Ketorolac
Synonym(s):(-)-Ketorolac;(1S)-5-Benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid;(S)-Ketorolac
- CAS NO.:74103-06-3
- Empirical Formula: C15H13NO3
- Molecular Weight: 255.27
- MDL number: MFCD00864281
- EINECS: 616-049-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-07-04 15:01:35
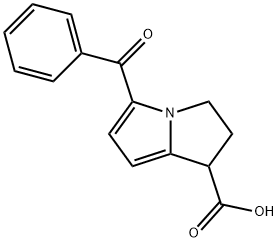
What is Ketorolac?
Absorption
Ketorolac is rapidly, and completely absorbed after oral administration with a bioavailability of 80% after oral administration. Cmax is attained 20-60 minutes after administration, and after intramuscular administration, the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) is proportional to the dose administered.
After intramuscular administration, ketorolac demonstrates a time to maximal plasma concentration (tmax) of approximately 45-50 minutes, and a tmax of 30-40 minutes after oral administration. The rate of absorption may be reduced by food; however, the extent of absorption remains unaffected.
Toxicity
The rate of adverse effects increases with higher doses of ketorolac. The most frequently observed adverse effects in patients occurring with an incidence of greater than 10% include: abdominal pain, dyspepsia, nausea, and headaches. Most adverse effects associated with short term use are mild in nature, related to the gastrointestinal tract and nervous system, and occur in roughly 39% of patients. Common symptoms of ketorolac overdose include nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, gastrointestinal bleeding, lethargy and drowsiness. More rare symptoms of overdose include acute renal failure, hypertension, respiratory depression, and coma.
Ketorolac is classified as Pregnancy Category C since there is a lack of evidence demonstrating safety in pregnant women. NSAIDs including ketorolac increase the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus in the 3rd trimester; therefore, beginning at 30 weeks gestation, pregnant women should avoid ketorolac.
Ketorolac has been shown to be excreted in breast milk, and although available data has not demonstrated any adverse effects in nursing infants, practitioners should proceed with caution when suggesting ketorolac for nursing mothers. The benefits should outweigh the risks and the mother should be counselled to monitor the infant closely and to contact the infant's healthcare provider should any adverse effects arise.
Women who are trying to conceive are not advised to take ketorolac since it's effect on prostaglandin synthesis may impair fertility.
Chemical properties
Light yellow solid
The Uses of Ketorolac
Ketorolac-d5 is a labeled analogue of Ketorolac, a Prostaglandin biosynthesis inhibitor. Analgesic; anti-inflammatory.
The Uses of Ketorolac
antiarrhythmic
The Uses of Ketorolac
prostaglandin F2a analogue
Indications
Ketorolac is a Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and has antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. It is indicated for short term management of acute pain that requires the calibre of pain management offered by opioids. Clinicians may choose to initiate ketorolac to manage post-operative pain, spinal and soft tissue pain, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, menstrual disorders and headaches among other ailments. Regardless of the etiology of pain, patients should use the lowest possible dose, and avoid using ketorolac for an extended period of time (ideally ≤ 5 days). A benefit of choosing ketorolac over other analgesics with similar potency is that that there does not appear to be a risk of dependence or tolerance with ketorolac use.
Background
Ketorolac is a Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and is commercially available as an oral tablet, injectable, nasal spray and as an ophthalmic solution.
It's analgesic properties make it a useful pain management tool across many settings including postoperative pain, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, menstrual disorders, headaches, spinal and soft tissue pain, and ankylosing spondylitis. Impressively, ketorolac has a similar efficacy to standard doses of morphine and meperidine making it a useful opioid sparing agent.
What are the applications of Application
Ketorolac is a heterocyclic acetic acid derivative that inhibits prostaglandins
Indications
Ketorolac (Toradol), an NSAID chemically related to indomethacin and tolmetin, is mainly used as an analgesic, not for the treatment of inflammatory disease. It is available in oral, parenteral, and topical formulations.
Definition
ChEBI: Ketorolac is a racemate comprising equimolar amounts of (R)-(+)- and (S)-(-)-5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid. While only the (S)-(-) enantiomer is a COX1 and COX2 inhibitor, the (R)-(+) enantiomer exhibits potent analgesic activity. A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, ketorolac is mainly used (generally as the tromethamine salt) for its potent analgesic properties in the short-term management of post-operative pain, and in eye drops to relieve the ocular itching associated with seasonal allergic conjunctivitis. It was withdrawn from the market in many countries in 1993 following association with haemorrhage and renal failure. It has a role as a cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor, a cyclooxygenase 1 inhibitor, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug and an analgesic. It contains a (R)-ketorolac and a (S)-ketorolac. It is a conjugate acid of a ketorolac(1-).
brand name
Acular (Allergan); Toradol (Roche).
World Health Organization (WHO)
Ketorolac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent used in the management of moderate to severe acute post-operative pain. It remains on the market in many countries with restrictions on its use.
