L(+)-Tartaric acid
Synonym(s):(2R,3R)-(+)-Tartaric acid;(2R,3R)-(+)-Tartaric acid;L -Threaric acid;2,3-Dihydroxybutanedioic acid;L(+)-Tartaric acid
- CAS NO.:87-69-4
- Empirical Formula: C4H6O6
- Molecular Weight: 150.09
- MDL number: MFCD00064207
- EINECS: 201-766-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-22 14:18:24
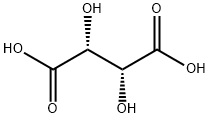
What is L(+)-Tartaric acid?
Description
L(+)-Tartaric acid is abundant in nature, especially in fruits. Its primary commercial source is as a byproduct of the wine industry. It is used as an additive in many foods, such as soft drinks, bakery products, and candies. Industrial uses include tanning, ceramics manufacture, and the production of tartrate esters for lacquers and textile printing.
Chemical properties
Tartaric acid occurs as colorless monoclinic crystals, or a white or almost white crystalline powder. It is odorless, with an extremely tart taste. L-(+)-Tartaric Acid is a naturally occurring chemical compound found in berries, grapes and various wines. It provides antioxidant properties and contributes to the sour taste within these products.
The Uses of L(+)-Tartaric acid
L-(+)-tartaric acid is an organic compound that is commonly used as a chiral auxiliary in reactions that involve the addition of a chiral nucleophile. It is also used as a resolving agent for the separation of enantiomers from a racemic mixture. Additionally, L-(+)-tartaric acid can also be used as a building block for the synthesis of other chiral compounds.
The Uses of L(+)-Tartaric acid
L-(+)-Tartaric acid is widely utilized in pharmaceutical industries. It is used in soft drinks, confectionaries, food products, gelatin desserts and as a buffering agent. It forms a compound, TiCl2(O-i-Pr)2 with Diels-Alder catalyst and acta as a chelate agent in metal industries. Owing to its efficient chelating property towards metal ions, it is used in farming and metal industries for complexing micronutrients and for cleaning metal surfaces, respectively.
Definition
ChEBI: L-tartaric acid is a tetraric acid that is butanedioic acid substituted by hydroxy groups at positions 2 and 3. It is a conjugate acid of a L-tartrate(1-). It is an enantiomer of a D-tartaric acid.
Production Methods
Tartaric acid occurs naturally in many fruits as the free acid or in
combination with calcium, magnesium, and potassium.
Commercially, L(+)-Tartaric acid is manufactured from potassium
tartrate (cream of tartar), a by-product of wine making.
Potassium tartrate is treated with hydrochloric acid, followed by the
addition of a calcium salt to produce insoluble calcium tartrate.
This precipitate is then removed by filtration and reacted with 70%
sulfuric acid to yield tartaric acid and calcium sulfate.
L-Tartaric acid applications
In the soft drink industry, confectionery products, bakery products, gelatin desserts, L-Tartaric acid is used as an acidulant. It is also used In photography, tanning, ceramics, manufacture of tartrates.
General Description
Tartaric Acid belongs to the group of carboxylic acids, and is abundantly found in grapes and wine. It is widely used in drugs, food, and beverage industry.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Pharmaceutical Applications
Tartaric acid is used in beverages, confectionery, food products, and
pharmaceutical formulations as an acidulant. It may also be used as
a sequestering agent and as an antioxidant synergist. In pharmaceutical
formulations, it is widely used in combination with
bicarbonates, as the acid component of effervescent granules,
powders, and tablets.
Tartaric acid is also used to form molecular compounds (salts
and cocrystals) with active pharmaceutical ingredients to improve
physicochemical properties such as dissolution rate and solubility.
Biochem/physiol Actions
L-(+)-Tartaric acid serves as a donor ligand for biological processes. It is used as a food additive in candies and soft drinks to impart a sour taste.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intravenous route. Mildly toxic by ingestion. Reaction with silver produces the unstable silver tartrate. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Safety
L(+)-Tartaric acid is widely used in food products and oral, topical, and
parenteral pharmaceutical formulations. It is generally regarded as
a nontoxic and nonirritant material; however, strong tartaric acid
solutions are mildly irritant and if ingested undiluted may cause
gastroenteritis.
An acceptable daily intake for L-(+)-tartaric acid has not been set
by the WHO, although an acceptable daily intake of up to 30 mg/kg
body-weight for monosodium L-(+)-tartrate has been established.
LD50 (mouse, IV): 0.49 g/kg
Storage
The bulk material is stable and should be stored in a well-closed container in a cool, dry place.
Incompatibilities
L(+)-Tartaric acid is incompatible with silver and reacts with metal carbonates and bicarbonates (a property exploited in effervescent preparations).
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IM and IV injections; oral solutions, syrups and tablets; sublingual tablets; topical films; rectal and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of L(+)-Tartaric acid
| Melting point: | 170-172 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 191.59°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 12 º (c=20, H2O) |
| Density | 1.76 |
| vapor density | 5.18 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | <5 Pa (20 °C) |
| FEMA | 3044 | TARTARIC ACID (D-, L-, DL-, MESO-) |
| refractive index | 12.5 ° (C=5, H2O) |
| Flash point: | 210 °C |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble1M at 20°C, clear, colorless |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 2.98, 4.34(at 25℃) |
| color | White or colorless |
| PH | 3.18(1 mM solution);2.55(10 mM solution);2.01(100 mM solution); |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. odorless |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +13.5±0.5°, c = 10% in H2O |
| Water Solubility | 1390 g/L (20 ºC) |
| JECFA Number | 621 |
| Merck | 14,9070 |
| BRN | 1725147 |
| Dielectric constant | 35.9(-10℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, bases, reducing agents. Combustible. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 87-69-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Butanedioic acid, 2,3-dihydroxy- [r-(r*,r*)]-(87-69-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tartaric acid (87-69-4) |
Safety information for L(+)-Tartaric acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for L(+)-Tartaric acid
| InChIKey | FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N |
L(+)-Tartaric acid manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![2-[(6-Hydroxy[1,1'-biphenyl]-3-yl)carbonyl]benzoic acid compd. with 1-[2-[(S)-(4-chlorophenyl)phenylmethoxy]ethyl]piperidine](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180808/GIF/220329-19-1.gif)
![Potassium (R)-[(3-ethoxy-1-methyl-3-oxoprop-1-enyl)amino]phenylacetate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/961-69-3.gif)
You may like
-
 L (+) TARTARIC ACID 99%View Details
L (+) TARTARIC ACID 99%View Details -
 L-Tartaric acid 98%View Details
L-Tartaric acid 98%View Details -
 L-Tartaric acid 99%View Details
L-Tartaric acid 99%View Details -
 L-(+)-Tartaric acid CAS 87-69-4View Details
L-(+)-Tartaric acid CAS 87-69-4View Details
87-69-4 -
 L-(+)-Tartaric Acid CAS 87-69-4View Details
L-(+)-Tartaric Acid CAS 87-69-4View Details
87-69-4 -
 L-(+)-Tartaric acid CAS 87-69-4View Details
L-(+)-Tartaric acid CAS 87-69-4View Details
87-69-4 -
 L Tartaric Acid CASView Details
L Tartaric Acid CASView Details -
 L Tartaric Acid CASView Details
L Tartaric Acid CASView Details
