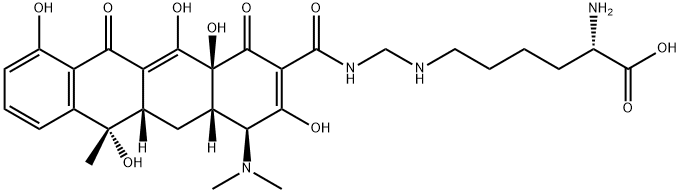
lymecycline
- CAS NO.:992-21-2
- Empirical Formula: C29H38N4O10
- Molecular Weight: 602.63
- MDL number: MFCD01716199
- EINECS: 213-592-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-27 11:17:45
What is lymecycline?
Absorption
Lymecycline is 77-88% absorbed after oral administration with a relative bioavailability of 70%. The Cmax of lymecycline is 2.1 mg/L and is achieved about 3 hours after administration. The AUC is 21.9 ± 4.3 mg·h/L.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 of lymecycline in rats is 3200 mg/kg. Overdoses with lymecycline are rare. In the case of an overdose, gastric lavage should be performed immediately. Provide supportive treatment and maintain fluid balance.
Chemical properties
Yellow, hygroscopic powder.
Originator
Armyl,Armour Pharm.
The Uses of lymecycline
Labelled Lymecycline. A semi-synthetic antibiotic related to Tetracycline (T291400). Antibacterial.
Indications
Lymecycline is used for the treatment of acne in addition to other susceptible infections; propionibacterium is often the cause of acne. Some of the infections that can be treated with lymecycline include upper respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, bronchitis, chlamydial infections, and rickettsial infections.
Background
Lymecycline is a broad-spectrum second-generation tetracycline antibiotic used for the treatment of acne and other susceptible bacterial infections. It has been proven a cost-effective alternative to treatment with minocycline with comparable safety and efficacy. Lymecycline was initially discovered in 1961. It is marketed by Galderma and used in the UK as well as New Zealand in addition to other countries. Lymecycline is not marketed in the USA, however, equivalent drugs are available, such as minocycline and tetracycline.
What are the applications of Application
Lymecycline is a semi-synthetic antibiotic related to Tetracycline (sc-205858)
Definition
ChEBI: A tetracycline-based broad-spectrum antibiotic. It is approximately 5000 times more soluble than tetracycline base and is unique amongst tetracyclines in that it is absorbed by the "active transport" process across the intestinal wall.
Manufacturing Process
Amido-N-(lysinomethyl)tetracycline hydrochloride:
To 18.3 g of L-lysine hydrochloride dissolved in 100 ml of water is added 10
ml of 37% aqueous solution of formaldehyde. To the resultant mixture is
added 44.0 g of anhydrous tetracycline dissolved in 500 ml of tetrahydrofuran.
After thorough mixing the product forms over a period of about 15 min as an
oily layer which after separation from the aqueous phase is added dropwise to
3 L of stirred isopropyl alcohol. The product after recovery by filtration, is
reslurried with acetone, filtered and dried at 65°C at reduced pressure.
The product thus obtained has a bioassay of 500 mcg/mg (K. pneumonlae
oxytetracyoline assay).
Therapeutic Function
Antibiotic
Pharmaceutical Applications
2-N-lysinomethyl-tetracycline. A water-soluble prodrug of
tetracycline available for oral administration.
Its antimicrobial activity is due to the tetracycline content. It
is lipophilic, rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and
widely distributed. Concentrations around 1 mg/kg have been
found in maxillary sinus tissue some 3 h after administration
of a conventional dose. The half-life is 7–14 h. Approximately
30% of an orally administered dose is excreted as active drug in
the urine, where it achieves concentrations of 300 mg/L.
Its untoward effects and clinical uses are those of tetracycline,
although it is claimed to be better tolerated.
Pharmacokinetics
Lymecycline, like other tetracyclines, exerts bacteriostatic actions on intracellular and extracellular bacteria, treating susceptible bacterial infections. It has been shown to be safe and effective in the treatment of moderate to severe acne.
It is important to note that like other tetracyclines, lymecycline may cause esophageal irritation and ulceration, which can be prevented by drinking adequate fluids during administration. It also has the potential to cause photosensitivity. Lymecycline can lead to renal tubular acidosis or hepatic toxicity. It is not recommended to administer this drug in patients with renal disease or severe hepatic disease.
Clinical Use
Antibacterial agent:
Also used for treatment of acne
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anticoagulants: possibly enhanced anticoagulant
effect of coumarins and phenindione.
Oestrogens: possibly reduce contraceptive effects of
oestrogens (risk probably small).
Retinoids: possible increased risk of benign
intracranial hypertension – avoid.
Metabolism
Not Available
Metabolism
The tetracyclines are excreted in the urine and in the faeces. Renal clearance is by glomerular filtration. Up to 60% of an intravenous dose, and up to 55% of an oral dose, is eliminated unchanged in the urine. Usually between 40% and 70% of a dose is excreted in the urine; urinary excretion is increased if urine is alkalinised.
Properties of lymecycline
| Melting point: | 192.5°C |
| Boiling point: | 648.97°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.53 |
| refractive index | 1.5500 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Amber Vial, -86°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | Very soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in methylene chloride. |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 2.50±0.24(Predicted) |
| color | Yellow to Dark Brown |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive, Temperature Sensitive |
Safety information for lymecycline
Computed Descriptors for lymecycline
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 992-21-2 Lymecycline 99%View Details
992-21-2 Lymecycline 99%View Details
992-21-2 -
 992-21-2 98%View Details
992-21-2 98%View Details
992-21-2 -
 Lymecycline 98%View Details
Lymecycline 98%View Details
992-21-2 -
 Lymecycline 992-21-2 98%View Details
Lymecycline 992-21-2 98%View Details
992-21-2 -
 992-21-2 99%View Details
992-21-2 99%View Details
992-21-2 -
 Lymecycline CAS 992-21-2View Details
Lymecycline CAS 992-21-2View Details
992-21-2 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details