Lipase
Synonym(s):CCL;PPL;Triacylglycerol lipase;PS Lipase;Triacylglycerol acylhydrolase
- CAS NO.:9001-62-1
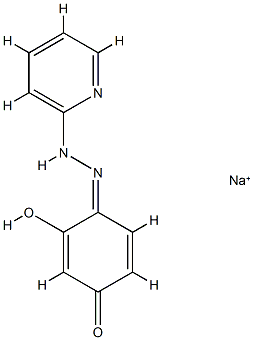
- Empirical Formula: C11H9N3NaO2+
- Molecular Weight: 238.19783
- MDL number: MFCD02685890
- EINECS: 232-619-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 13:37:16
What is Lipase?
Description
Lipase is obtained from two primary sources: (1) the edible fore stomach tissue of calves, kids, or lambs and; (2 ) animal pancreatic tissue. It is produced as purified edible tissue preparations or as aqueous extracts. It is dispersible in water and insoluble in alcohol. The major active principle is lipase, IUB No. 3.1.1.3, CAS No. 9001-62-1.
Description
Produced by the controlled fermentation of Aspergillus niger var. as an off-white to tan amorphous powder. Soluble in water (the solution is usually light yellow), but practically insoluble in alco hol, chloroform or ether. The major active principle is lipase, IUB No. 3.1.1.3, CAS No. 9001-62-1.
Description
Produced by the controlled fermentation of Aspergillus oryzae var. as an off-white to tan amorphous powder or a liquid. Soluble in water (the solution is usually light yellow), but practically insol uble in alcohol, chloroform or ether. The major active principle is lipase, IUB No. 3.1.1.3, CAS No. 9001-62-1.
Description
Produced by the controlled fermentation of Candida rugosa as an off-white to tan powder. Soluble in water but practically insoluble in alcohol, chloroform or ether. The major active principle is lipase, IUB No. 3.1.1.3, CAS No. 9001-62-1.
Chemical properties
powder
The Uses of Lipase
To split fats without damaging sensitive constituents, such as vitamins or unsaturated fatty acids. In food processing for flavor improvement; in detergents for the improvement of cleaning action. For review of industrial applications of microbial lipases, see Seitz, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 51, 12 (1974).
The Uses of Lipase
Trans fatty acids (TFAs) are fatty acids with at least one double bond in (E)-
configuration. The consumption of TFAs increases the risk of coronary heart
diseases. Thus, their concentrations in lipid-containing products should be reduced
[87]. Naturally, TFAs occur in small amounts in meat and milk of ruminants, but
the most significant concentrations of TFAs develop during partial hydrogenation
and deodorization of fats [88]. The formation of TFAs during fat hardening can be
avoided by lipase catalyzed transesterification to increase the slip melting points of
fats.
For enzymatic transesterification between different lipids, triacylglycerol lipases
(triacylglycerol acylhydrolase, EC 3.1.1.3) acting on the SN1 and SN3 positions
of the triglyceride are used. Various lipases have been applied for the
production of table margarine out of fat-oil blends. Lipases of the ascomycetes
Thermomyces lanuginosa and Rhizomucor miehei, as well as a lipase of the proteobacterium
Pseudomonas sp., were used for transesterification of fat blends
consisting of palm stearin and vegetable oil. Fully hydrogenated oils in
blends with vegetable oils also have been used. In all studies, an increase of
the slip melting points and the solid fat content was achieved in the fat-oil blend,
thus indicating an alternative method for fat hardening via hydrogenation.
The Uses of Lipase
Lipase, is used as a catalyst in the preparation of biodiesels?and in the preparation of esters of chiral epoxy alcohols.?Lipases are used industrially for the resolution of chiral compounds and the transesterification production of biodiesel.
Definition
lipase: An enzyme secreted by thepancreas and the glands of the smallintestine of vertebrates that catalysesthe breakdown of fats into fatty acidsand glycerol.
General Description
Pancrelipase (Cotazym) has agreater lipolytic action than other pancreatic enzyme preparations.Hence, it is used to help control steatorrhea and inother conditions in which pancreatic insufficiency impairsthe digestion of fats in the diet.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Biochem/physiol Actions
Amano lipase M is capable of catalyzing Michael addition of pyrimidine with disaccharide acrylates in organic media.
Properties of Lipase
| Density | 1.2 |
| vapor pressure | 0.004Pa at 25℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 2 mg/mL, hazy with insoluble particles, faintly yellow |
| form | solution |
| color | yellow-brown |
| Water Solubility | It is soluble in water. |
| Merck | 13,5533 |
| Stability: | Moisture sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 9001-62-1 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lipase, triacylglycerol (9001-62-1) |
Safety information for Lipase
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H334:Sensitisation, respiratory |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P285:In case of inadequate ventilation wear respiratory protection. P304+P341:IF INHALED: If breathing is difficult, remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P342+P311:IF experiencing respiratory symptoms: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P403:Store in a well-ventilated place. |
Computed Descriptors for Lipase
Lipase manufacturer
HRV Global Life Sciences
Meteoric Biopharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd.
Enzyme BioScience pvt Ltd
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran





You may like
-
 Lipase from Porcine Pancreas CAS 9001-62-1View Details
Lipase from Porcine Pancreas CAS 9001-62-1View Details
9001-62-1 -
 Lipase CAS 9001-62-1View Details
Lipase CAS 9001-62-1View Details
9001-62-1 -
 Lipase (Steapsin) ex. Aspergillus Sp. CAS 9001-62-1View Details
Lipase (Steapsin) ex. Aspergillus Sp. CAS 9001-62-1View Details
9001-62-1 -
 Lipase from Candida rugosa Type VII CAS 9001-62-1View Details
Lipase from Candida rugosa Type VII CAS 9001-62-1View Details
9001-62-1 -
 LIPASE from Aspergillus niger CAS 9001-62-1View Details
LIPASE from Aspergillus niger CAS 9001-62-1View Details
9001-62-1 -
 Amano Lipase PS, from Burkholderia cepacia CASView Details
Amano Lipase PS, from Burkholderia cepacia CASView Details -
 Amano Lipase from Pseudomonas fluorescens CAS 9001-62-1View Details
Amano Lipase from Pseudomonas fluorescens CAS 9001-62-1View Details
9001-62-1 -
 Amano Lipase PS CASView Details
Amano Lipase PS CASView Details