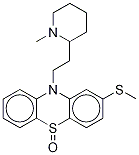
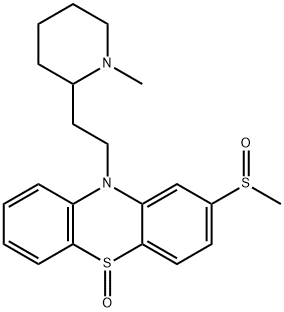
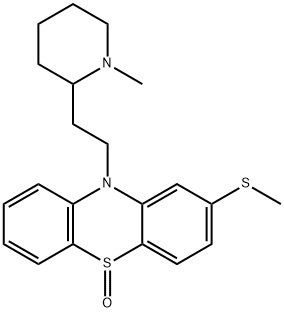
mesoridazine
- CAS NO.:5588-33-0
- Empirical Formula: C21H26N2OS2
- Molecular Weight: 386.57
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 23:16:16

What is mesoridazine?
Absorption
Well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Toxicity
Oral LD50 is 560 ± 62.5 mg/kg and 644 ± 48 mg/kg in mouse and rat, respectively. Symptoms of overdose may include emesis, muscle tremors, decreased food intake and death associated with aspiration of oral-gastric contents into the respiratory system.
Chemical properties
Pale Pink Solid
Originator
Serentil,Sandoz,US,1970
The Uses of mesoridazine
Mesoridazine is an antipsychotic.
The Uses of mesoridazine
Mesoridazine (Thioridazine EP Impurity B) is an antipsychotic.
Background
A phenothiazine antipsychotic with effects similar to chlorpromazine.
Indications
Used in the treatment of schizophrenia, organic brain disorders, alcoholism and psychoneuroses.
Definition
ChEBI: A phenothiazine substituted at position 2 (para to the S atom) by a methylsulfinyl group, and on the nitrogen by a 2-(1-methylpiperidin-2-yl)ethyl group.
Manufacturing Process
10.0 g of 3-methylmercapto phenothiazine and 17.5 cc of acetic acid
anhydride are refluxed for 8 hours from an oil bath maintained at a
temperature of 180°C. After concentration of the solution the residue is
crystallized from ethanol. The pure 3-methylmercapto-10-acetyl phenothiazine
melts at 89° to 91°C. For the purpose of oxidation 5.0 g of 3-
methylmercapto-10-acetyl phenothiazine are dissolved in 50 cc of ethanol,
refluxed from an oil bath maintained at 120°C and 1.6 cc of a 40% hydrogen
peroxide solution are then added dropwise in the course of 30 minutes.
Heating is continued for another 5 hours and the reaction mixture is
concentrated after 50 cc of water have been added. The residue is taken up in
40 cc of benzene and the benzene layer washed with 10 cc of water. After
having been concentrated, the residue, crude 3-methylsulfinyl-10-acetyl
phenothiazine, is dissolved in 55 cc of a 90% methanol solution for splitting
off the acetyl group and, after 2.9 g of potassium carbonate have been added,
it is boiled for 2 hours under reflux on an oil bath kept at a temperature of
120°C. After concentration, the residue is taken up in 50 cc of chloroform, the
chloroform layer is washed with a total of 25 cc of water, dried over potassium
carbonate, filtered and concentrated. After twice crystallizing the residue, each
time from 50 cc of ethanol, analytically pure 3-methylsulfinyl phenothiazine
(MP 193° to 195°C) is obtained.
A mixture of 10.0 g of 3-methylsulfinyl phenothiazine (MP 193° to 195°C), 6.1
g of finely powdered sodium hydroxide and 125 cc of toluene is boiled for 1
hour under reflux with a water separator on an oil bath kept at a temperature
of 150°C, while the mixture is stirred. Without interrupting the boil a solution
of 7.0 g of 2-(N-methyl-piperidyl-2')-1-chloroethane (BP 84°C/10 mm Hg) in
10 cc of toluene is added dropwise in the course of 1 hour, after which boiling
is continued for another 3 hours. When the reaction mixture has cooled it is
first washed with 25 cc of water three times and then extracted with 75 cc of
a 15% aqueous tartaric acid solution. The tartaric acid extract is shaken out
with 25 cc of benzene, 20 cc of concentrated caustic soda are added until the
phenolphthalein reaction is alkaline, and the separated oily base is taken up in
a total of 150 cc of benzene.
After having been washed with 50 cc of water the benzene layer is dried over
potassium carbonate, filtered, allowed to stand over 10 g of alumina for about
1? hours for partial decolorization, filtered again and concentrated under
reduced pressure. The oily base which remains as a residue is directly
converted into the tartrate. A solution cooled to 0°C, of 6.50 g of the free
base in 100 cc of acetic acid ethyl ester is thoroughly shaken and poured into
an ice cold solution of 2.66 g of tartaric acid in 410 cc of acetic acid ethyl
ester. The precipitated, analytically pure, tartrate of 3-methylsulfinyl-10-[2'-Nmethyl-piperidyl-2')-ethyl-l']-phenothiazine melts at 115° to 120°C (foam
formation) and sinters above 80°C. The base is reacted with benzene sulfonic
acid in a suitable solvent to give the besylate.
brand name
Serentil (Novartis).
Therapeutic Function
Tranquilizer
Pharmacokinetics
Mesoridazine, the besylate salt of a metabolite of thioridazine, is a phenothiazine tranquilizer. Pharmacological studies in laboratory animals have established that mesoridazine has a spectrum of pharmacodynamic actions typical of a major tranquilizer. In common with other tranquilizers it inhibits spontaneous motor activity in mice, prolongs thiopental and hexobarbital sleeping time in mice and produces spindles and block of arousal reaction in the EEG of rabbits. It is effective in blocking spinal reflexes in the cut and antagonizes d-amphetamine excitation and toxicity in grouped mice. It shows a moderate adrenergic blocking activity in vitro and in vivo and antagonizes 5-hydroxytryptamine in vivo. Intravenously administered, it lowers the blood pressure of anesthetized dogs. It has a weak antiacetylcholine effect in vitro.
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of mesoridazine
| Melting point: | 128-131 °C |
| Boiling point: | 570.5±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.1234 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5950 (estimate) |
| solubility | Acetonitrile: slightly soluble; DMSO: slightly, heated; Methanol: slightly soluble |
| pka | 9.84±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Sticky Solid |
| color | Pale Yellow to Orange |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for mesoridazine
Computed Descriptors for mesoridazine
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![2-methylsulfonyl-10-[2-[1-(trideuteriomethyl)piperidin-2-yl]ethyl]phenothiazine](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180528/GIF/1329652-09-6.gif)
You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
