Isobutyronitrile
Synonym(s):2-Methylpropanenitrile;2-Methylpropionitrile;Isopropyl cyanide
- CAS NO.:78-82-0
- Empirical Formula: C4H7N
- Molecular Weight: 69.11
- MDL number: MFCD00001873
- EINECS: 201-147-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
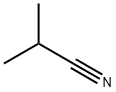
What is Isobutyronitrile?
Description
Isobutyronitrile, often called isopropyl cyanide, is a highly toxic liquid with the aroma of almonds. An early synthesis of the compound from isobutyl alcohol and ammonia was reported by Tohoru Hara and Shigeru Komatsu at Kyoto Imperial University in 1925. Today, isobutyronitrile is generally made by passing isobutyl alcohol or isobutyraldehyde and ammonia over a suitable catalyst at high temperatures.
Isobutyronitrile has only a few uses. It is an industrial solvent and a starting material for producing insecticides such as diazinon. Recently, several patents mention isobutyronitrile as a cosolvent in battery electrolytes.
Despite its relative obscurity, isobutyronitrile made big news in 2014, when astronomers detected it in the interstellar medium. Hundreds of other molecules have been found in space, but isobutyronitrile was unique in that its carbon chain is branched, as opposed to linear. Using the then-new Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array telescope in Chile, Arnaud Belloche and colleagues at the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy (Bonn, Germany) found the molecule in a massive star-forming region called Sagittarius B2.
This finding was especially significant because it may be a clue that branched-chain amino acids are also present in star-forming regions.
Chemical properties
Colorless liquid with a foul odor. Insoluble in water, easily soluble in ethanol and ether.
The Uses of Isobutyronitrile
Isobutyronitrile can be derived from isobutyraldehyde. It is used in organic synthesis, as a catalyst in the polymerization of ethylene and in the petroleum industry as a gasoline additive. Isobutyronitrile is also used to synthesize the intermediate 2-isopropyl-4-methyl-6-hydroxypyrimidine of the organophosphorus insecticide diazinon.
Production Methods
Isobutyronitrile is prepared from isobutyraldehyde by cyanation with ammonia.
Definition
ChEBI: Isobutyronitrile is an aliphatic nitrile that is acetonitrile in which two of the hydrogens have been replaced by methyl groups. It has a role as a polar aprotic solvent. It is an aliphatic nitrile and a volatile organic compound.
Production Methods
Isobutyronitrile is usually obtained by the catalytic gas-phase reaction of isobutyraldehyde or isobutanol with ammonia. Its major use is the synthesis of the insecticide diazinon.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid. Flash point 47°F. Less dense than water. Vapors heavier than air. Toxic oxides of nitrogen produced during combustion.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Isobutyronitrile is incompatible with the following: Oxidizers, reducing agents, strong acids & bases .
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption.
Health Hazard
Isobutyronitrile is considered highly hazardous and full precautions should be taken to prevent skin contact or inhalation of vapor. Inhaled isobutyronitrile is about 2.4 times as toxic as acetonitrile in rats. may be fatal if inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through skin. Contact may cause burns to skin and eyes. (Non-Specific -- Nitriles) Primarily, they are skin and eye irritants. Large doses cause collapse and stop breathing. In order to protect workers, the recommended TWA limit is obtained by dividing that for acetonitrile by the factor 2.4. NIOSH has therefore recommended that employee exposure should not exceed 8 p.p.m. (22 mg/m3) for either compound as a TLV-TWA.
Fire Hazard
Vapor may explode if ignited in an enclosed area. Toxic oxides of nitrogen are produced during combustion. Isobutyronitrile is a flammable/combustible material and may be ignited by heat, sparks, or flames. Vapors may travel to a source of ignition and flash back. Container may explode in heat of fire. Vapor explosion and poison hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Hazardous polymerization may not occur.
Metabolism
Thiocyanate was present in the urine of rats dosed orally with isobutyronitrile.
Purification Methods
Shake the nitrile with conc HCl (to remove isonitriles), then with water and aqueous NaHCO3. After a preliminary drying with silica gel or Linde type 4A molecular sieves, it is shaken or stirred with CaH2 until hydrogen evolution ceases, then decanted and distilled from P2O5 (not more than 5g/L, to minimize gel formation) or Drierite (b 101-103o/760mm). Finally it is refluxed with, and slowly distilled from CaH2 (5g/L), taking precautions to exclude moisture. [Beilstein 2 H 294, 2 I 129, 2 II 263, 2 III 655, 2 IV 853.]
Properties of Isobutyronitrile
| Melting point: | -72 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 107-108 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.770 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.38 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 100 mm Hg ( 54.4 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 39 °F |
| storage temp. | Flammables area |
| solubility | slightly soluble in water and acetone, very soluble in alcohol and
ether |
| appearance | colorless liquid |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear colorless to light yellow |
| Water Solubility | 35 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,5156 |
| BRN | 1340512 |
| Dielectric constant | 23.9(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable. Flammable. May form explosive mixtures with air. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 78-82-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Propanenitrile, 2-methyl-(78-82-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Isobutyronitrile (78-82-0) |
Safety information for Isobutyronitrile
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. |
Computed Descriptors for Isobutyronitrile
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Isobutyronitrile CAS 78-82-0View Details
Isobutyronitrile CAS 78-82-0View Details
78-82-0 -
 IsobutyronitrileView Details
IsobutyronitrileView Details
78-82-0 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
