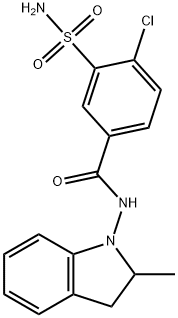
Indapamide
Synonym(s):N-(4-Chloro-3-sulfamoylbenzamido)-2-methylindoline;Indapamide
- CAS NO.:26807-65-8
- Empirical Formula: C16H16ClN3O3S
- Molecular Weight: 365.83
- MDL number: MFCD00079375
- EINECS: 248-012-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-12 18:45:48
What is Indapamide?
Absorption
The bioavailability of indapamide is virtually complete after an oral dose and is unaffected by food or antacids. Indapamide is highly lipid-soluble due to its indoline moiety - a characteristic that likely explains why indapamide’s renal clearance makes up less than 10% of its total systemic clearance. The Tmax occurs approximately 2.3 hours after oral administration. The Cmax and AUC0-24 values are 263 ng/mL and 2.95 ug/hr/mL, respectively.
Toxicity
Indapamide overdose symptoms may include but are not limited to nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal disorders, electrolyte disturbances and weakness. Other signs of overdose include respiratory depression and severe hypotension. In cases of overdose, supportive care interventions may be necessary to manage symptoms. Emesis and gastric lavage may be recommended to empty the stomach; however, patients should be monitored closely for any electrolyte or fluid imbalances.
Description
Indapamide is a derivative of benzolsulfonamide and its mechanism of action is analogous to that of thiazides. It is intended for lowering arterial blood pressure and as an adjuvant drug for treating edema caused by cardiac insufficiency.
Description
Indapamide (Item No. 21308) is an analytical reference standard that is categorized as a sulfonamide diuretic that blocks delayed-rectifier potassium currents. Formulations containing indapamide are used to treat hypertension, but it is abused by athletes to reduce body weight rapidly or mask the presence of other athletic-enhancing substances. Indapamide can be detected in urine. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Originator
Natrilix,Pharmacodex,W. Germany,1976
The Uses of Indapamide
Used as an antihypertensive. Diuretic
The Uses of Indapamide
diuretic, antihypertensive
The Uses of Indapamide
Used as an antihypertensive. Diuretic.
Background
The most significant modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease and the most prominent contributor to all-cause mortality is hypertension. Characterized by an office blood pressure of ≥140/90, hypertension is pervasive and impacts an estimated 25% of adults globally. Treatment for hypertension should include a number of lifestyle changes (ie. reduced sodium intake) along with pharmacotherapy - it should be noted that treatment with several antihypertensive agents may be required in order to achieve blood pressure targets.
Thiazide-like diuretics such as indapamide are a valuable tool for the treatment of hypertension and continue to grow in popularity, falling behind only ACE inhibitors in terms of prescription frequency. When compared to hydrochlorothiazide (another commonly prescribed diuretic), indapamide has been shown to be superior at lowering systolic blood pressure, reducing left ventricular mass index, lowering oxidative stress, inhibiting platelet aggregation, and reducing microalbuminuria associated with diabetes. Interestingly, unlike thiazide diuretics, several sources suggest that indapamide is not associated with glucose or lipid disturbances.
Indapamide is characterized by both a methylindoline and a sulfamoyl chlorobenzamide functional group, with the former being largely responsible for the molecule’s lipid solubility.
Indications
Indapamide is a diuretic indicated for use as monotherapy or in combination with other blood pressure-lowering agents to treat hypertension. It may also be used to treat fluid and salt retention associated with congestive heart failure.
What are the applications of Application
Indapamide is an NCCT inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: A sulfonamide formed by condensation of the carboxylic group of 4-chloro-3-sulfamoylbenzoic acid with the amino group of 2-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-1-amine.
