action. Inhibits c-myc expression and induces myeloid differentiation of HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Anticancer antibiotic. Inhibits transcription and protein synthesis. Binds to DNA in native chromatin. Substrate of Pgp in MDR phenotypes.
Pharmacokinetics
Plicamycin is lethal to Hela cells in 48 hours at concentrations as low as 0.5 micrograms per milliliter of tissue culture medium. Plicamycin has shown significant anti-tumor activity against experimental leukemia in mice when administered intraperitoneally.
Metabolism
Not Available
storage
Store at -20°C
Purification Methods
Purify mithramycin A by crystallisation from CHCl3. It is soluble in MeOH, EtOH, Me2CO, EtOAc, Me2SO and H2O, and moderately soluble in CHCl3, but is slightly soluble in *C6H6 and Et2O. It is a fluorescent antitumour agent used in flow cytometry. [Thiem & Meyer Tetrahedron 37 551 1981, NMR: Yu et al. Nature 218 193 1968, Beilstein 17/1 V 672.]
Toxicity evaluation
Mithramycin inhibits mRNA and protein synthesis by adhering to DNA. Mithramycin appears to affect bone resorption by stimulating osteoclast activity and results in hypocalcemia and hypophosphatemia. It is believed to lower serum calcium concentrations, but the exact mechanism is unknown. It may act by blocking hypercalcemic action of vitamin D or by inhibiting the effect of parathyroid hormone on osteoclasts. Its inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA synthesis appears to render osteoclasts unable to fully respond to parathyroid hormone with the biosynthesis necessary for osteolysis.
References
1) Lin?et al. (2007),?Mithramycin A inhibits DNA methyltransferase and metastasis potential of lung cancer cells; Anticancer Drugs,?18?1157 2) Jia?et al.?(2010),?Combined treatment of pancreatic cancer cells with mithramycin A and tolfenamic acid promotes Sp1 degradation and synergistic anti-tumor activity; Cancer Res.,?70?1111 3) Lee?et al. (2006),?Mithramycin A sensitizes cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by down-regulation of XIAP gene promoter through Sp1 sites; Mol. Cancer Ther.,?5?2737
Properties of MITHRAMYCIN A
| Melting point: | 180-183 °C |
| Boiling point: | 761.72°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D20 -51° (c = 0.4 in ethanol) |
| Density | 1.1576 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6500 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 20 mg/ml) or in Ethanol (up to 10 mg/ml) |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 4.54±0.60(Predicted) |
| color | Red to brown |
| Merck | 13,7619 |
| BRN | 5236667 |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Plicamycin (18378-89-7) |
Safety information for MITHRAMYCIN A
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for MITHRAMYCIN A
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Mithramycin A from Streptomyces plicatus CAS 18378-89-7View Details
Mithramycin A from Streptomyces plicatus CAS 18378-89-7View Details
18378-89-7 -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4