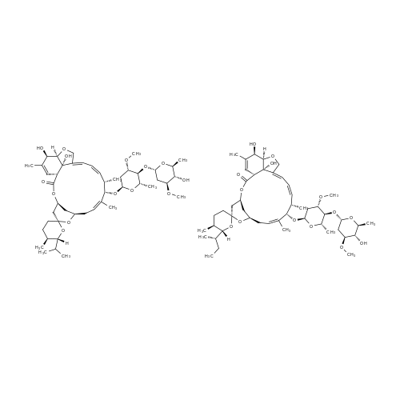
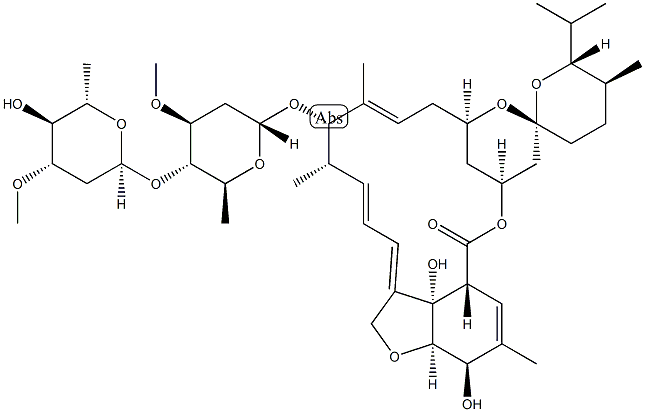
Ivermectin
Synonym(s):22,23-Dihydroavermectin B1;Ivermectin;MK-933
- CAS NO.:70288-86-7
- Empirical Formula: C48H74O14
- Molecular Weight: 875.09
- MDL number: MFCD00869511
- EINECS: 274-536-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-24 14:33:46
What is Ivermectin?
Description
Ivermectin is an antiparasitic agent effective in the treatment of onchocerciasis, or "river blindness". Since ivermectin acts to prevent the adult worm from producing microfilariae, it needs to be administered only once or twice a year.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Originator
Merck (USA)
The Uses of Ivermectin
Semi-synthetic derivative of Abamectin; consists of a mixture of not less than 80% component B1a and not more than 20% component B1b. Antihelmintic (Onchocerca)
The Uses of Ivermectin
beta-lactamase inhibitor; antibiotic
The Uses of Ivermectin
antiparasitic
The Uses of Ivermectin
Positive allosteric modulator of α7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; also modulates glutamate-GABA-activated chloride channels.
The Uses of Ivermectin
Semi-synthetic derivative of Abamectin; consists of a mixture of not less than 80% component B1a and not more than 20% component B1b. Anthelmintic (Onchocerca).
Background
Ivermectin is a semi-synthetic antiparasitic medication derived from avermectins, a class of highly-active broad-spectrum antiparasitic agents isolated from the fermentation products of Streptomyces avermitilis. Ivermectin itself is a mixture of two avermectins, comprising roughly 90% 5-O-demethyl-22,23-dihydroavermectin A1a (22,23-dihydroavermectin B1a) and 10% 5-O-demethyl-25-de(1-methylpropyl)-22,23-dihydro--25-(1-methylethyl)avermectin A1a (22,23-dihydroavermectin B1b).
Ivermectin is mainly used in humans in the treatment of onchocerciasis, but may also be effective against other worm infestations (such as strongyloidiasis, ascariasis, trichuriasis and enterobiasis). Applied topically, it may be used in the treatment of head lice infestation.
With the advent of 2020 and the COVID-19 pandemic, ivermectin began garnering notoriety due to its off-label use for the prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19. While studies are still ongoing, much of the evidence for ivermectin in COVID-19 relies on pre-print in vitro data, and the clinical utility of this data remains unclear. Due to a number of factors - for example, the relatively low number of patients per trial and the speed at which these trials were conducted - studies on the use of ivermectin in COVID-19 have been fraught with statistical errors and accusations of plagiarism. In addition, the use of aggregate patient data in large-scale meta-analyses (as opposed to individual patient data (IPD)) has been shown to disguise otherwise blatant data errors, such as extreme terminal digit bias and the duplication of blocks of patient records.
