Lauric acid
Synonym(s):ABL;Dodecanoic acid;Lauric acid;NSC 5026
- CAS NO.:143-07-7
- Empirical Formula: C12H24O2
- Molecular Weight: 200.32
- MDL number: MFCD00002736
- EINECS: 205-582-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 08:49:36
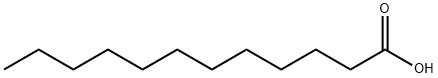
What is Lauric acid?
Description
Lauric acid, also known as dodecanoic acid, is a saturated fatty acid with a 12-carbon atom chain, thus falling into the medium chain fatty acids, is a white crystalline carboxylic acid with a faint odor of bay oil or soap. It has been found at high levels in coconut oil. Lauric acid induces the activation of NF-κB and the expression of COX-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and IL-1α in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 μM.
Physical properties
Lauric acid occurs as a white crystalline powder with a slight odor of bay oil or a fatty odor. It is practically insoluble in water but is soluble in alco- hol, chloroform, and ether. It is a common constituent of most diets; large doses may produce gastrointestinal upset.
Occurrence
Lauric acid, as a component of triglycerides, comprises about half of the fatty acid content in coconut oil, laurel oil, and in palm kernel oil (not to be confused with palm oil) , Otherwise it is relatively uncommon. It is also found in human breast milk ( 6.2 % of total fat), cow's milk (2.9%), and goat's milk (3.1 %).
The Uses of Lauric acid
Given its foaming properties, the derivatives of lauric acid (h-dodecanoic acid) are widely used as a base in the manufacture of soaps, detergents, and lauryl alcohol. Lauric acid is a common constituent of vegetable fats, especially coconut oil and laurel oil. It may have a synergistic effect in a formula to help fight against mircoorganisms. It is a mild irritant but not a sensitizer, and some sources cite it as comedogenic.
Background
Lauric acid is an inexpensive, non-toxic and safe to handle compound often used in laboratory investigations of melting-point depression. Lauric acid is a solid at room temperature but melts easily in boiling water, so liquid lauric acid can be treated with various solutes and used to determine their molecular masses. It is mainly used for the production of soaps and cosmetics. For these purposes, lauric acid is neutralized with sodium hydroxide to give sodium laurate, which is a soap. Most commonly, sodium laurate is obtained by saponification of various oils, such as coconut oil. These precursors give mixtures of sodium laurate and other soaps.
What are the applications of Application
Lauric Acid is a common saturated fatty acid compound. It can be obtained from coconut oil and other plant fats. It is used as a liquid crystal intermediate, lubricant, adhesive and defoamer.
Definition
ChEBI: Lauric acid is a straight-chain, twelve-carbon medium-chain saturated fatty acid with strong bactericidal properties; the main fatty acid in coconut oil and palm kernel oil. It has a role as a plant metabolite, an antibacterial agent and an algal metabolite. It is a straight-chain saturated fatty acid and a medium-chain fatty acid. It is a conjugate acid of a dodecanoate. It derives from a hydride of a dodecane.
Production Methods
Lauric acid is a fatty carboxylic acid isolated from vegetable and animal fats or oils. For example, coconut oil and palm kernel oil both contain high proportions of lauric acid. Isolation from natural fats and oils involves hydrolysis, separation of the fatty acids, hydrogenation to convert unsaturated fatty acids to saturated acids, and finally distillation of the specific fatty acid of interest.
Definition
A white crystalline carboxylic acid, used as a plasticizer and for making detergents and soaps. Its glycerides occur naturally in coconut and palm oils.
Aroma threshold values
Aroma characteristics at 1.0%: fatty, creamy, cheeselike, candle waxy with egglike richness
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 5 ppm: waxy,fatty and oily, tallowlike, creamy and dairylike with a coating mouthfeel
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 32, p. 5931, 1991 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)79429-9
General Description
White solid with a slight odor of bay oil.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Lauric acid is a carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acids donate hydrogen ions if a base is present to accept them. They react in this way with all bases, both organic (for example, the amines) and inorganic. Their reactions with bases, called "neutralizations", are accompanied by the evolution of substantial amounts of heat. Neutralization between an acid and a base produces water plus a salt. Carboxylic acids in aqueous solution and liquid or molten carboxylic acids can react with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Such reactions occur in principle for solid carboxylic acids as well, but are slow if the solid acid remains dry. Even "insoluble" carboxylic acids may absorb enough water from the air and dissolve sufficiently in Lauric acid to corrode or dissolve iron, steel, and aluminum parts and containers. Carboxylic acids, like other acids, react with cyanide salts to generate gaseous hydrogen cyanide. The reaction is slower for dry, solid carboxylic acids. Insoluble carboxylic acids react with solutions of cyanides to cause the release of gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases and heat are generated by the reaction of carboxylic acids with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides. Carboxylic acids, especially in aqueous solution, also react with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Their reaction with carbonates and bicarbonates generates a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) but still heat. Like other organic compounds, carboxylic acids can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents. These reactions generate heat. A wide variety of products is possible. Like other acids, carboxylic acids may initiate polymerization reactions; like other acids, they often catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions. Lauric acid can react with oxidizing materials.
Health Hazard
May be harmful by inhalation, ingestion or skin absorption. Vapor or mist is irritating to eyes, mucous membrane and upper respiratory tract. Causes eye and skin irritation.
Fire Hazard
Behavior in Fire: May cause dust explosion.
