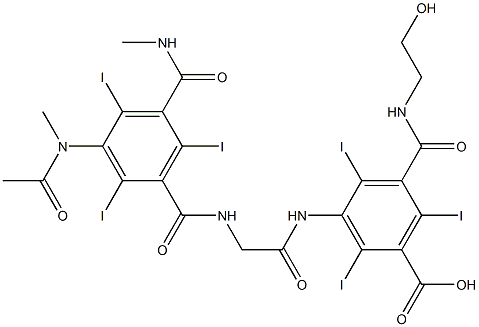
IOXAGLIC ACID (100 MG)
Synonym(s):N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-5-{2-[2,4,6-triiodo-3-(N-methylacetamido)-5-(methylcarbamoyl)benzamido]acetamido}isophthalamic acid
- CAS NO.:59017-64-0
- Empirical Formula: C24H21I6N5O8
- Molecular Weight: 1268.88
- MDL number: MFCD00867945
- EINECS: 261-560-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
What is IOXAGLIC ACID (100 MG)?
Absorption
Following the intravascular route of injection, Ioxaglic acid is rapidly transported through the circulatory system to the kidneys.
The pharmacokinetics of radiopaque contrast media given by the IV route are described by a two-compartment model with a rapid alpha phase for drug distribution and a slow beta phase for the elimination of the drug. Following the intravenous administration of 50 mL of ioxaglic acid in 10 healthy volunteers, the mean peak plasma concentration occurred at two (1-3) minutes, reaching a concentration of 2.1 (1.8-2.8) mg/mL.
Approximately 50 percent of the intravenously administered dose was recovered in the urine at two hours, and 90% percent was recovered at the 24 hour time point .
Toxicity
Adverse reactions after administration of iodinated contrast agents may be worsened in patients displaying agitation, anxiety, and pain. Appropriate management, such as sedation, may be required before the procedure . Adequate hydration and normal electrolyte balance must be ensured, especially in elderly patients, infants, small children, patients with renal damage (oliguria, polyuria) or hyperuricemia, multiple myeloma, patients diagnosed with plasmacytoma or diabetes mellitus, particularly if it is longstanding .
As this drug is a contrast agent, it may cause minor or major reactions that may be serious or lethal . They may be rapid (within 60 minutes) or delayed (up to 1 week) .
Emergency measures must be immediately available in high risk individuals, especially in patients taking B-blockers in whom adrenaline and vascular perfusion would not be effective .
There are several conditions in which caution must be observed while administering this contrast drug :
Renal Disease/Hepatic Disease
Particular attention is required if the patient has both hepatic and renal failure, which increases the risk of contrast agent retention .
Cardiovascular Disease
In patients with manifest or incipient heart failure, coronary disease, pulmonary hypertension, or valvular heart disease, the risks of pulmonary edema, myocardial ischemia and arrhythmia and severe hemodynamic disturbances is heightened after the administration of an iodinated contrast agent.
Cases of Torsade de Pointes have been identified in patients using sodium and meglumine ioxaglate, therefore loxaglic acid should be administered very carefully to patients who have/may develop prolongation of QTc, including patients taking other medicines that contribute to cardiovascular QT prolongation .
Pheochromocytoma Patients
Patients with phaeochromocytoma may suddenly develop hypertension after intravascular administration of a contrast agent, which may require appropriate management before the examination
Thyroid Disease
Following injection of iodinated contrast agent, specifically in patients with goiter or a history of hypothyroidism, there is a risk of either an episode of hyperthyroidism or induction of a new episode of hypothyroidism.
There is also a risk of hypothyroidism in newborns who have received, or whose mother has received, an iodinated contrast agent.
Screening for hypothyroidism should be performed routinely after administration of the product to newborns and judiciously to premature babies by assaying TSH and possibly free T4, 7-10 days and 1 month after iodine overload .
Asthma
Asthma should be controlled before injecting the iodinated contrast agent .
Particular attention is required if the asthmatic attack has occurred within eight days prior to administration of loxagic acid, because of the increased risk for bronchospasm.
Myasthenia gravis
Administration of a contrast agent may exacerbate the symptoms of myasthenia gravis .
Use in pregnancy
In the patient screening and with appropriate tests, it is advisable to identify possible pregnancy in women of childbearing age. Exposure of the female genital tract to x-rays warrants careful evaluation of the benefit-to-risk ratio .
Chemical properties
White or almost white, hygroscopic powder.
The Uses of IOXAGLIC ACID (100 MG)
Diagnostic aid(radiopaque medium).
The Uses of IOXAGLIC ACID (100 MG)
Ioxaglic Acid is used as a contrast medium during coronary angiograpy.
Indications
This medicinal product is for diagnostic use only in adults and children as a low-osmolality medium , .
Background
Ioxaglic acid is marketed as Hexabrix. This drug is an ionic tri-iodinated benzoate used as a low-osmolality contrast agent during diagnostic imaging procedures. Like other organic iodine compounds, ioxaglic acid blocks x-rays and is opaque in its appearance on x-ray film, improving the visualization of important structures and organs during angiography, arteriography, arthrography, cholangiography, urography, and computed tomography .
Ioxaglic acid has a low osmolarity and is associated with fewer side effects compared to older contrast agents .
Definition
ChEBI: A benzenedicarboxamide compound having N-substituted carbamoyl groups at the 1- and 3-positions, iodo substituents at the 2-, 4- and 6-positions and an acetyl(methyl)amino group at the 5-position.
Pharmacokinetics
This drug allows for the visualization of important organs and structures in the body. It binds to tissues, allowing the blockage of X-rays and diagnostic visualization in various soft tissues and body cavities .
The joint spaces in addition to the uterus and fallopian tubes may be visualized by the direct injection of the contrast medium into the region to be studied .
Metabolism
Excreted unchanged .
Properties of IOXAGLIC ACID (100 MG)
| Melting point: | 302°C |
| Boiling point: | 887.9±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 2.4120 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | Very slightly soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), very slightly soluble in methylene chloride. It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides. |
| form | neat |
| pka | 0.89±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| EPA Substance Registry System | [(methylamino)carbonyl]benzoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-5-[[(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2,4,6-triiodo- (59017-64-0) |
Safety information for IOXAGLIC ACID (100 MG)
Computed Descriptors for IOXAGLIC ACID (100 MG)
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Ioxaglic acid CAS 59017-64-0View Details
Ioxaglic acid CAS 59017-64-0View Details
59017-64-0 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1