Until high-quality, peer-reviewed data regarding both the safety and efficacy of ivermectin for COVID-19 in humans becomes available, the use of ivermectin for these purposes should be avoided in favour of thoroughly-vetted therapies (e.g. COVID-19 vaccines like Comirnaty).
Indications
Administered topically, ivermectin cream is indicated for the treatment of inflammatory lesions associated with rosacea. An over-the-counter ivermection lotion is commercially available and indicated for the topical treatment of head lice infestations in patients ≥6 months of age.
Orally administered ivermectin is indicated as a broad-spectrum anti-parasitic for the treatment of intestinal strongyloidiasis caused by Strongyloides stercoralis and onchocerciasis caused by Onchocerca volvulus. Systemic ivermectin therapy is used internationally for the treatment of various tropical diseases, including filariasis, cutaneous larva migrans, and Loa loa infection, amongst others.
Indications
Ivermectin (Mectizan) acts on parasite-specific inhibitory glutamate-gated chloride channels that are phylogenetically related to vertebrate GABA-gated chloride channels. Ivermectin causes hyperpolarization of the parasite cell membrane and muscle paralysis.At higher doses it can potentiate GABA-gated chloride channels. It does not cross the blood-brain barrier and therefore has no paralytic action in mammals, since GABA-regulated transmission occurs only in the central nervous system (CNS). Ivermectin is administered by the oral and subcutaneous routes. It is rapidly absorbed. Most of the drug is excreted unaltered in the feces. The half-life is approximately 12 hours.
Preparation
The synthesis of ivermectin involves the hydrogenation of the naturally occurring avermectin B1 (abamectin) at the double bond linking C-22 and C-23. This results in a mixture of two homologues, 22, 23-dihydroavermectin B1a (H2B1a) and 22, 23-dihydroavermectin B1b (H2 B1b). The a- and b- nomenclature refers to the presence on C-25, of either a secondary butyl side chain or an isopropyl group, respectively. The biological activities of H2B1a and H2B1b are similar. Large-scale separation of the two homologues is not practical, and, hence, ivermectin is marketed as a mixture of H2 B1a (>80%) and H2 B1b (<20%).
Definition
ChEBI: LSM-5397 is a milbemycin.
Manufacturing Process
Avermectin is produced by biotechnological methods with the aid of
Streptomyces avermitilis.
Preparation of Catalyst I
Rhodium trichloride trihydrate (1.00 g, 3.80 mmol) was dissolved in water
(5.0 ml) with heating (70°C). A solution of triphenylphosphine (1.95 g, 7.43
mmol) in acetone (25.0 ml) was then added under a nitrogen atmosphere in
the course of 20 min. After 10 min hydrazine hydrate (1.90 ml; 39.09 mmol)
was added with stirring and the mixture was heated at reflux temperature for
3 hours, then kept at 45°C for a further 1 hour. The crystalline solid was
filtered off under nitrogen and washed with a little acetone and then with
diethyl ether. 1.05 g of an orange-coloured solid were obtained.
Hydrogenation with catalyst I
The catalyst (10 mg) was dissolved in toluene (25 ml) and added under argon
to the solution of a mixture (1.1 g) of avermectin B1a (96%) and avermectin
B1b (4%) and of 100 mg of triphenylphosphine in toluene (25 ml) in a
stainless steel autoclave. This starting material was then hydrogenated at
88°C under a hydrogen pressure of 20 bar with stirring of the solution. After
10 hours, HPLC analysis revealed a content of 86% dihydro-avermectin B1a
and of 4 % dihydroavermectin B1b, and also of 3% tetrahydroavermectin B1a.
Preparation of Catalyst II
Under an atmosphere of argon, a mixture of 7.5 mg of rhodium trichloride,
30.0 mg of tris-(hexylphenyl)-phosphine, 3 ml of acetone and 15 ml of
hydrazine hydrate is heated with stirring and reflux cooling for 4 hours.
Hydrogenation with catalyst II
The catalyst is added to a solution of 4.3 g of avermectin (B1a and B1b
mixture) in 25 ml of a mixture of acetone and cyclohexane in a ratio of 2:1.
After addition of 51.4 mg of tris-(mexylphenyl)phosphine, the hydrogenation
is carried out in a steel autoclave at a hydrogen pressure 5 bar and at 88°C.
After a hydrogenation time of 4 hours, 8.9% of starting material, 89.9% of
ivermectin (B1a and B1b mixture), tetrahydroavermectin content <0.1% was
obtained (according to HPLC analysis).