Manufacturing Process
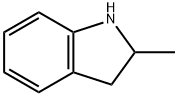
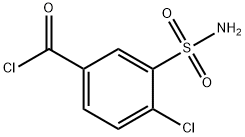
A total of 8.9 parts of 3-sulfamyl-4-chloro-benzoylchloride in a solution of 50 parts of anhydrous tetrahydrofuran are added portionwise in the course of 60 minutes, while stirring, to a solution of 5.2 parts of N-amino-2-methyl indoline and 3.5 parts of triethylamine in 150 parts of anhydrous tetrahydrofuran. The reaction mixture is left to stand 3 hours at room temperature, then the precipitated chiorhydrate of triethylamine is filtered off. The filtrate is evaporated under vacuum and the residue is crystallized from a solution of 60 parts of isopropanol in 75 parts of water. There are obtained 9 parts of N-(3- sulfamyl-4-chlorobenzamido)-2-methyl indoline, MP (K) 184° to 186°C, MP (MK) 160° to 162°C (isopropanol/water). [The melting points beingdetermined on a Kofler heater plate under the microscope (MK) or on a Kofler Bank (K)].
brand name
Lozol (Sanofi Aventis).
Therapeutic Function
Diuretic Indapamide
Pharmacokinetics
Classified as a sulfonamide diuretic, indapamide is an effective antihypertensive agent and by extension, has shown efficacy in the prevention of target organ damage.
Administration of indapamide produces water and electrolyte loss, with higher doses associated with increased diuresis. Severe and clinically significant electrolyte disturbances may occur with indapamide use - for example, hypokalemia resulting from renal potassium loss may lead to QTc prolongation. Further electrolyte imbalances may occur due to renal excretion of sodium, chloride, and magnesium.
Other indapamide induced changes include increases in plasma renin and aldosterone, and reduced calcium excretion in the urine. In many studies investigating the effects of indapamide in both non-diabetic and diabetic hypertensive patients, glucose tolerance was not significantly altered. However, additional studies are necessary to assess the long term metabolic impacts of indapamide, since thiazide related impaired glucose tolerance can take several years to develop in non-diabetic patients.
Clinical Use
Indapamide is an effective diuretic drug when GFR falls below 40 mL/min. The duration of action is approximately 24 hours, with the normal oral adult dosage starting at 2.5 mg given each morning. The dose may be increased to 5.0 mg/day, but doses beyond this level do not appear to provide additional results.
Side Effects
Effects on urine content and side effects are similar to effects induced by thiazide diuretics.
Synthesis
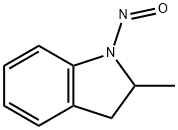
Indapamide, 4-chloro-N-(2-methyl-1-indolinyl)-3-sulfamoylbenzamide (21.3.33), is synthesized from 2-methylendoline, the nitrosation of which gives 2-methyl- 1-nitrosoindoline (21.3.31). Reducing this with lithium aluminum hydride leads to formation of 1-amino-2-methylendoline (21.3.32). Acylating this with 3-sulfonylamino-4-chlorbenzoic acid chloride leads to (21.3.33).

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Analgesics: increased risk of nephrotoxicity with
NSAIDs; antagonism of diuretic effect.
Anti-arrhythmics: hypokalaemia leads to increased
cardiac toxicity; effects of lidocaine and mexiletine
antagonised.
Antibacterials: avoid administration with
lymecycline.
Antidepressants: increased risk of hypokalaemia
with reboxetine; enhanced hypotensive effect with
MAOIs; increased risk of postural hypotension with
tricyclics.
Antiepileptics: increased risk of hyponatraemia with
carbamazepine.
Antifungals: increased risk of hypokalaemia with
amphotericin.
Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect;
increased risk of first dose hypotension with postsynaptic
alpha-blockers like prazosin; hypokalaemia
increases risk of ventricular arrhythmias with sotalol.
Antipsychotics: hypokalaemia increases risk
of ventricular arrhythmias with amisulpride;
enhanced hypotensive effect with phenothiazines;
hypokalaemia increases risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with pimozide - avoid.
