LCZ696
- CAS NO.:936623-90-4
- Empirical Formula: C48H58N6O8
- Molecular Weight: 847.03
- MDL number: MFCD29477717
- EINECS: 000-000-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-22 20:27:16
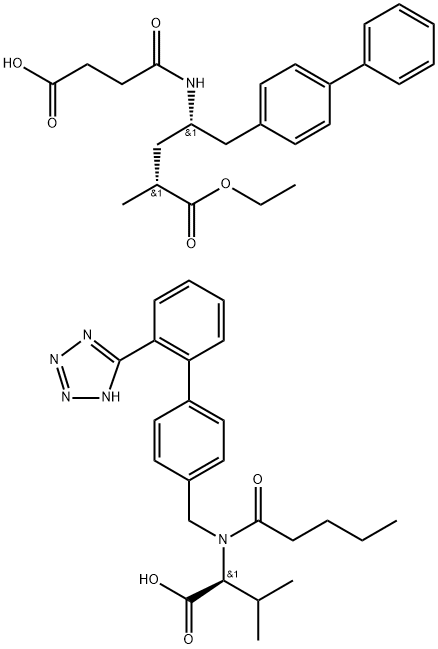
What is LCZ696?
Description
LCZ696 is a dual angiotensin II receptor antagonist and neprilysin inhibitor that is a combination of the nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist valsartan and AHU377 , a prodrug of LBQ657 , which is an inhibitor of the zinc metallopeptidase neprilysin., LCZ696 (2-60 mg/kg) induces a dose-dependent decrease in mean arterial pressure in rats expressing human renin and angiotensinogen, a double-transgenic model for angiotensin II-dependent hypertension. Formulations containing LCZ696 are under clinical investigation for the treatment of mild to moderate hypertension and chronic heart failure.
Mechanism of action
LCZ696 is a molecule that combines the moieties of valsartan and sacubitril (the neprilysin inhibitor) in a single substance. By inhibiting neprilysin, the degradation of natriuretic peptides, bradykinin, and other peptides is slowed. Hence, high circulating levels of natriuretic peptides enhance diuresis , natriuresis, myocardial relaxation, and anti-remodelling, on top of the ARB effects of valsartan.
Clinical Use
LCZ696 (Novartis Pharmaceuticals), a first-in-class inhibitor of dualacting angiotensin-2 type-I receptor and neprilysin inhibitors, was developed as a molecule composed of molecular moieties of valsartan and neprilysin inhibitor prodrug AHU377 in a 1:1 ratio. Several phase 2 randomised clinical trials have been done or are underway in patients with hypertension. In a proof-of-concept randomised trial, LCZ696 was compared with valsartan in 1328 patients with mild-to-moderate hypertension, and provided fully additive reduction of blood pressure. No cases of angio-oedema were reported in the 8 week treatment period. This tolerance should be confirmed, particularly in black patients, for whom omapatrilat resulted in a higher occurrence of angio-oedema than in white patients. Indeed, in the proof-of-concept trial only about 8% of patients were black.
References
1. McMurray, John J. V. et al. “Angiotensin-neprilysin inhibition versus enalapril in heart failure.” The New England journal of medicine 371 11 (2014): 993-1004. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1409077
2. Gu, Jessie et al. “Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of LCZ696, a Novel Dual‐Acting Angiotensin Receptor—Neprilysin Inhibitor (ARNi).” The
Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 50 (2010): n. pag. DOI: 10.1177/0091270009343932
3. Langenickel, T.H., & Dole, W.P. (2012). Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibition with LCZ696: a novel approach for the treatment of heart failure. Drug Discovery Today: Therapeutic Strategies, 9. DOI: 10.1016/J.DDSTR.2013.11.002
4. Suematsu, Yasunori et al. “LCZ696, an angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitor, improves cardiac function with the attenuation of fibrosis in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction in streptozotocin‐induced diabetic mice.” European Journal of Heart Failure 18 (2016): n. pag. DOI: 10.1002/ejhf.474
Properties of LCZ696
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | ≥45.05 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥11.28 mg/mL in H2O; ≥28.5 mg/mL in EtOH |
| form | solid |
| color | White to light yellow |
Safety information for LCZ696
Computed Descriptors for LCZ696
| InChIKey | XTKIDERFOUYBDE-NOFROVMTNA-N |
| SMILES | C(C1C=CC(C2C=CC=CC=2C2=NN=NN2)=CC=1)N(C(=O)CCCC)[C@H](C(=O)O)C(C)C.C(C1C=CC(C2C=CC=CC=2)=CC=1)[C@@H](NC(=O)CCC(=O)O)C[C@@H](C)C(=O)OCC |&1:25,45,55,r| |
LCZ696 manufacturer
Exemed Pharmaceuticals (Oneiro Chemicals Pvt Ltd)
Blue Jet Healthcare Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
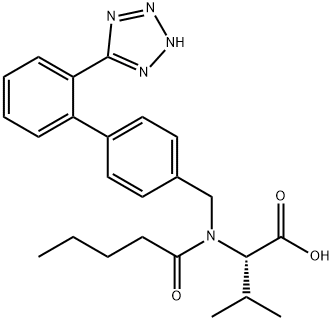
![(S)-5-[(Biphenyl-4-yl)carbonyl]pyrrolidin-2-one](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20150408/GIF/195137-95-2.gif)
![(2R,4S)-4-([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-ylmethyl)-2-methyl-4-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)butanoic acid](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180702/GIF/1639970-62-9.gif)
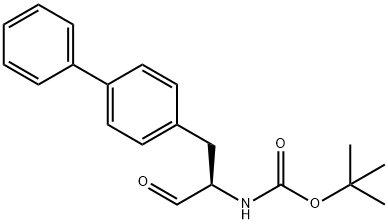
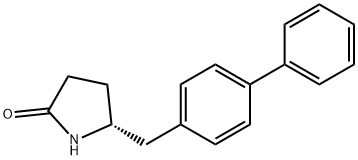
![(2R,4S)-ethyl 5-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-aMino-2-Methylpentanoate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20150408/GIF/149690-12-0.gif)
![(2R,4S)-5-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)aMino)-2-Methylpentanoic acid](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20150408/GIF/1012341-50-2.gif)
![(2R,4S)-ethyl 5-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-4-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)aMino)-2-Methylpentanoate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20150408/GIF/149709-60-4.gif)
You may like
-
 936623-90-4 Sacubitril/Valsartan LCZ API 98%View Details
936623-90-4 Sacubitril/Valsartan LCZ API 98%View Details
936623-90-4 -
 936623-90-4 98%View Details
936623-90-4 98%View Details
936623-90-4 -
 SACUBITRIL VALSARTAN 99%View Details
SACUBITRIL VALSARTAN 99%View Details
936623-90-4 -
 Sacubitril Valsartan trisodium hydrate 936623-90-4 98%View Details
Sacubitril Valsartan trisodium hydrate 936623-90-4 98%View Details
936623-90-4 -
 936623-90-4 Sacubitril Valsartan >98%View Details
936623-90-4 Sacubitril Valsartan >98%View Details
936623-90-4 -
 Lcz696 95% CAS 936623-90-4View Details
Lcz696 95% CAS 936623-90-4View Details
936623-90-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1