Removing of the catalyst system
The crude product after distillative removal of the solvent mixture, dissolved
in a mixture of 35 ml of methanol and 20 ml of water and this solution is
extracted with 25 ml of cyclohexane in a separating funnel. The phases are
separated and concentrated under reduced pressure. The extraction is
repeated twice in the same manner.
brand name
Stromectol (Merck);Mectizan.
Therapeutic Function
Antiprotozoal
Antimicrobial activity
It is also active against O. volvulus and other filarial worms, but the effect is chiefly directed against the larval forms (microfilariae). Uniquely among anthelmintic agents it exhibits activity against some ectoparasites, including Sarcoptes scabiei.
Biological Activity
Positive allosteric modulator of the α 7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and the purinergic P2X 4 receptor. Antihelmintic. Also modulates glutamate- and GABA-activated chloride channels. Potentiates glycine-gated currents at low concentrations (30 nM).
Mechanism of action
Two mechanisms of action are thought to be involved in the action of IVM. The first is an indirect action in which motility of microfalaria is reduced, which in turn allows cytotoxic cells of the host to adhere to the parasite, resulting in elimination from the host. This action may occur by virtue of the ability of IVM to act either as a γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) agonist or as an inducer of chloride ion influx, leading to hyperpolarization and muscle paralysis. The chloride ion influx appears to be the more plausible mechanism. Recently, it has been shown that IVM binds irreversibly to the glutamate-gated chloride channel of the nematode Haemonchus contortus, whereas the channel is in an open conformation. The binding then remains locked in the open conformation, allowing ions to cross the membrane, leading to the paralytic action of IVM. The result of this action is a rapid decrease in microfilarial concentrations.
A second action of IVM leads to the degeneration of microfilariae in utero. This action would result in fewer microfilariae being released from the female worms, and it occurs over a longer period of time. The presence of degenerated microfilariae in utero prevents further fertilization and production of microfilariae.
Pharmacokinetics
Ivermectin is a semisynthetic, anthelminitic agent. It is an avermectin, a group of pentacyclic sixteen-membered lactones (i.e. a macrocyclic lactone disaccharide) derived from the soil bacterium Streptomyces avermitilis. Avermectins are potent and broad-spectrum anti-parasitic agents.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: c. 60%
Cmax 12 mg oral: c. 30–47 ng/mL after 4 h
Plasma half-life: c. 12 h
Volume of distribution: 46.9 L
Plasma protein binding: 93%
It is rapidly metabolized in the liver and the metabolites are excreted in the feces over about 12 days with minimal (<1%) urinary excretion. Highest concentrations occur in the liver and fat. Extremely small amounts are found in the brain.
Clinical Use
Onchocerciasis
Non-disseminated strongyloidiasis
Lymphatic filariasis (in combination with albendazole)
Scabies
If the patient is harboring Asc. lumbricoides, the worms will be passed in the feces. Head lice will also be killed, which is very much welcomed by the treated patients. Ivermectin has been widely used in the veterinary field, where use is also made of its effect on ectoparasites.
Clinical Use
Ivermectin (Cardomec, Eqvalan, Ivomec) is a mixtureof 22,23-dihydro derivatives of avermectins B1a and B1bprepared by catalytic hydrogenation. Avermectins aremembers of a family of structurally complex antibioticsproduced by fermentation with a strain of Streptomycesavermitilis. Their discovery resulted from an intensivescreening of cultures for anthelmintic agents from naturalsources. Ivermectin is active in low dosage against awide variety of nematodes and arthropods that parasitizeanimals.
Ivermectin has achieved widespread use in veterinarypractice in the United States and many countries throughoutthe world for the control of endoparasites and ectoparasitesin domestic animals. It has been found effective forthe treatment of onchocerciasis (“river blindness”) in humans, an important disease caused by the roundwormOncocerca volvulus, prevalent in West and Central Africa,the Middle East, and South and Central America.Ivermectin destroys the microfilariae, immature forms ofthe nematode, which create the skin and tissue nodules thatare characteristic of the infestation and can lead to blindness.It also inhibits the release of microfilariae by theadult worms living in the host. Studies on the mechanismof action of ivermectin indicate that it blocks interneuron–motor neuron transmission in nematodes by stimulatingthe release of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA.The drug has been made available by the manufacturer ona humanitarian basis to qualified treatment programsthrough the World Health Organization.