Atomoxetine: hypokalaemia increases risk of
ventricular arrhythmias.
Cardiac glycosides: increased toxicity if hypokalaemia
occurs.
Ciclosporin: increased risk of nephrotoxicity and
possibly hypomagnesaemia.
Cytotoxics: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
due to hypokalaemia with arsenic trioxide; increased
risk of nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity with platinum
compounds.
Lithium excretion reduced (increased toxicity).
Metabolism
As a result of extensive metabolism in the liver, the majority of indapamide excreted is metabolized, with only 7% remaining unchanged. In humans, as many as 19 distinct indapamide metabolites may be produced, although not all have been identified.
There are several metabolic routes through which indapamide may be metabolized, and CYP3A4 is the main enzyme involved in the corresponding hydroxylation, carboxylation, and dehydrogenation reactions.
Indapamide can undergo dehydrogenation to form M5, then oxidation to form M4, then further hydroxylation at the indole moiety to form M2. These reactions are facilitated by CYP3A4.
Another route of metabolism occurs when indapamide is first hydroxylated to M1 by CYP3A4. M1 then undergoes dehydrogenation to form M3 and is further oxidized to form M2. Hydroxylation of indapamide’s indole moiety is thought to form the major metabolite (M1), which is less pharmacologically active compared to its parent compound according to animal studies.
Indapamide may also undergo epoxidation via CYP3A4 to form a reactive epoxide intermediate. The unstable epoxide intermediate may then undergo dihydroxylation via microsomal epoxide hydrolase to form M6, or glutathione conjugation to form M7.
Metabolism
Indapamide is strongly bound to red blood cells, and is taken up by the vascular wall in smooth vascular muscle according to its high lipid solubility. 60-70% of a single oral dose is eliminated by the kidneys and 23% by the gastrointestinal tract. Indapamide is extensively metabolised with 5-7% of unchanged drug found in the urine during the 48 hours following administration. About 16-23% of dose is excreted in the faeces
Properties of Indapamide
| Melting point: | 160-162°C |
| Boiling point: | 110.4°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | -0.8~+0.8°(D/20℃) (c=5, C2H5OH) |
| Density | 1.2895 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6100 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). |
| form | neat |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa (25°) 8.8 ± 0.2 |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in ethanol. Insoluble in water |
| Merck | 14,4935 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 26807-65-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzamide, 3-(aminosulfonyl)-4-chloro-N-(2,3-dihydro-2-methyl-1H-indol-1-yl)- (26807-65-8) |
Safety information for Indapamide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H362:Reproductive toxicity, effects on or via lactation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P263:Avoid contact during pregnancy/while nursing. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Indapamide
| InChIKey | NDDAHWYSQHTHNT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Indapamide manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
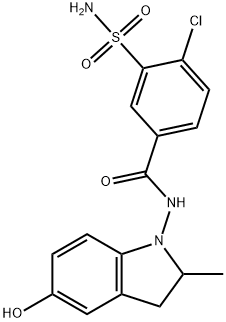
 Indapamide 99%View Details
Indapamide 99%View Details -
 Indapamide 26807-65-8 98%View Details
Indapamide 26807-65-8 98%View Details
26807-65-8 -
 26807-65-8 Indapamide 99%View Details
26807-65-8 Indapamide 99%View Details
26807-65-8 -
 Indapamide 99%View Details
Indapamide 99%View Details
26807-65-8 -
 INDAPAMIDE 26807-65-8 95-99 %View Details
INDAPAMIDE 26807-65-8 95-99 %View Details
26807-65-8 -
 Indapamide CAS 26807-65-8View Details
Indapamide CAS 26807-65-8View Details
26807-65-8 -
 Indapamide >98% (HPLC) CAS 26807-65-8View Details
Indapamide >98% (HPLC) CAS 26807-65-8View Details
26807-65-8 -
 Indapamide API PowderView Details
Indapamide API PowderView Details
26807-65-8
