iodamide
- CAS NO.:440-58-4
- Empirical Formula: C12H11I3N2O4
- Molecular Weight: 627.94
- MDL number: MFCD00867954
- EINECS: 207-125-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-04-23 13:52:06
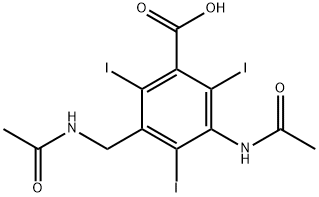
What is iodamide?
Originator
Uromiro,Heyden,W. Germany,1965
The Uses of iodamide
Diagnostic aid (radiopaque medium).
Definition
ChEBI: A benzoic acid compound having iodo substituents at the 2-, 4- and 6-positions, an acetamido substituent at the 3-position and an acetamidomethyl substituent at the 5-position.
Manufacturing Process
65.4 g (0.24 mol) 3-acetylaminomethyl-4-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid were
dissolved in a mixture of 48 ml 10N sodium hydroxide and 1,800 ml water. 12
g of a 10% palladium catalyst on a carbon carrier were added, and the
nitrobenzoic acid derivative was hydrogenated at slightly elevated temperature
and at atmospheric pressure. The hydrogen was avidly absorbed. The nitro
group was fully reduced to the corresponding amino radical within about 20 to
40 minutes, and 99 to 100% of the amount of chlorine ions to be theoretically
expected was formed. Hydrogen absorption then stopped.
The catalyst was removed by filtration. The filtrate was diluted to about 18
liters, and was acidified with 15 ml concentrated hydrochloric acid. With
vigorous stirring, 1,152 ml N KlCl2 solution were run into the diluted filtrateover a period of about 20 to 30 minutes. A solid precipitate was formed, and
was filtered off after about six hours. The solid material was washed with
water, with sodium bisulfite solution, and again with water. It was dissolved in
aqueous ammonium hydroxide solution, the solution was filtered, and the
filtrate was acidified with concentrated hydrochloric acid containing a small
amount of sodium bisulfite. After a short time, the precipitate formed was
filtered with suction, washed with water, and dried.
There were obtained 109 g 3-acetylaminomethyl-5-amino-2,4,6-triiodobenzoic
acid which decomposes and melts at approximately 230°C. The equivalent
weight was determined experimentally as being 591, as compared to a
theoretical value of 586.
A suspension of 40 g 3-acetylaminomethyl-5-amino-2,4,6-triodobenzoic acid
in 180 ml acetic anhydride were mixed with 0.4 ml concentrated sulfuric acid.
An exothermic reaction was thereby initiated. Acetylation was completed by
heating to 80°C for three hours. The reaction mixture was then evaporated to
dryness in a vacuum at a temperature not exceeding 50°C. The residue was
treated with a mixture of 30 ml concentrated aqueous ammonium hydroxide
and 40 ml water, whereby the solid material dissolved with spontaneous
heating. Within a few minutes, the ammonium salt of the acetylated product
started precipitating. The precipitate and residual liquid were cooled externally
with ice after about 15 minutes. The salt was separated from the liquid by
filtration with suction, and was washed with ice cold saturated ammonium
chloride solution.
The salt was dissolved in 300 ml water, and insoluble matter was removed
from the solution by filtration. The free acid was precipitated from the filtrate
at 50°C to 60°C by the addition of 40 ml 1:1 hydrochloric acid. The
precipitate was filtered off after a few hours, washed with water, and dried.
There were obtained 34 g 3-acetylaminomethyl-5-acetylamino-2,4,6-
triiodobenzoic acid (79% of theoretical yield) having a melting point of 246°C
to 248°C. The equivalent weight of this practically pure acid was found to be
631 as compared to the calculated value of 627.96.
When recrystallized from glacial acetic acid, the pure acid melts at 255°C to
257°C.
brand name
Renovue (Bracco).
Therapeutic Function
Diagnostic aid (radiopaque medium)
Safety Profile
Mildly toxic by intraperitoneal andintravenous routes. When heated to decomposition it emitsvery toxic fumes of NOx and HI.
Properties of iodamide
| Melting point: | 255-257° |
| Boiling point: | 683.4±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 2.3140 (estimate) |
| pka | 1.08±0.10(Predicted) |
| Water Solubility | 3g/L(20 ºC) |
Safety information for iodamide
Computed Descriptors for iodamide
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4