Methidathion
Synonym(s):S-2,3-Dihydro-5-methoxy-2-oxo-1,3,4-thiodiazol-3-yl-methyl-O,O-dimethyl-phosphodithioate
- CAS NO.:950-37-8
- Empirical Formula: C6H11N2O4PS3
- Molecular Weight: 302.33
- MDL number: MFCD00055286
- EINECS: 213-449-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
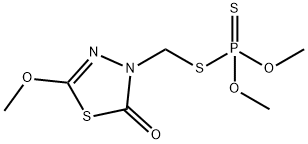
What is Methidathion?
Description
Methidathion is an organophosphate insecticide that inhibits insect cholinesterase. It reduces cattle lice (L. vituli, D. bovis, and H. eurysternus) infestation by 99.1% when administered topically at a dose of 3.5 mg/kg. Methidathion is selectively toxic to lice over cattle, only inhibiting cattle plasma acetylcholinesterase activity by 20% with no effect on survival when administered topically at a dose of 24 mg/kg. It increases sister chromatid exchange (SCE) in a concentration-dependent manner and induces cell cycle arrest at the M1 phase in V79 cells when used at a concentration of 40 μg/ml. Dietary administration of methidathion (1.4-4.7 mg/kg) increases alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, sorbitol dehydrogenase, and alkaline phosphatase activity, inhibits cholinesterase, and induces chronic liver inflammation in male beagle dogs. It also induces loss of striation and myocytolysis of cardiomyocytes and reduces serum cholinesterase activity in rats when administered orally at a dose of 5 mg/kg.
Description
Methidation is used as an insecticide. Cross-sensitivity was described to dichlorvos.
Chemical properties
Crystalline solid. Almost insoluble in water; soluble in common organic solvents.
Chemical properties
Methidathion is a colorless crystalline pesticide at room temperature. It is sparingly soluble in water, but very soluble in octanol, ethanol, xylene, acetone, and cyclohexane. Methidathion is a non-systemic organophosphorous insecticide and acaricide with stomach and contact action. It is used to control a variety of insects and mites on crops and fruit plants. Methidathion is highly toxic to animals and humans. The US EPA grouped methidathion as a class I toxic substance and as an RUP.
Chemical properties
Methidathion is a colorless crystalline solid.
The Uses of Methidathion
Methidathion is an organophosphate insecticide and was examined for human health and toxicological concerns.
The Uses of Methidathion
Insecticide, acaricide.
The Uses of Methidathion
Insecticide and acaricide.
The Uses of Methidathion
Methidathion is used to control a wide range of insects in many different crops.
Definition
ChEBI: Methidathion is an organic thiophosphate and an organothiophosphate insecticide. It has a role as an EC 3.1.1.7 (acetylcholinesterase) inhibitor, an acaricide and an agrochemical. It is functionally related to a 5-methoxy-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3H)-one.
General Description
Methidathion is a colourless crystalline pesticide at room temperature. It is sparingly soluble in water but very soluble in octanol, ethanol, xylene, acetone, and cyclohexane.
Air & Water Reactions
Stable in neutral or weak acid solution. Hydrolyzed by alkali. [EPA, 1998].
Reactivity Profile
Organophosphates, such as Methidathion, are susceptible to formation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion, a cholinesterase inhibitor.
Health Hazard
Methidathion is poisonous to humans. Its toxic effects are by action on the nervous system. Human volunteers ingesting 0.11 mg/kg/day for 6 weeks had no clinical effects.
Health Hazard
Acute and prolonged exposures to methidathion cause poisoning in animals and humans. The symptoms include, but are not limited to, nausea, vomiting, cramps, diarrhea, salivation, headache, dizziness, muscle twitching, diffi culty breathing, blurred vision, and tightness in the chest, pulmonary edema, respiratory depression, and respiratory paralysis. Acute exposures to high concentrations of methidathion cause intense breathing problems, including paralysis of the respiratory muscles.
Fire Hazard
(Non-Specific -- Organophosphorus Pesticide, n.o.s.) Container may explode in heat of fire. Fire and runoff from fire control water may produce irritating or poisonous gases. Stable in neutral or weak acid solution. Hydrolyzed by alkali.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide: A U.S. EPA restricted Use Pesticide (RUP). Not approved for use in EU countries . There are no residential uses for methidathion. Methidathion is a non-systemic organophosphate insecticide and acaricide with stomach and contact action. The compound is used to control a variety of insects and mites in many crops such as nuts, artichokes, olives, cotton, fruits, vegetables, tobacco, alfalfa, and sunflowers, and also in greenhouses and on rose cultures. It is especially useful against scale insects.
Trade name
CIBA-GEIGY® GS 13005®; COBRACIDE®; FISONS NC® 2964; GEIGY® 13005; GS-13005®; SOMONIC®; SOMONIL®; SURPRACIDE®; SUPRATHION®; ULTRACID®; ULTRACIDE®
Contact allergens
Methidation is an organophosphorus compound used as an insecticide. Cross-sensitivity was described to Dichlorvos.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and skin contact. Moderately toxic by inhalation. Human mutation data reported. Human systemic effects: coma, lachrymation, miosis. A severe eye irritant. An insecticide. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx, POx, and SOx
Potential Exposure
Those involved in the manufacture, formulation, and application of this nonsystemic insecticide.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove any contact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least 15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts the skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Speed in removing material from skin is of extreme importance. Shampoo hair promptly if contaminated. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medical facility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit. Keep victim quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Effects may be delayed; keep victim under observation.
