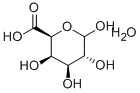
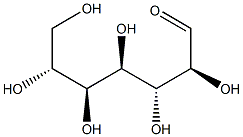
L-Fucose
Synonym(s):L- (−)-Fucose;6-Deoxy-L -galactose
- CAS NO.:2438-80-4
- Empirical Formula: C6H12O5
- Molecular Weight: 164.16
- MDL number: MFCD00135607
- EINECS: 219-452-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:24
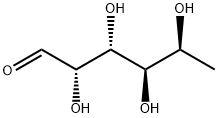
What is L-Fucose?
Description
L-(−)-Fucose is a deoxyhexose monosaccharide found on N- and O-linked glycans and glycolipids of a wide variety of organisms. It can exist as a terminal modification of glycan structures or serve as a point of attachment for adding other sugars. In humans, L-(−)-fucose plays a role in A and B blood group antigen substructure determination, selectin-mediated leukocyte-endothelial adhesion, and host-microbe interactions.
Chemical properties
White crystalline powder, soluble in methanol, ethanol, DMSO and other organic solvents.
Chemical properties
l-fucose is a six-carbon sugar also known as 6-deoxy-l-galactose. Its molecular formula is C6H12O5 and its melting point is 150.0–153.0 °C. It is a white crystalline powder that easily absorbs moisture, and its hydrophilicity is weaker than that of other monosaccharides. l-fucose is the main form of fucose found in nature and is also the only levorotatory sugar used by mammals, while d-fucose is found only in some glycosides[1].
Occurrence
L-Fucose exists in nature in various biological niches. A major natural source of L-fucose is the brown algal polysaccharide fucoidan. It is also present in the polysaccharides of tragacanth, potatoes, kiwi, soybeans, varieties of wing peas, canola and other plants.L-Fucose is a minor component in plant cell wall polysaccharides, specifically rhamnogalacturonan, xyloglucan and also arabinogalactan proteins that are involved in plant cell elongation.
The Uses of L-Fucose
L-Fucose was isolated from seaweed. It finds application in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and dietary supplements. It is used in the determination of antigen in A and B blood group. It is also used in the selection-mediated leukocyte-endothelial adhesion and host-microbe interactions. L-Fucose is also used in anti aging creams as well as to promote the accelerated healing of wounds and to reduce allergy.
What are the applications of Application
L-(?)-Fucose is a glycan modifying carbohydrate
Definition
ChEBI: L-fucopyranose is the pyranose form of L-fucose. It has a role as an Escherichia coli metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a L-fucose and a fucopyranose.
Reactions
L-Fucose is oxidised by the enzyme L-fucose dehydrogenase in the presence of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+) to L-fucono-1,5-lactone with the formation of reduced nicotinamideadenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) (1).
(L-fucose dehydrogenase) (1)
L-Fucose + NADP+ --> L-fucono-1,5-lactone + NADPH + H+
The amount of NADPH formed in this reaction is stoichiometric with the amount of L-fucose. It is the NADPH which is measured by the increase in absorbance at 340 nm.
Biological Functions
l-fucose has many biological functions like the antitumor effect and relieving intestinal disease, and exhibits potential as an emulsifier in the food industry. It can be used as a functional food and one of the components of bacteriostatic agents. Moreover, it also has an anti-aging function[1].
Biological Activity
L-Fucose (6-Deoxy-L-galactose) is used in studies of fucoidan polysaccharides containing glycans. It is studied as a glycan modifying carbohydrate that generates antigenic sites recognized by IgE antibodies. It is used as a substrate to identify, differentiate, and characterize enzymes such as fucosidase(s),l-fucose isomerase(s), and L-fucose dehydrogenase(s). It may be used to study organelles, and bacterial microcompartments, involved in the degradation of plant and algal cell wall sugars. L-Fucose may also be used as a reference compound in rare sugar identification and analysis.
References
[1] Yan Wang . “Research progress on the functions, preparation and detection methods of l-fucose.” Food Chemistry 433 (2023): Article 137393.
Properties of L-Fucose
| Melting point: | 150-153 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 211.61°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | -73~-77°(D/20℃)(c=4,H2O,24hr) |
| Density | 1.1738 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | -75.5 ° (C=10, H2O) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 g/mL, clear, colorless |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 12.50±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | Beige to light brown to purple-grayish |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,4279 |
| BRN | 1723321 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 2438-80-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | L-Galactose, 6-deoxy- (2438-80-4) |
Safety information for L-Fucose
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for L-Fucose
| InChIKey | SHZGCJCMOBCMKK-DLABPRKASA-N |
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![FUCOSE, L-, [6-3H],L-FUCOSE, [6-3H]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/122760-10-5.gif)


You may like
-
 L-Fucose CAS 2438-80-4View Details
L-Fucose CAS 2438-80-4View Details
2438-80-4 -
 L-(-)-Fucose CAS 2438-80-4View Details
L-(-)-Fucose CAS 2438-80-4View Details
2438-80-4 -
 L-Fucose extrapure CAS 2438-80-4View Details
L-Fucose extrapure CAS 2438-80-4View Details
2438-80-4 -
 L-Fucose 95% CAS 2438-80-4View Details
L-Fucose 95% CAS 2438-80-4View Details
2438-80-4 -
 L-Fucose CAS 2438-80-4View Details
L-Fucose CAS 2438-80-4View Details
2438-80-4 -
 L-(-)-Fucose 95.00% CAS 2438-80-4View Details
L-(-)-Fucose 95.00% CAS 2438-80-4View Details
2438-80-4 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
