Mefenamic acid
Synonym(s):N-(2,3-Xylyl)anthranilic acid;2-[(2,3-Dimethylphenyl)amino]benzoic acid
- CAS NO.:61-68-7
- Empirical Formula: C15H15NO2
- Molecular Weight: 241.29
- MDL number: MFCD00051721
- EINECS: 200-513-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-25 20:05:57
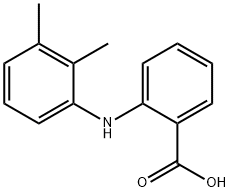
What is Mefenamic acid ?
Absorption
Mefenamic acid is rapidly absorbed after oral administration.
Toxicity
Oral, rat LD50: 740 mg/kg. Symptoms of overdose may include severe stomach pain, coffee ground-like vomit, dark stool, ringing in the ears, change in amount of urine, unusually fast or slow heartbeat, muscle weakness, slow or shallow breathing, confusion, severe headache or loss of consciousness.
Chemical properties
white or light yellow crystalline powder, odorless, insoluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, chloroform, slightly soluble in ether. Melting point 230-231°C, mefenamic acid is an anti-inflammatory analgesic with antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
Originator
Ponstan,Parke Davis,UK,1963
The Uses of Mefenamic acid
Mefenamic acid has the same indications as flumic acid. It can be used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, dysmenorrhoea, as well as mild to moderate pain, inflammation and fever.
Background
A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent with analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties. It is an inhibitor of cyclooxygenase.
What are the applications of Application
Mefenamic acid is a compound with antiproliferative activity against colorectal cancer cells
Definition
ChEBI: An aminobenzoic acid that is anthranilic acid in which one of the hydrogens attached to the nitrogen is replaced by a 2,3-dimethylphenyl group. Although classed as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, its anti-inflammatory properties are considered to b minor. It is used to relieve mild to moderate pain, including headaches, dental pain, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Indications
Mefenamic acid (Ponstel) is indicated only for analgesia and primary dysmenorrhea when therapy will not exceed 1 week.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 800 g of potassium o-bromo-benzoate, 1,500 ml of bis-(2- methoxyethyl)ether, 355 g of N-ethyl-morpholine, 375 g of 2,3- dimethylaniline, and 30 g of cupric acetate is heated gradually with stirring to 140°C over a period of 90 minutes. The hot reaction mixture is then acidified with 260 mi of concentrated hydrochloric acid and the acidified mixture divided into 2 equal portions. One liter of water is added to each portion and the mixtures allowed to cool. The N-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)anthranilic acid which separates upon cooling is collected by filtration and recrystallized from bis(2-methoxyethyl)ether; MP 229° to 230°C (corr.).
brand name
Ponstel (Sciele, Parke Davis, USA), Lysalgo (SIT, Italy), Opustan (Opus Pharm, UK), Parkemed (Parke Davis, Germany), Ponstan (Werner-Lambert, Switzerland), Pontal (Sankyo, Japan).
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 45, p. 2127, 1980 DOI: 10.1021/jo01299a020
General Description
Mefenamic acid (Ponstel, Ponstan) is one of the oldestNSAIDs, introduced into the market in 1967 for mild tomoderate pain and for primary dysmenorrhea. It is rapidly absorbed with peak plasma levels occurring 2 to 4 hoursafter oral administration. It undergoes hepatic benzylic hydroxylationof its 3'methyl group regioselectively into twoinactive metabolites, 3'-hydroxymethylmefenamic acid andthe 3'carboxylate metabolite (via further oxidation of thebenzylic alcohol group). The parent drugs and these metabolitesare conjugated with glucuronic acid and excreted primarilyin the urine. Thus, although patients with knownliver deficiency may be given lower doses, it is contraindicatedin patients with preexisting renal dysfunction.
Common side effects associated with its use include diarrhea,drowsiness, and headache. The possibility of blood disordershas also prompted limitation of its administration to 7days. It is not recommended for children or during pregnancy.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Mefenamic acid is an analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug. It acts as a cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme inhibitor. It is hepatoxic and implicated in liver injury. Contrarily, mefenamic acid elicits neuroprotection in in vivo ischemic stroke models by inhibiting cell toxicity induced by glutamate. Mefenamic due its inhibitory effect on prostaglandin synthesis can be used in reducing edema and ache.
Mechanism of action
Mefenamic acid inhibits both COX isoforms with some preference for COX-2 and modifies ion channels.