Carcinogenicity
In a chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity study, rats were fed diets with 0, 4, 40, or 100 ppm methidathion (equivalent to 0, 0.16, 1.72, or 4.91 mg/kg/day (males) and 0, 0.22, 2.20, or 6.93 mg/kg/day (females)) for 2 years, and there was no evidence of carcinogenicity in either males or females . Body weight decreases occurred in both sexes at the highest dose throughout the study.
Environmental Fate
Photolytic. When methidathion in an aqueous buffer solution (25°C and pH 7.0) was
exposed to filtered UV light (l >290 nm) for 24 hours, 17% decomposed to 5-methoxy-
3H-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-one. At 50°C, 56% was degraded after 24 hours. Degradation
occurred via hydrolysis of the thiol bond of the phosphorodithioic ester. Under acidic and
alkaline conditions, hydrolytic cleavage occurred at the C-S and P-S bonds, respectively
(Burkhard and Guth, 1979). Smith et al. (1978) demonstrated that methidathion degraded
to methidathion oxon at a faster rate in six air-dried soils than in moist soils. Half-lives
for methidathion in the air-dried soils ranged from 19 to 110 days. In addition, methidathion
degraded faster in an air-dried soil exposed to ozone (half-lives 2.5 to 7.0 days).
Chemical/Physical. Emits toxic fumes of phosphorus, nitrogen and sulfur oxides when
heated to decomposition (Sax and Lewis, 1987). Methidathion oxon was also found in
fogwater collected near Parlier, CA (Glotfelty et al., 1990). It was suggested
Metabolic pathway
The main route of methidathion metabolism in animals and plants is via hydrolysis or oxidation (or hydrolysis of the oxon) to yield the 3- thiomethyl-5-methoxy-1,3,4-thiadiazoldee rivative. This may either lose methanethiol to yield the methoxy-1,3,4thiadiazolinone or be conjugated as the cysteine derivative via a route involving desmethylmethidathion (in plants). In plants and mammals an additional route involves the methylation of the thiomethyl methoxy-1,3,4-thiadiazolinone derivative by S-adenosylmethionine followed by oxidation to the corresponding sulfoxide and sulfone which are excreted in the urine in mammals. Another route of detoxification in insects, plants and mammals is via demethylation of the 5-methoxy group of the 1,3,4-thiadiazolinone ring to form a metabolite which may be conjugated in plants. As is common with many phosphorothioates, the active acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, methidaoxon, is usually detected in metabolism studies but at very low concentration due to its rapid rate of hydrolysis.
Metabolism
The principal degradation route is similar both in animals and plants, that is, cleavage of the P?S bond via oxidative desulfuration (activation) to the oxon followed by hydrolysis to O,O-dimethyl hydrogen phosphorothioate and the 3-thiomethyl-5-methoxythiadiazole derivative, which is further degraded or conjugated. Methidathion is rapidly degraded in soil; DT50 in soil is 3–18 d.
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Store in a secure poison location. Prior to working with this chemical you should be trained on its proper handling and storage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area.
Shipping
Color code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Store in a secure poison location. Prior to working with this chemical, personnel should be trained on its proper handling and storage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, wellventilated area
Degradation
Methidathion is rapidly hydrolysed in alkaline solution but it is relatively stable in neutral and slightly acidic media. The DT50 for hydrolysis at pH 13 (25 °C) was 30 min (PM).
Toxicity evaluation
The acute oral LD50 for rats is 25–54 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats is 3.6 mg/L air. NOEL (2 yr) for rats is 4 mg/kg diet (0.2 mg/kg/d). ADI is 1 μg/kg b.w. Methidathion administered to animals is rapidly metabolized and excreted.
Incompatibilities
None listed
Waste Disposal
Treat with strong alkali, mix with soil and bury in the case of small quantities. For large quantities, use incineration with effluent gas scrubbing
Precautions
Occupational workers should be very careful during use and chemical management of methidathion. As this chemical substance is a highly toxic pesticide, it has been grouped by the US EPA as toxicity class I. The containers and labels of the products should bear the signal word DANGER. Methidathion is an RUP, except for use in nurseries, and on saffl ower and sunfl owers.
Properties of Methidathion
| Melting point: | 39-40°C |
| Boiling point: | 347.7±52.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.51 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 2.5×10-4 Pa (20 °C) |
| Flash point: | 100 °C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | solid |
| pka | -4.17±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | Colourless |
| Water Solubility | 0.024 g/100 mL |
| BRN | 619915 |
| Stability: | Air Sensitive, Moisture Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 950-37-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Methidathion(950-37-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Methidathion (950-37-8) |
Safety information for Methidathion
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Methidathion
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Methidathion CAS 950-37-8View Details
Methidathion CAS 950-37-8View Details
950-37-8 -
 Methidathion CAS 950-37-8View Details
Methidathion CAS 950-37-8View Details
950-37-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8