Pharmaceutical Applications
pharmaceutical applications it has also been examined for use as an enhancer for topical penetration and transdermal absorption, rectal absorption, buccal delivery,(14) and intestinal absorption. It is also useful for stabilizing oil-in-water emulsions. Lauric acid has also been evaluated for use in aerosol formulations.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Substrate for CYP 4A11
Safety
Lauric acid is widely used in cosmetic preparations, in the
manufacture of food-grade additives, and in pharmaceutical
formulations. General exposure to lauric acid occurs through the
consumption of food and through dermal contact with cosmetics,
soaps, and detergent products. Lauric acid is toxic when
administered intravenously.
Occupational exposure may cause local irritation of eyes, nose,
throat, and respiratory tract, although lauric acid is considered
safe and nonirritating for use in cosmetics. No toxicological
effects were observed when lauric acid was administered to rats at
35% of the diet for 2 years. Acute exposure tests in rabbits
indicate mild irritation. After subcutaneous injection into mice,
lauric acid was shown to be noncarcinogenic.
LD50 (mouse, IV): 0.13 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 12 g/kg
Synthesis
Produced from synthetic lauryl alcohol
in vitro
previous study showed that lauric acid could induce apoptosis in both caco-2 and iec-6 cells when compared to butyrate. moreover, lauric acid reduced gsh availability and generated ros in caco-2 cells. mechanistic study indicated that lauric acid reduced caco-2 and iec-6 cells in g0/g1and arrested cells in the s and g2/m phases. in addition, it was found that butyrate protected iec-6 cells from ros-induced damage, while lauric acid induced higher levels of ros when compared with butyrate [1].
in vivo
mouse in vivo study found that both epicutaneous application and intradermal injection of lauric acid could decrease the number of p. acnes colonized in mouse ears effectively, thus relieving p. acnes-induced granulomatous inflammation and ear swelling [2].
Carcinogenicity
Lauric acid was not carcinogenic in the BALB/c:CFW mouse after repeated subcutaneous injections. Lauric acid applied twice weekly for 20 weeks did not promote tumors in mice initiated with 9,10- dimethyl-1,2-benzanthracene. After more extended application (daily, 6 days/week, for 31 weeks), lauric acid caused an increase in skin papillomas, but no histologically malignant tumors were found. Lauric acid was not carcinogenic in rats after exposure in the diet to 35% lauric acid for 2 years.
Metabolism
Storage
Lauric acid is stable at normal temperatures and should be stored in a cool, dry place. Avoid sources of ignition and contact with incompatible materials.
Purification Methods
Distil the acid in a vacuum. Also crystallise it from absolute EtOH, or from acetone at -25o. Alternatively, purify it via its methyl ester (b 140.0o/15mm), as described for capric acid. It has also been purified by zone melting. [cf Beilstein 1 III 2913.]
Incompatibilities
Lauric acid is incompatible with strong bases, reducing agents, and oxidizing agents.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Lauric acid is listed as a food additive in the EAFUS list compiled by the FDA. Reported in the EPA TSCA Inventory.
References
[1] fauser jk,matthews gm,cummins ag,howarth gs. induction of apoptosis by the medium-chain length fatty acid lauric acid in colon cancer cells due to induction of oxidative stress. chemotherapy.2013;59(3):214-24.
[2] nakatsuji t,kao mc,fang jy,zouboulis cc,zhang l,gallo rl,huang cm. antimicrobial property of lauric acid against propionibacterium acnes: its therapeutic potential for inflammatory acne vulgaris. j invest dermatol.2009 oct;129(10):2480-8.
[3] kate l. feltrin et al. acute oral administration of lauric acid reduces energy intake in healthy males. e-spen journal. 2014 april; 9 (2): e69–e75
Properties of Lauric acid
| Melting point: | 44-46 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 225 °C/100 mmHg (lit.) |
| Density | 0.883 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 121 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4304 |
| FEMA | 2614 | LAURIC ACID |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 4.81mg/l |
| form | Crystalline Powder of Flakes |
| pka | pKa 4.92(H2O,t =25.0) (Uncertain) |
| Specific Gravity | 0.883 |
| color | White |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. mild fatty coconut bay oil |
| explosive limit | 0.6%(V) |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| λmax | 207nm(MeOH)(lit.) |
| JECFA Number | 111 |
| Merck | 14,5384 |
| BRN | 1099477 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with bases, oxidizing agents, reducing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 143-07-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Dodecanoic acid(143-07-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lauric acid (143-07-7) |
Safety information for Lauric acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Lauric acid
| InChIKey | POULHZVOKOAJMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Lauric acid manufacturer
Paxal Chemical Industry Private Limited
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Dodecanoic acid CAS 143-07-7View Details
Dodecanoic acid CAS 143-07-7View Details
143-07-7 -
 Dodecanoic acid CAS 143-07-7View Details
Dodecanoic acid CAS 143-07-7View Details
143-07-7 -
 Dodecanoic acid CAS 143-07-7View Details
Dodecanoic acid CAS 143-07-7View Details
143-07-7 -
 Lauric Acid CASView Details
Lauric Acid CASView Details -
 Lauric Acid FlakesView Details
Lauric Acid FlakesView Details
143-07-7 -
 Lauric Acid PowderView Details
Lauric Acid PowderView Details
143-07-7 -
 Lauric AcidView Details
Lauric AcidView Details
143-07-7 -
 Lauric Acid, Packaging Size: 25View Details
Lauric Acid, Packaging Size: 25View Details
143-07-7
