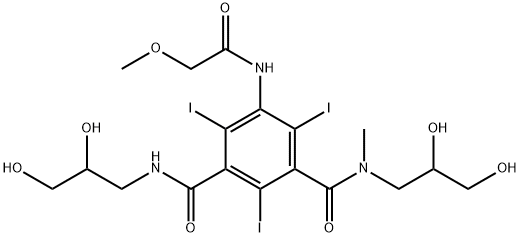
Iopromide
- CAS NO.:73334-07-3
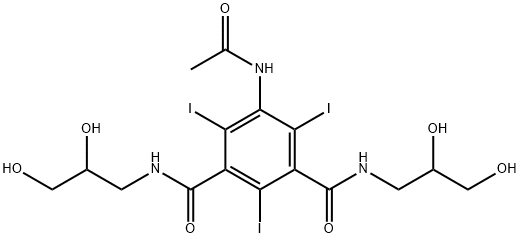
- Empirical Formula: C18H24I3N3O8
- Molecular Weight: 791.11
- MDL number: MFCD00867924
- EINECS: 277-385-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 16:48:35
What is Iopromide?
Absorption
Immediately following intravascular injection, iopromide reaches peak plasma concentrations and is then rapidly distributed throughout the extracellular fluid compartment. It displays little tendency to bind to serum or plasma proteins. Iodinated contrast agents cross a disrupted blood-brain barrier.
Toxicity
There are no data on iopromide use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Iopromide crosses the placenta and reaches fetal tissues in small amounts. In animal reproduction studies, intravenous administration of iopromide to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis at doses up to 0.35 and 0.7 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose based on body surface area resulted in no relevant adverse developmental effects.
The safety and efficacy of iopromide have been established in pediatric patients aged 2 years and older for radiographic evaluation of cardiac chambers and related arteries, excretory urography, and contrast computed tomography of the head and body. The use of iopromide in these age groups for these indications is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adults and additional safety data in pediatric patients aged 2 years and older, including data from published studies.
Pediatric patients who are at higher risk of experiencing an adverse reaction during and after the administration of any contrast agent include those with asthma, sensitivity to medication and/or allergens, cyanotic and acyanotic heart disease, congestive
heart failure, or serum creatinine greater than 1.5 mg/dL.
Thyroid function tests indicative of thyroid dysfunction, characterized by hypothyroidism or transient thyroid suppression have been reported following iodinated contrast media administration in pediatric patients, including term and preterm neonates; Some patients were treated for hypothyroidism. After exposure to iodinated contrast media, individualize thyroid function monitoring in pediatric patients 0 to 3 years of age based on underlying risk factors, especially in term and preterm neonates.
The clearance of iopromide decreases with increasing degree of renal impairment and results in delayed opacification of the urinary system. In addition, preexisting renal impairment increases the risk of acute kidney injury. Iopromide can be removed by dialysis.
Long-term animal studies have not been performed with iopromide to evaluate carcinogenic potential or effects on fertility. Iopromide was not genotoxic in a series of studies including the Ames test, an in vitro human lymphocytes analysis of chromosomal aberrations, an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay, and an in vivo mouse dominant lethal assay.
The manifestations of overdosage are life-threatening and affect mainly the pulmonary and cardiovascular systems. Treatment of overdosage is directed toward the support of all vital functions, and prompt institution of symptomatic therapy.
The most common adverse reactions (>1%) are headache, nausea, injection site and infusion site reactions, vasodilatation, vomiting, back pain, urinary urgency, chest pain, pain, dysgeusia, and abnormal vision. Inadvertent intrathecal administration may cause death, convulsions, cerebral hemorrhage, coma, paralysis, arachnoiditis, acute renal failure, cardiac arrest, seizures, rhabdomyolysis, hyperthermia, and brain edema.
Description
Iopromide is a non-ionic, water-soluble X-ray contrast agent for intravascular administration. Iopromide can cause acute kidney injury and is used in animal models of contrast-induced nephropathy.
Chemical properties
White Solid
The Uses of Iopromide
Labelled Iopromide. Nonionic, injectable radio-contrast medium. Diagnostic aid (radiopaque medium).
