MELAMINE RESIN
Synonym(s):CCK1;CCL28;MEC;MGC71902
- CAS NO.:9003-08-1
- Empirical Formula: (C3H6N6.CH2O)x
- Molecular Weight: 156.15
- MDL number: MFCD00197733
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-19 08:02:35
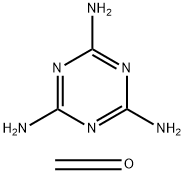
What is MELAMINE RESIN?
The Uses of MELAMINE RESIN
Melamine formaldehyde is used for the treatment of heavy fabrics, draperies, coatings, collars, and apparel; in water- and oil-repellent and flame-retardant hrllsIies (effective on synthetic and natural fibers).
The Uses of MELAMINE RESIN
Suggested starting dilutions are as follows: IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000, WB: 1:500-1:3000. Not yet tested in other applications. Optimal working dilutions should be determined experimentally by the end user.
Definition
A type of amino resin made from melamine and formaldehyde. The first step in resin formation is the production of trimethylol melamine, C3N3(NHCH2OH)3, the molecules of which contain a ring with three carbon and three nitrogen atoms, the –NHCH2OH groups being attached to the carbon atoms. This molecule can combine further with others of the same kind by a condensation reaction. Excess formaldehyde or melamine can also react with trimethylol melamine or its polymers, providing many possibilities of chain growth and cross-linking. The nature and degree of polymerization depend upon pH, but heat is always needed for curing. Melamine resins are more waterand heat-resistant than urea resins. They may be water-soluble syrups (low molecular weight) or insoluble powders (high molecular weight) dispersible in water. Widely used as molding compounds with α-cellulose, wood flour, or mineral powders as fillers and with coloring materials; also for laminating, boil-proof adhesives, increasing wet strength of paper, textile treatment, leather processing, and for dinnerware and decorative plastic items. Butylated melamine resins are formed by incorporating butyl or other alcohols during resin formation, whereupon the –NHCH2OH groups convert to –NHCH2OC4H9. These resins are soluble in paint and enamel solvents and in surface coatings, often in combination with alkyds. They give exceptional curing speed, hardness, wear resistance, and resistance to solvents, soaps, and foods. Melamine-acrylic resins are water soluble and used for formation of water-base industrial and automotive finishes.
Preparation
Melamine resin is a resin with melamine rings terminated with multiple hydroxyl groups derived from formaldehyde. This thermosetting plastic material is made from melamine and formaldehyde.
Production Methods
The monomer used for preparing melamine formaldehyde is formed by reacting melamine with formaldehyde to yield hexamethylolmelamine. The monomer can further condense in the presence of an acid catalyst; ether linkages can also form. A wide variety of resins can be obtained by careful selection of pH, reaction temperature, reactant ratio, amino monomer, and extend of condensation. Liquid coating resins are prepared by reacting methanol or butanol with the initial methylolated products. These can be used to produce extreme surface hardness, discoloration and solvent-resistant coatings by heating with a variety of hydroxy, carboxyl, and amide functional polymers to produce a cross-linked film.
Origin
Melamine-formaldehyde was first commercialized by the American Cyanamid Co. in 1939.
Industrial uses
This is a synthetic resin of the alkyd type madeby reacting melamine with formaldehyde. Theresin is thermosetting, colorless, odorless, andresistant to organic solvents. It is more resistantto alkalies and acids than urea resins, has betterheat and color stability, and is harder. Themelamine resins have the general uses of moldingplastics, and also are valued for dishes forhot foods or acid juices and they will not softenor warp when washed in hot water. Melamine,a trimer of cyanamide, has the composition(NC·NH2)3.
The melamine resins have good adhesivenessbut are too hard for use alone in coatingsand varnishes. They are combined with alcoholmodifiedurea-formaldehyde resins to give coatingmaterials of good color, gloss, flexibility, andchemical resistance. Urea-modified melamineformaldehyderesins are used for coatings andvarnishes. Melamine-formaldehyde moldingresin, with cellulose filler, has a tensile strengthof 51 MPa and dielectric strength per mil of12.8×106V/m.
Melamine-urea-formaldehyde resin with alignin extender is used as an adhesive for waterresistantplywood. Phenol-modified melamineformaldehyderesin solution is used for laminatingfibrous materials. Highly translucentmelamine-formaldehyde resin is used for moldinghigh-gloss buttons. Methylol-melamine,made by alkylating a melamine-formaldehyderesin with methyl alcohol, is used for shrinkproofingwoolen fabrics.
Biochem/physiol Actions
This gene belongs to the subfamily of small cytokine CC genes. Cytokines are a family of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The CC cytokines are proteins characterized by two adjacent cysteines. The cytokine encoded by this gene displays chemotactic activity for resting CD4 or CD8 T cells and eosinophils. The product of this gene binds to chemokine receptors CCR3 and CCR10. This chemokine may play a role in the physiology of extracutaneous epithelial tissues, including diverse mucosal organs. [provided by RefSeq]
Properties of MELAMINE RESIN
| Melting point: | >330 °C (decomp) |
| Density | 1.13-1.14 g/cm3 |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| form | buffered aqueous solution |
| Dielectric constant | 5.5(Ambient) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Melamine polymer with formaldehyde (9003-08-1) |
Safety information for MELAMINE RESIN
Computed Descriptors for MELAMINE RESIN
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Anti-CCL28 antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details
Anti-CCL28 antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
