Indium(III) antimonide
- CAS NO.:1312-41-0
- Empirical Formula: InSb
- Molecular Weight: 236.58
- MDL number: MFCD00016146
- EINECS: 215-192-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
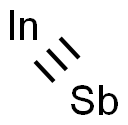
What is Indium(III) antimonide?
Chemical properties
Crystalline solid.
Physical properties
Black cubic crystal; zincblende structure; density 5.775 g/cm3; melts at525°C; density of melt 6.48 g/mL; dielectric constant 15.9; insoluble in water.
The Uses of Indium(III) antimonide
In semiconductor electronics. Grown p-n junctions(Indium(III) antimonide) have been made by doping a melt with an acceptor impurity such as zinc or cadmium, and dipping in an n-type crystal. Rate-grown junctions have also been made. Broad-area surface junctions have been produced by out-diffusing antimony in vacuum from the surface of an n-type crystal, producing a p-n junction just inside the surface. Also has photoconductive, photoelectromagnetic, and magnetoresistive properties. Useful as an infrared detector and filter, and in Hall effect devices.
The Uses of Indium(III) antimonide
Crystal structure: Zinc blende structure, cubic
The Uses of Indium(III) antimonide
Indium antimonide finds use in infrared detectors, including FLIR systems, thermal imaging cameras, infrared astronomy and in infrared homing missile guidance systems, in fast transistors. It is used in thermal image detectors using photo-electromagnetic detectors or photodiodes.
Production Methods
Intermetallic semiconductors of indium are formed from group III and group V elements, requiring very high purity of the elements (0.1 ppm).
Preparation
Indium antimonide may be synthesized from its elements by fusion of sto-ichiometric amounts of indium and antimony at elevated temperatures in anevacuated, sealed ampule.
Production Methods
Single crystals are grown by using the Kyropoulus method—by pulling up from the melt composed
of stoichiometric In and Sb because both elements have low vapor pressure. Impurities are Zn and
Cd, which cannot be removed by zone refining. As a result, it is important to use pure source
materials. It is soft and fragile, and it is required to be cut carefully by a diamond cutter. The same
polishing method for Si and Ge is possible.
Films are deposited using the vapor phase method. In and Sb (or In(CH3) and SbH3) are
encapsuled in a vacuum and these source materials are heated to evaporate and then deposited
on the substrate placed at a lower temperature portion. The electrical properties of the films
deposited by this method are slightly different from those of bulk.
General Description
This product has been enhanced for energy efficiency.
Hazard
See indium; antimony.
Structure and conformation
The space lattice of InSb belongs to the cubic system and zinc-blende-type structure called InSb-I at room temperature and under atmospheric pressure has a lattice constant of a=0.64789 nm and In–Sb=0.280 nm. A single crystal has cleavage of (110) plane. It transforms to white tin-type InSb-II at high temperatures and under high pressure.
Properties of Indium(III) antimonide
| Melting point: | 535°C |
| Density | 5,76 g/cm3 |
| form | crystal |
| Specific Gravity | 5.76 |
| color | black |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water. |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic, Sphalerite Structure - Space Group F(-4)3m |
| Merck | 14,4948 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.5 mg/m3; TWA 0.1 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 50 mg/m3; TWA 0.5 mg/m3; TWA 0.1 mg/m3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1312-41-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Antimony, compd. with indium (1:1) (1312-41-0) |
Safety information for Indium(III) antimonide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. |
Computed Descriptors for Indium(III) antimonide
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
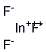
You may like
-
 Indium antimonide CAS 1312-41-0View Details
Indium antimonide CAS 1312-41-0View Details
1312-41-0 -
 Indium antimonide CAS 1312-41-0View Details
Indium antimonide CAS 1312-41-0View Details
1312-41-0 -
 55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1 (S)-Methyl 3-amino-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)propanote Hydrochloride (DAP-OMe. HCl) 99%View Details
181228-33-1