The Uses of Iopromide
Contrast molecule
Background
Iopromide is a low osmolar, non-ionic X-ray contrast agent for intravascular administration. It functions as a contrast agent by opacifying blood vessels in the flow path of the contrast agent, permitting radiographic visualization of the internal structures until significant hemodilution occurs. Although iopromide can cause several serious adverse effects, including cardiac events, thromboembolism, hypersensitivity reaction, and even death if administered intrathecally inadvertently, it is still deemed to have a favorable safety profile, with only 0.7% of patients in a 2 years study experiencing adverse events. Although the mechanism is unclear, women and outpatients tend to have a higher incidence of adverse events compared to other population groups.
Approved by the FDA in 1995 and Health Canada in 1994 under the brand name ULTRAVIST, iopromide is used in radiological diagnosis, including, but not limited to, intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography (IA-DSA), cerebral and peripheral arteriography, peripheral venography, excretory urography, brain computer tomography (CT), coronary arteriography, left ventriculography, visceral angiography, and orthography.
Indications
Iopromide, as the product IOVIST, is approved by the FDA for use as an intra-arterial or intravenous X-ray contrast agent. For intra-arterial administration, iopromide is indicated for cerebral arteriography, peripheral arteriography, coronary arteriography, left ventriculography, visceral angiography, and aortography in adults and radiographic evaluation of cardiac chambers and related arteries in pediatric patients aged 2 years and older. For intravenous administration, iopromide is indicated for excretory urography in adults and pediatric patients aged 2 years and older, contrast Computed Tomography (CT) of the head and body (intrathoracic, intra-abdominal, and retroperitoneal regions) for the evaluation of neoplastic and non-neoplastic lesions in adults and pediatric patients aged 2 years and older, and contrast mammography to visualize known or suspected lesions of the breast in adults, as an adjunct following mammography and/or ultrasound.
Iopromide is also approved by Health Canada as an intravascular contrasting agent, although the indications differ depending on the dosage. At 300 mg I/mL, iopromide is indicated for computed tomography (CT), excretory urography, pediatric excretory urography, renal arteriography, peripheral arteriography (bifemoral pelvis/leg), cerebral arteriography, phlebography of the extremities, and arthrography.
What are the applications of Application
Iopromide is a nonionic radio-contrast medium
Definition
ChEBI: A dicarboxylic acid diamide that consists of N-methylisophthalamide bearing three iodo substituents at positions 2, 4 and 6, a methoxyacetyl substituent at position 5 and two 2,3-dihydroxypropyl groups attached to the amide nitrogens. A ater soluble x-ray contrast agent for intravascular administration.
brand name
Ultravist (Berlex).
General Description
Iopromide is a low-osmolar,nonionic monomer with 48% bound iodine content. It is indicatedfor use in angiography, excretory urography, andnumerous CT procedures.
Pharmacokinetics
After intravenous injection, opacification of the renal parenchyma begins within 1 minute. Excretion of the contrast agent becomes apparent in 1 to 3 minutes with optimal contrast in the calyces and collecting system occurring between 5 and 15 minutes. In nephropathic conditions, particularly when excretory capacity has been altered, the excretion rate varies unpredictably and opacification may be delayed for several hours after injection. the degree of contrast enhancement is related to the iodine concentration in the tissue of interest.
Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (>1%) are headache, nausea, injection site and infusion site reactions, vasodilatation, vomiting, back pain, urinary urgency, chest pain, pain, dysgeusia, and abnormal vision.
Metabolism
Iopromide does not undergo significant metabolism, deiodination, or biotransformation.
Properties of Iopromide
| Melting point: | broad (160?C transition) |
| Boiling point: | 840.9±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 2.173±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Freely soluble in water and in dimethyl sulfoxide, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent) and in acetone. |
| form | neat |
| pka | 10.62±0.70(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to off-white |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 73334-07-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,3-Benzenedicarboxamide, N1,N3-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-5-[(2-methoxyacetyl)amino]-N1-methyl- (73334-07-3) |
Safety information for Iopromide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Iopromide
Abamectin manufacturer
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 73334-07-3 Iopromide 98%View Details
73334-07-3 Iopromide 98%View Details
73334-07-3 -
 Iopromide >98%View Details
Iopromide >98%View Details -
 Iopromide CAS 73334-07-3View Details
Iopromide CAS 73334-07-3View Details
73334-07-3 -
 Iopromide 95.00% CAS 73334-07-3View Details
Iopromide 95.00% CAS 73334-07-3View Details
73334-07-3 -
 Iopromide 98.00% CAS 73334-07-3View Details
Iopromide 98.00% CAS 73334-07-3View Details
73334-07-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4