Losartan
Synonym(s):1-[1-[[2′-(2H-Tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl]-2-butyl-4-chloro-1H-imidazol-5-yl]methanol;2-Butyl-4-chloro-1-[[2′-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl-4-yl]methyl]-1H-imidazole-5-methanol;2-Butyl-4-chloro-1-[[2′-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-1H-imidazole-5-methanol;DUP 89
- CAS NO.:114798-26-4
- Empirical Formula: C22H23ClN6O
- Molecular Weight: 422.91
- MDL number: MFCD00865831
- EINECS: 601-329-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
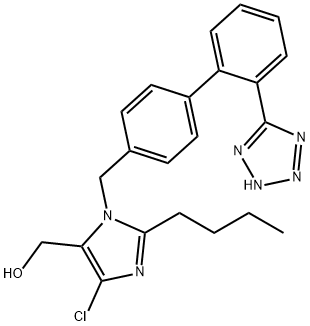
What is Losartan?
Absorption
Losartan is approximately 33% orally bioavailable. Losartan has a Tmax of 1 hour and the active metabolite has a Tmax of 3-4 hours. Taking losartan with food decreases the Cmax but does only results in a 10% decrease in the AUC of losartan and its active metabolite. A 50-80mg oral dose of losartan leads to a Cmax of 200-250ng/mL.
Toxicity
The oral TDLO in mice is 1000mg/kg and in rats is 2000mg/kg. In humans the TDLO for men is 10mg/kg/2W and for women is 1mg/kg/1D.
Symptoms of overdose are likely to include hypotension, tachycardia, or bradycardia due to vagal stimulation. Supportive treatment should be instituted for symptomatic hypotension. Hemodialysis will not remove losartan or its active metabolite due to their high rates of protein binding.
Description
Losartan is a drug used to treat high blood pressure. Its?synthesis was patented by DuPont scientists?in 1992, but it was not until DuPont collaborated with Merck and FDA approval was obtained that it was marketed in 1995 under the Merck trade name Cozaar. It has been a generic drug since 2009. Like many hypertension treatments, losartan is an angiotensin II type 1 antagonist. It has also shown promise for treating diabetic nephropathy and reducing the progression of renal disease in type 2 diabetics.
Originator
Alsartan, Aristo Pharmaceutical Ltd., India
The Uses of Losartan
Losartan is a nonpeptide angiotensin II AT1-receptor antagonist. Antihypertensive.
The Uses of Losartan
antihypertensive;antagonist of angiotensin type 1
Background
Losartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) used to treat hypertension. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors are used for a similar indication but are associated with a cough. When patients with ACE inhibitor associated coughs are switched to ARBs like losartan, they have an incidence of cough similar to placebo or hydrochlorothiazide. Losartan is available as losartan potassium oral tablets as well as a combination tablet of losartan potassium and hydrochlorothiazide. Patients taking losartan should have their renal function and potassium levels monitored. Losartan was granted FDA approval on 14 April 1995.
Indications
Losartan is indicated to treat hypertension in patients older than 6 years, reduce the risk of stroke in patients with hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy (though this benefit may not extend to patients with African heritage), and to treat diabetic nephropathy with elevated serum creatinine and proteinuria in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Losartan with hydrochlorothiazide is indicated to treat hypertension and to reduce the risk of stroke in patients with hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy (though this benefit may not extend to patients with African heritage).
What are the applications of Application
Losartan is an AT1 inhibitor which prevents the initiation of a signal cascade which causes vasoconstriction
Definition
ChEBI: A biphenylyltetrazole where a 1,1'-biphenyl group is attached at the 5-position and has an additional trisubstituted imidazol-1-ylmethyl group at the 4'-position
Manufacturing Process
2-Butyl-4-chloro-1-(2'-(tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-ylmethyl)-1H-imidazole-5- methanolpotassium was synthesized in 5 stages.
1. Methyl 4'-methylbiphenyl-2-carboxylate (44.2 mmol), 0.5 N KOH in methanol (133 mmol), and water (50 mL) were mixed and refluxed under nitrogen. After 5 hours, the solvent was removed in vacuo and water (200 mL) and ethyl acetate (200 mL) added. The aqueous layer was acidified with concentrated hydrochloric acid to a pH of 3 and the layers were separated. The aqueous phase was extracted with ethyl acetate, the organic layers collected, dried (MgSO4) and the solvent removed in vacuo to yield 8.71 g of a 4'-methylbiphenyl-2-carboxylic acid, melting point 140.0-145.0°C.
2. 4'-Methylbiphenyl-2-carboxylic acid (41 mmol) and thionyl chloride (411 mmol) were mixed and refluxed for 2 hours. The excess thionyl chloride was removed in vacuo and the residue was taken up in toluene. The toluene was removed by rotary evaporation. The crude acid chloride was then added slowly to cold (0°C) concentrated NH4OH (50 mL) so that the temperature was kept below 15°C. After 15 minutes of stirring, water (100 mL) was added and solids precipitated. These were collected, washed with water and dried under high vacuum over P2O5 to yield 7.45 g of a white solid, melting point 126.0-128.5°C. The above product amide (35 mmol) and thionyl chloride (353 mmol) were mixed and refluxed for 3 hours. The thionyl chloride was removed using the same procedure as described above. The residue was washed with a little hexane to yield 6.64 g of 4'-methyl-2-cyanobiphenyl, melting point 44.0- 47.0°C.
