INDENO(1,2,3-C,D)PYRENE
Synonym(s):IP;IP2;NEMO;IPD2;IP1
- CAS NO.:193-39-5
- Empirical Formula: C22H12
- Molecular Weight: 276.33
- MDL number: MFCD00152577
- EINECS: 205-893-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
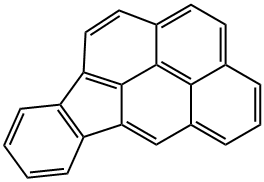
What is INDENO(1,2,3-C,D)PYRENE?
Chemical properties
solid
The Uses of INDENO(1,2,3-C,D)PYRENE
Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) and a known carcinogen. Indeno[ 1,2,3-cd]pyrene is listed as a priority pollutant by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Indeno [1,2,3-cd]pyrene has been detected in automobile engine exhaust, charcoal broiled foods, ground water, river sediments as well as cigarette smoke condensate.
The Uses of INDENO(1,2,3-C,D)PYRENE
A component of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, also known as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, usually bound to small particulate matter present in urban air, industrial and natural combustion emissions, and cigarette smoke.
The Uses of INDENO(1,2,3-C,D)PYRENE
Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) and a known carcinogen. Indeno[ 1,2,3-cd]pyrene is listed as a priority pollutant by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene has been detected in automobile engine exhaust, charcoal broiled foods, ground water, river sediments as well as cigarette smoke condensate.
What are the applications of Application
Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon for oncology research
Definition
ChEBI: Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene is a member of pyrenes.
General Description
Yellow crystals.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Vigorous reactions, sometimes amounting to explosions, can result from the contact between aromatic hydrocarbons, such as INDENO(1,2,3-C,D)PYRENE, and strong oxidizing agents. They can react exothermically with bases and with diazo compounds. Substitution at the benzene nucleus occurs by halogenation (acid catalyst), nitration, sulfonation, and the Friedel-Crafts reaction.
Hazard
Possible carcinogen.
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: Toxic.
Health Hazard
Indeno(1,2,3-cd)pyrene causes lung cancer inanimals. There is sufficient evidence of itscarcinogenic actions in animals. However, thecancer-causing effects of this compound inhumans are un known. There is no report onits toxicity.
Fire Hazard
Some may burn but none ignite readily. Containers may explode when heated. Some may be transported hot.
Carcinogenicity
The IARC has determined that there is sufficient evidence for the carcinogenicity of IP in animals.4 No human data are available because exposures typically involve chemical mixtures containing numerous polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons. IP is considered possibly carcinogenic to humans.
Source
No MCLGs or MCLs have been proposed (U.S. EPA, 2000).
Detected in 8 diesel fuels at concentrations ranging from 0.056 to 0.85 mg/L with a mean
value of 0.143 mg/L (Westerholm and Li, 1994). Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene was also reported in
gasoline (59 μg/L), fresh motor oil (30 μg/L), and used motor oil (34.0 to 83.2 mg/kg) (quoted,
Verschueren, 1983). Also detected in asphalt fumes at an average concentration of 5.92 ng/m3
(Wang et al., 2001).
The concentration of indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene in coal tar and the maximum concentration
reported in groundwater at a mid-Atlantic coal tar site were 1,200 and 0.002 mg/L, respectively
(Mackay and Gschwend, 2001). Based on laboratory analysis of 7 coal tar samples, indeno[1,2,3-
cd]pyrene concentrations ranged from ND to 1,400 ppm (EPRI, 1990). Identified in hightemperature
coal tar pitches used in roofing operations at concentrations ranging from ND to 2,460
mg/kg (Malaiyandi et al., 1982).
Nine commercially available creosote samples contained indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene at
concentrations ranging from 1 to 40 mg/kg (Kohler et al., 2000).
Schauer et al. (2001) measured organic compound emission rates for volatile organic
compounds, gas-phase semi-volatile organic compounds, and particle phase organic compounds
from the residential (fireplace) combustion of pine, oak, and eucalyptus. The particle-phase
emission rates of indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene were 0.518 mg/kg of pine burned and 0.168 mg/kg of
eucalyptus burned.
Particle-phase tailpipe emission rates from gasoline-powered automobiles with and without
catalytic converters were 0.436 and 92.0 μg/km, respectively (Schauer et al., 2002).
Environmental Fate
Chemical/Physical. Indeno[1,2,3-cd] will not hydrolyze (Kollig, 1993).
Properties of INDENO(1,2,3-C,D)PYRENE
| Melting point: | 164℃ |
| Boiling point: | 536°C |
| Density | 1.1847 (estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 1.01 x 10-10 mmHg at 25 °C (McVeety and Hites, 1988) |
| refractive index | 1.9800 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | -18 °C |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C
|
| solubility | Soluble in most solvents (U.S. EPA, 1985) including low molecular weight liquid hydrocarbons
such as benzene, ethylene, and toluene. |
| form | neat |
| pka | >15 (Christensen et al., 1975) |
| color | Light Yellow to Very Dark Orange |
| Water Solubility | 62 μg/L (Sims et al., 1988) |
| BRN | 1879312 |
| Henry's Law Constant | (x 10-7 atm?m3/mol):
1.78, 2.86, 5.63, 6.02, 7.60, and 10.36 at 10.0, 20.0, 35.0, 40.1, 45.0, and 55.0 °C, respectively
(wetted-wall column, ten Hulscher et al., 1992) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 193-39-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. Sup 7, 92) 2010 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene (193-39-5) |
Safety information for INDENO(1,2,3-C,D)PYRENE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H351:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for INDENO(1,2,3-C,D)PYRENE
| InChIKey | SXQBHARYMNFBPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
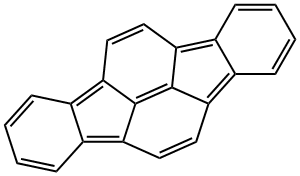
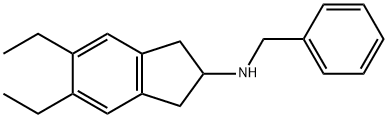
![2(1H)-Quinolinone, 5-[(1R)-2-[(5,6-diethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-2-yl)(phenylmethyl)amino]-1-hydroxyethyl]-8-(phenylmethoxy)-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20200611/GIF/1384189-12-1.gif)
You may like
-
 193-39-5 98%View Details
193-39-5 98%View Details
193-39-5 -
 193-39-5 98%+View Details
193-39-5 98%+View Details
193-39-5 -
![Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene CAS 193-39-5](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene CAS 193-39-5View Details
Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene CAS 193-39-5View Details
193-39-5 -
![Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene CAS 193-39-5](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene CAS 193-39-5View Details
Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene CAS 193-39-5View Details
193-39-5 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