Pharmacokinetics
Mefenamic acid, an anthranilic acid derivative, is a member of the fenamate group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activities. Similar to other NSAIDs, mefenamic acid inhibits prostaglandin synthetase.
Clinical Use
Mefenamic acid is synthesised from o-chlorobenzoic acid and 2,3-dimethylaniline under catalytic conditions. It is the only derivative of mefenamic acid that produces central and peripheral analgesia. It is indicated for short-term relief of moderate pain and primary dysmenorrhoea.
Safety
Mefenamic acid has mild anti-inflammatory properties and is used primarily as a short-term analgesic. Gastrointestinal disturbances, including possibly allergic diarrhea and potential renal toxicity, limit its use.
Synthesis
Mefenamic acid, N-(2,3-xylyl)anthranylic acid (3.2.19), is synthesized
in basically the same manner, by the reaction of the potassium salt of 2-bromobenzoic acid
with 2,3-dimethylaniline in the presence of copper (II) acetate [80,81].
Synthesis 2: mefenamic acid is prepared via
the Jourdan – Ullmann – Goldberg synthesis utilizing either anthranilic acid and 3-bromo-1,2-
dimethylbenzene or 2,3-dimethylaniline and an
o-halobenzoic acid in the presence of a copper
catalyst and a proton acceptor.
Metabolism
Mefenamic acid is absorbed rapidly following oral administration, with peak plasma levels being attained within 2 to 4 hours. It is highly bound to plasma proteins (78.5%) and has a plasma half-life of 2 to 4 hours. Metabolism occurs through regioselective oxidation of the 3′-methyl group and glucuronidation of mefenamic acid and its metabolites. Urinary excretion accounts for approximately 50 to 55% of an administered dose, with unchanged drug accounting for 6%, the 3′-hydroxymethyl metabolite (primarily as the glucuronide) accounting for 25%, and the remaining 20% as the dicarboxylic acid (of which 30% is the glucuronide conjugate). These metabolites are essentially inactive.
Side Effects
Common side effects of Mefenamic acid include: upset stomach or stomach pain; constipation or diarrhoea; flatulence or heartburn; nausea and vomiting, dizziness, headache, rash or itching. Serious side effects can lead to myocardial infarction and stroke, inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, bleeding, ulcers or perforation, and bronchospasm (in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma) . Rarely, severe anaphylactoid reactions, drug reactions with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or multiorgan hypersensitivity reactions, exfoliative dermatitis, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevensohnson syndrome, and severe hepatic reactions (e.g., fulminant hepatitis, hepatic necrosis, or failure).
Properties of Mefenamic acid
| Melting point: | 230 °C |
| Boiling point: | 384.06°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0944 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5200 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent) and in methylene chloride. It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides |
| form | neat |
| pka | 4.2(at 25℃) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Pale Yellow |
| Water Solubility | It is soluble in acetone, chloroform, dichloromethane, methanol. Insoluble in water. |
| Merck | 14,5798 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 61-68-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Mefenamic acid(61-68-7) |
Safety information for Mefenamic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Mefenamic acid
| InChIKey | HYYBABOKPJLUIN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Mefenamic acid manufacturer
Nira Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Solara Active Pharma Sciences Ltd
Infinity Laboratories Private Limited
Shree Chemopharma Ankleshwar Pvt., Ltd.
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 4-(3-chloropropyl)morpholine phenylhydrazine hydrochloride (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran







You may like
-
 MEFENAMIC ACID 98%View Details
MEFENAMIC ACID 98%View Details -
 Mefenamic acid 99%View Details
Mefenamic acid 99%View Details -
 Mefenamic acid 97% CAS 61-68-7View Details
Mefenamic acid 97% CAS 61-68-7View Details
61-68-7 -
 Mefenamic acid, 98% CAS 61-68-7View Details
Mefenamic acid, 98% CAS 61-68-7View Details
61-68-7 -
 Mefenamic Acid CAS 61-68-7View Details
Mefenamic Acid CAS 61-68-7View Details
61-68-7 -
 Mefenamic Acid 99%View Details
Mefenamic Acid 99%View Details -
 MEFENAMIC ACID CAS 61-68-7View Details
MEFENAMIC ACID CAS 61-68-7View Details
61-68-7 -
 Mefenamic acid CAS 61-68-7View Details
Mefenamic acid CAS 61-68-7View Details
61-68-7