Clinical Use
Ivermectin has broad-spectrum activity in that it can affect nematodes, insects, and acarine parasites. It is the drug of choice in onchocerciasis and is quite useful in the treatment of other forms of filariasis, strongyloidiasis, ascariasis, loiasis, and cutaneous larva migrans. It is also highly active against various mites. It is the drug of choice in treating humans infected with Onchocerca volvulus, acting as a microfilaricidal drug against the skin-dwelling larvae (microfilaria). Annual treatment can prevent blindness from ocular onchocerciasis. Ivermectin is clearly more effective than diethylcarbamazine in bancroftian filariasis, and it reduces microfilaremia to near zero levels. In brugian filariasis diethylcarbamazine- induced clearance may be superior. It also is used to treat cutaneous larva migrans and disseminated strongyloidiasis. Its safe use in pregnancy has not been fully established.
Toxicity
Used appropriately, topically applied ivermectin lotions and creams are unlikely to cause significant toxicity. With accidental or intentional significant exposure to unknown quantities of veterinary formulations of ivermectin (by ingestion, inhalation, injection, or significant body surface area exposure) patients have reported rash, edema, headache, dizziness, asthenia, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Other less common effects include seizure, ataxia, dyspnea, abdominal pain, paresthesia, urticaria, and contact dermatitis. Overdosage with orally administered ivermectin was lethal in mice and rats (at doses several-fold higher than the recommended dose), with death preceded by significant ataxia, bradypnea, tremors, ptosis, decreased activity, emesis, and mydriasis.
If overdosage of ivermectin is suspected, initiate supportive therapy as clinically indicated, including the use of parenteral fluids and electrolytes, respiratory support, and pressor agents to manage hypotension. Induction of emesis and/or gastric lavage may be considered alongside other purgatives and routine anti-poison measures if clinically indicated.
Side Effects
In the treatment of onchocerciasis mild Mazzotti-type reactions occur, with occasional neurological problems. Although it is highly effective against L. loa, care must be taken to avoid treating patients with high microfilarial counts: there is one report of a patient with a concomitant L. loa infection who died when treated for onchocerciasis. Mild gastrointestinal and nervous system signs may occur following treatment for strongyloidiasis.
Side Effects
The side effects are minimal, with pruritus, fever, and tender lymph nodes occasionally seen. The side effects are considerably less than those associated with diethylcarbamazine administration.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Ivermectin is approved in horses for the control of: large strongyles
(adult) (Strongylus vulgaris, S. edentatus, S. equinus, Triodontophorus
spp.), small strongyles, pinworms (adults and 4th stage larva), ascarids
(adults), hairworms (adults), large-mouth stomach worms
(adults), neck threadworms (microfilaria), bots (oral and gastric
stages), lungworms (adults and 4th stage larva), intestinal threadworms
(adults), and summer sores (cutaneous 3rd stage larva) secondary
to Hebronema or Draschia Spp.
In cattle, ivermectin is approved for use in the control of gastrointestinal
roundworms (adults and 4th stage larva), lungworms
(adults and 4th stage larva), cattle grubs (parasitic stages), sucking
lice, and mites (scabies). For a listing of individual species covered,
refer to the product information.
In swine, ivermectin is approved for use to treat GI roundworms,
lungworms, lice, and mange mites. For a listing of individual species
covered, refer to the product information.
In reindeer, ivermectin is approved for use in the control of
warbles.
In American Bison, ivermectin is approved for use in the control
of grubs.
In dogs and cats, ivermectin is approved only for use as a preventative
for heartworm. It has also been used as a microfilaricide,
slow-kill adulticide, ectoparasiticide, and endoparasiticide.
Absorption
Moderately well absorbed. Improved absorption with high fat meal.
Metabolism
Primarily hepatic. Ivermectin and/or its metabolites are excreted almost exclusively in the feces over an estimated 12 days, with less than 1 % of the administered dose excreted in the urine.
Metabolism
Ivermectin is rapidly absorbed, is bound to a great extent to plasma protein, and is excreted in the urine or feces either unchanged or as the 3′-O-demethyl-22,23-dihydroavermectin B1α or as the dihydroavermectin B1α monosaccharide. The absorption of IVM is significantly affected by the presence of alcohol. Administration of IVM as an alcoholic solution may result in as much as a 100% increase in absorption.