Biological Functions
Ketorolac (Toradol) is an NSAID with very mild antiinflammatory and antipyretic activity. It is a potent analgesic for postoperative pain. Its efficacy is equivalent to that of low doses of morphine in the control of pain. For this reason it is often combined with opioids to reduce opioid dose and related side effects while providing adequate pain relief. It is also used to replace the opioids in some patients with opioid sensitivity. The mechanism of action of ketorolac involves the inhibition of COX and decreased formation of prostaglandins. However, some evidence exists that ketorolac may stimulate the release of endogenous opioids as a part of its analgesic activity.
General Description
Ketorolac tromethamine (Toradol), marketed as a mixture of(R)- and (S)-ketorolac enantiomers, is a potent NSAID analgesicindicated for the treatment of moderately severe, acutepain. It should be noted that the pharmacokinetic dispositionof ketorolac in humans is subject to marked enantioselectivity.Thus, it is important to monitor the individual blood levelsso an accurate assessment of its therapeutic action can bemade correctly. However, it should be noted that, beingone of the conventional NSAIDs with highest risk of GIcomplications, its administration should not exceed 5 days.
Pharmacokinetics
Ketorolac is a non-selective NSAID and acts by inhibiting both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes which are normally responsible for converting arachidonic acid to prostaglandins. The COX-1 enzyme is constitutively active and can be found in platelets, gastric mucosa, and vascular endothelium. On the other hand, the COX-2 enzyme is inducible and mediates inflammation, pain and fever.
As a result, inhibition of the COX-1 enzyme is linked to an increased risk of bleeding and risk of gastric ulceration, while the desired anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties are linked to inhibition of the COX-2 enzyme. Therefore, despite it's effectiveness in pain management, ketorolac should not be used long-term since this increases the risk of serious adverse effects such as gastrointestinal bleeding, peptic ulcers, and perforations.
Clinical Use
Ketorolac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug mainly used for the treatment of moderate to severe postoperative pain. Ketorolac shows a balanced inhibition of COX-1 and COX-2 in cultured human cells . Ketorolac is mostly used as the tromethamine salt. Due to a number of severe side effects including gastrointestinal disturbances, impairment of liver functions, renal failures, skin irritations, and other hypersensitivity reaction it has been withdrawn in many countries.
Synthesis
Benzoylation of 2-methylthiopyrrole
with N,N-dimethylbenzamide in the
presence of POCl3 in refluxing CH2Cl2 gives
5-benzoyl-2-methylthiopyrrole, which is condensed
with spiro-5,7-dioxa-6,6-dimethyloctane-
4,8-dione by means of NaH in DMF.
Oxidation of this product with m-chloroperbenzoic
acid in CH2Cl2 affords the sulfone, which
is submitted to methanolysis with methanol and
HCl giving 1-(3,3-dimethoxycarbonylpropyl)-
2-methanesulfonyl-5-benzoylpyrrole. Cyclization with NaH inDMFyields dimethyl-5-benzoyl-
1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrrolopyrrole-1,1-
dicarboxylate, which is finally hydrolyzed and
decarboxylated withKOHin refluxing methanol
.
Metabolism
Ketorolac is heavily metabolized via hydroxylation or conjugation in the liver; however, it appears that the key metabolic pathway is glucuronic acid conjugation. Enzymes involved in phase I metabolism include CYP2C8 and CYP2C9, while phase II metabolism is carried out by UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 2B7.
Properties of Ketorolac
| Melting point: | 160-161°C |
| Boiling point: | 493.2±40.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.33±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 3.49 ±0.02(at 25℃) |
| color | Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 183mg/L(32 ºC) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 74103-06-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1H-Pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid, 5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro- (74103-06-3) |
Safety information for Ketorolac
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Ketorolac
Ketorolac manufacturer
SPARKVEE FINE CHEMICALS PRIVATE LIMITED
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Ketorolac 74103-06-3 99%View Details
Ketorolac 74103-06-3 99%View Details
74103-06-3 -
 74103-06-3 Ketorolac 98%View Details
74103-06-3 Ketorolac 98%View Details
74103-06-3 -
 74103-06-3 98%View Details
74103-06-3 98%View Details
74103-06-3 -
 74103-06-3 Ketorolac 98%View Details
74103-06-3 Ketorolac 98%View Details
74103-06-3 -
 5-Benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid 95-99%View Details
5-Benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid 95-99%View Details
74103-06-3 -
 74103-06-3 KETOROLAC TROMETHAMINEView Details
74103-06-3 KETOROLAC TROMETHAMINEView Details
74103-06-3 -
 Ketorolac 99% (HPLC) CAS 74103-06-3View Details
Ketorolac 99% (HPLC) CAS 74103-06-3View Details
74103-06-3 -
 Ketorolac 98.00% CAS 74103-06-3View Details
Ketorolac 98.00% CAS 74103-06-3View Details
74103-06-3
