methallenestril
- CAS NO.:517-18-0
- Empirical Formula: C18H22O3
- Molecular Weight: 286.369
- MDL number: MFCD00068962
- EINECS: 2082326
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-04 17:34:39
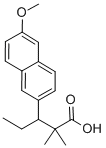
What is methallenestril?
Chemical properties
Crystals.Soluble in ether, vegetable oils.
Originator
Vallestril ,Searle,US,1952
The Uses of methallenestril
Medicine (estrogen).
Definition
ChEBI: Methallenestril is a member of naphthalenes.
Manufacturing Process
A first step involves the preparation of 2-cyano-6-methoxynaphthalene
(cyanonerolin). 90 g of 2-bromo-6-methoxynaphthalene are heated with 60 g
of cuprous cyanide in a metal bath at 240° to 250°C stirring for one hour. At
the instant when the cuprous cyanide begins to react and dissolves, the mass
turns brown, liquefies and heats up strongly. The molten mass is poured onto
a cold surface, is pulverized and sifted. This powder is treated with dilute
ammonia (1 liter of water to 300 cc of commercial ammonia solution). The
solution is filtered on a Buchner filter and the precipitate that remains on the
filter is washed with dilute ammonia and then with water.
After drying, the residue is treated in a Kumagawa extracting apparatus with
boiling benzene. The benzene is evaporated and the residue is distilled in
vacuo. About 50 g of cyanonerolin (BP = 205° to 208°C/14 mm) are obtained
with a yield of about 70%. By recrystallization in 200 cc of methyl alcohol, 40
g of the product are obtained in absolutely pure state, in the shape of
beautiful colorless needles (MP = 103°C with the Maquene block). By
concentrating the mother liquor to half its original volume, a further 3.6 g of
pure product are obtained.
The 2-cyano-6-methoxy-naphthaleneis in turn converted by successive
reactions into: (a) β-ketonic ester, (b) ester-alcohol, (c) β-ethylene ester by
dehydration, (d) saturated ester, and (e) [3-(6-methoxy-2-naphthyl)]2,2-
dimethyl pentanoic acid which is the required product.
(A) Obtaining a β-Ketonic Ester by Reacting Ethyl Bromoisobutyrate with
Cyanonerolin: 9 g of cyanonerolin are heated in a reflux apparatus for 40
minutes with 7 g of zinc and 19 g of ethyl bromoisobutyrate in the presence of 150 cc of anhydrous benzene. After cooling, the mixture is filtered to
eliminate unreacted zinc and is hydrolyzed by stirring for one hour with dilute
sulfuric acid (10 cc of sulfuric acid to 200 cc of water). The benzene layer is
washed, dried and the solvent is eliminated. It is purified by recrystallization
in methyl alcohol. 12.5 g of ketonic ester (MP = 72.5° to 73.5°C) are thus
obtained in the form of large prismatic crystals.
(B) Obtaining an Ester-Alcohol by Reacting Magnesium Ethyl Bromide with the
Previous Ketonic Ester: 10 g of the previous ester dissolved in 40 cc of
anhydrous benzene are gradually poured while stirring into an iced solution of
magnesium ethyl bromide prepared from 1.035 g of magnesium, 4.15 cc of
ethyl bromide and 40 cc of anhydrous ether. After heating in a reflux
apparatus for one-half hour, the mixture is poured into ice in the presence of
ammonium chloride.
After washing the ether-benzene layer, the solvents are eliminated in vacuo
and an ester-alcohol is thus obtained with a yield of 98%, in the form of a
transparent resin. This resin, if treated with petroleum ether, yields 6.35 g of
ester-alcohol in the form of fine needles (MP = 66.68°C) which are very
soluble in the chief organic solvents and in petroleum ether.
(C) Conversion into Ethyl [3(6-Methoxy-2-Naphthyl)] 2,2-Dimethyl-3-
Pentanoate by Dehydrating the Previous Ester-Alcohol: The semi-oily raw
product of the previous reaction is dehydrated by heating with its own weight
of potassium bisulfate to 180°C until boiling stops. After cooling, the magma
is removed from the anhydrous ether in small portions. The ether is then
evaporated and an ethylene ester is obtained in the form of an oil which
slowly solidifies, with a yield of 98%. The product, after being purified by
chromatography, melts at 48° to 51°C.
(D) Obtaining Ethyl [3-(6-Methoxy-2-Naphthyl)] 2,2-Dimethyl Pentanoate by
Hydrogenation of the Previous Ethylene Ester: 3.5 g of the previous ethylene
ester, purified by chromatography, are hydrogenated in the presence of 3.6 g
of platinum in 30 cc of ether. The quantity of hydrogen fixed corresponds to
the theoretical quantity calculated. After filtering, the ether is evaporated,
3.45 g of ester are thus obtained in the form of an oil which quickly solidifies.
Purification is effected by chromatography.
(E) Obtaining [3-(6-Methoxy-2-Naphthyl)] 2,2-Dimethyl Pentanoic Acid: 2.5 g
of the previous ester are saponified by means of 15 cc of soda lye and 25 cc
of methyl glycol. The mixture is boiled for one hour, diluted with water and,
after cooling, is treated twice with ether in order to eliminate the remaining
neutral fractions. The aqueous layer is precipitated by means of 15 cc of
acetic acid. 2.1 g of raw acid are obtained. After effecting two crystallizations
in 10 parts of acetic acid mixed with 3 parts of water, fine needles are
obtained which are grouped in rosettes and melt at 131.5° to 132.5°C.
Therapeutic Function
Estrogen
Properties of methallenestril
| Melting point: | 139-140° |
| Boiling point: | 437.0±20.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.108±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 4.88±0.50(Predicted) |
Safety information for methallenestril
Computed Descriptors for methallenestril
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid Electrolytic Iron Powder 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole N-Boc-L-proline methyl ester 2-(BOC-Amino)4-picoline 1-(4-Methylphenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,3-benzotriazole 1-(2-Chlorobenzyl)-4-nitro-1H-pyrazoleRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 181228-33-1 99%View Details
181228-33-1 99%View Details
181228-33-1 -
 Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
1169630-40-3 -
 1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 -
 127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5