Storage
+4°C
Toxicity evaluation
Ivermectin toxicity has been reported in collie dogs and may be due to increased penetration of drug across the blood-brain barrier to the central nervous system (91) and/or the release of γ -aminobutyric acid in the central nervous system (92). Vomiting, salivation, diarrhea, melena, and death have resulted when dogs with Dirofilaria immitis microfilariae were treated with ivermectin (93,94). Adverse reactions in horses with Onchocerca cervicalis microfilariae at the time of therapy may manifest as transient, ventral, subcutaneous edema (95).
References
References/Citations 1) Wagstaff?et al.?(2012),?Ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of importin α/β-mediated nuclear import able to inhibit replication of HIV-1 and dengue virus; Biochem. J.,?443?851 2) Caly?et al.?(2020),?The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro; Antiviral Res.,?178?104787 3) Ottesen and Campbell (1994),?Ivermectin in human medicine; J. Antimicrob. Chemother.,?34?195
Properties of Ivermectin
| alpha | D +71.5 ± 3° (c = 0.755 in chloroform) |
| RTECS | IH7891500 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: ≤1.0% KF |
| form | powder |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | 4mg/L(temperature not stated) |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20° for up to 3 months. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 70288-86-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ivermectin (70288-86-7) |
Safety information for Ivermectin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H300:Acute toxicity,oral H311:Acute toxicity,dermal H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Ivermectin
| InChIKey | AZSNMRSAGSSBNP-XPNPUAGNSA-N |
Ivermectin manufacturer
Allas Chem Technologies Pvt Ltd
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
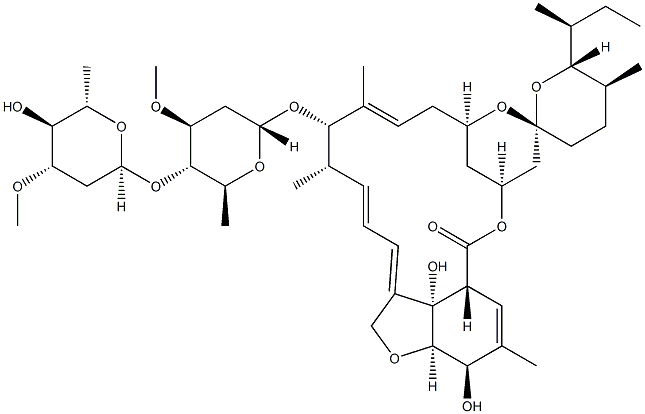
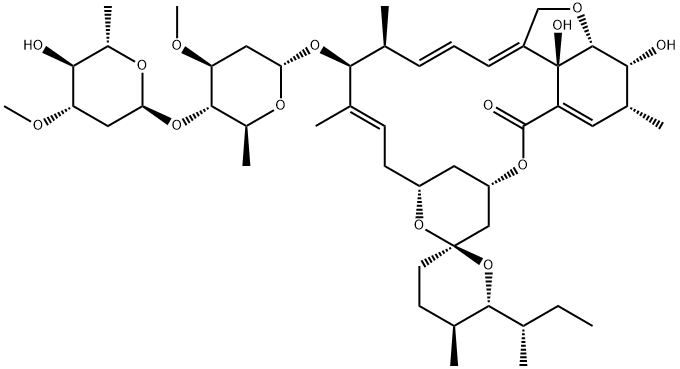




You may like
-
 70288-86-7 98%View Details
70288-86-7 98%View Details
70288-86-7 -
 Ivermectin 99%View Details
Ivermectin 99%View Details -
 Ivermectin 70288-86-7 98%View Details
Ivermectin 70288-86-7 98%View Details
70288-86-7 -
 Ivermectin 99%View Details
Ivermectin 99%View Details -
 Ivermectin 99%View Details
Ivermectin 99%View Details -
 Ivermectin 98% CAS 70288-86-7View Details
Ivermectin 98% CAS 70288-86-7View Details
70288-86-7 -
 Ivermectin Api PowderView Details
Ivermectin Api PowderView Details
70288-86-7 -
 6mg Ivermectin TabletsView Details
6mg Ivermectin TabletsView Details
70288-86-7