3. 4'-Methyl-2-cyanobiphenyl (5.59 g) was brominated using benzoyl peroxide as an initiator. The product was recrystallized from ether to yield 4.7 g of 4'- bromomethyl-2-cyanobiphenyl, melting point 114.5-120.0°C.
4. 4'-Bromomethyl-2-cyanobiphenyl (4.6 g) was alkylated onto 2-n-butyl-4-
chloro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-imidazole. For separation of the product was used a
flash chromatography in 1:1 hexane/ethyl acetate over silica gel. The
regioisomeric products yielded 2.53 g of the faster eluting isomer.
Recrystallization from acetonitrile yielded 1.57 g of analytically pure 2-n-butyl4-chloro-1-[2'-cyanobiphenyl-4-yl)methyl]-5-(hydroxymethyl)-imidazole,
melting point 153.5 -155.5°C.
5. 2-n-Butyl-4-chloro-1-[(2'-cyanobiphenyl-4-yl)-methyl]-5-(hydroxymethyl)-
imidazole (10 mmole), sodium azide (10 mmol), and ammonium chloride (30
mmol) were mixed in DMF (150 mL) under N2 at 100°C for 2 days, after
which the temperature was raised to 120°C for 6 days. The reaction was
cooled and 3 more equivalents each of ammonium chloride and sodium azide
were added. The reaction was again heated for 5 days at 120°C. The reaction
was cooled, the inorganic salts filtered, and the filtrate solvent removed in
vacuo. Water (200 mL) and ethyl acetate (200 mL) were added to the residue
and the layers were separated. The aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl
acetate, the organic layers were collected, dried (MgSO4) and the solvent
removed in vacuo, to yield a dark yellow oil. The product was purified by flash
chromatography in 100% ethyl acetate to 100% ethanol over silica gel to
yield 5.60 g of a light yellow 2-n-butyl-4-chloro-5-hydroxymethyl-1-[(2'-(1Htetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl]imidazole. Recrystallization from acetonitrile
yielded 4.36 g of light yellow crystals which still melted broadly. The crystals
were taken up in 100 mL of hot acetonitrile. The solid that did not dissolve
was filtered off to yield 1.04 g of product as a light yellow solid, melting point
of 2-n-butyl-4-chloro-5-hydroxymethyl-1-[(2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-
yl)methyl]imidazole 183.5-184.5°C.
2-n-Butyl-4-chloro-5-hydroxymethyl-1-[(2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-
yl)methyl]imidazole may be converted to potassium salt.
brand name
Cozaar (Merck).
Therapeutic Function
Antihypertensive
General Description
Losartan, 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[p-(o-1H-tetrazol-5-yl-phenyl)benzyl]imidazole-5-methanol monopotassiumsalt (Cozarr), was the first nonpeptide imidazole to beintroduced as an orally active angiotensin II antagonist withhigh specificity for AT1. When administered to patients, itundergoes extensive first-pass metabolism, with the 5-methanol being oxidized to a carboxylic acid. This metabolismis mediated by CYP 2C9 and 3A4 isozymes. The 5-methanol metabolite is approximately 15 times more potentthan the parent hydroxyl compound. Because the parent hydroxylcompound has affinity for the AT1 receptor, strictlyspeaking, it is not a prodrug.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmacokinetics
Losartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker used to treat hypertension, diabetic nephropathy, and to reduce the risk of stroke. Losartan has a long duration of action as it is given once daily. Patients taking losartan should be regularly monitored for hypotension, renal function, and potassium levels.
Metabolism
Losartan is metabolized to an aldehyde intermediate, E-3179, which is further metabolized to a carboxylic acid, E-3174, by cytochrome P450s like CYP2C9. Losartan can also be hydroxylated to an inactive metabolite, P1. Approximately 14% of losartan is metabolized to E-3174. Losartan can be metabolized by CYP3A4, CYP2C9, and CYP2C10. Losartan can also be glucuronidated by UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A10, UGT2B7, and UGT 2B17.
Properties of Losartan
| Melting point: | 183-184 C |
| Boiling point: | 682.0±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.35±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| vapor pressure | 0.002Pa at 20℃ |
| storage temp. | under inert gas (nitrogen or Argon) at 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 5-6(at 25℃) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 4.8mg/L at 20℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 114798-26-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1H-Imidazole-5-methanol, 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[[2'-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]- (114798-26-4) |
Safety information for Losartan
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H362:Reproductive toxicity, effects on or via lactation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P263:Avoid contact during pregnancy/while nursing. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Losartan
Losartan manufacturer
Sainor Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Divis Laboratories Ltd
Ralington Pharma
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 114798-26-4 Losartan Base 99%View Details
114798-26-4 Losartan Base 99%View Details
114798-26-4 -
 Losartan 98%View Details
Losartan 98%View Details -
 Losartan 98.00% CAS 114798-26-4View Details
Losartan 98.00% CAS 114798-26-4View Details
114798-26-4 -
 Losartan 114798-26-4 98%View Details
Losartan 114798-26-4 98%View Details
114798-26-4 -
 Losartan 99%View Details
Losartan 99%View Details
114798-26-4 -
 Losartan 99%View Details
Losartan 99%View Details
114798-26-4 -
 Losartan >98% (HPLC) CAS 114798-26-4View Details
Losartan >98% (HPLC) CAS 114798-26-4View Details
114798-26-4 -
 Losartan CAS 114798-26-4View Details
Losartan CAS 114798-26-4View Details
114798-26-4