Indan
Synonym(s):Hydrindene
- CAS NO.:496-11-7
- Empirical Formula: C9H10
- Molecular Weight: 118.18
- MDL number: MFCD00003795
- EINECS: 207-814-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
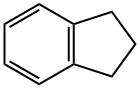
What is Indan?
Chemical properties
Indane is a colourless to faintly yellow liquid. Insoluble in water, soluble in alcohol, ether and other organic solvents in any proportion.
The Uses of Indan
Indane, is used as a catalytic agent, Petrochemical additive, used in organic synthesis. It is also used as pharmaceutical and chemical intermediate.
Definition
ChEBI: Indane is an ortho-fused bicyclic hydrocarbon consisting of a benzene ring fused to a cyclopentane ring; a high-boiling (176°C) colourless liquid. It is a member of indanes and an ortho-fused bicyclic hydrocarbon.
What are the applications of Application
Indane is used as anti-vibration agent for aviation fuel and anti-vibration agent for rubber industry. Its derivatives can be used in pharmaceuticals and solvents. Indane can be cracked to produce benzene compounds.
Preparation
Taking heavy benzene with a Indan content of 35% as a raw material, rectifying it through an emulsification tower, and cutting the 182°C fraction from the top of the tower, that is, Indan with a content of more than 90%.?
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 111, p. 314, 1989 DOI: 10.1021/ja00183a048
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 41, p. 1184, 1976 DOI: 10.1021/jo00869a022
Hazard
Irritant to skin and eyes.
Synthesis
3-phenyl-1-propene is isomerized to give indane in the presence of AlCl3:
Source
Detected in distilled water-soluble fractions of 87 octane gasoline (0.40 mg/L), 94 octane gasoline (0.23 mg/L), Gasohol (0.50 mg/L), No. 2 fuel oil (0.05 mg/L), jet fuel A (0.15 mg/L), and diesel fuel (0.06 mg/L) (Potter, 1996). Based on laboratory analysis of 7 coal tar samples, indan concentrations ranged from ND to 3,800 ppm (EPRI, 1970).
Environmental Fate
Photolytic. Gas-phase reaction rate constants for OH radicals, NO3 radicals, and ozone at 24 °C were 1.9 x 10-11, 6.6 x 10-15, and <3 x 10-19 cm3/molecule?sec, respectively (Kwok et al., 1997).
Purification Methods
Shake indane with conc H2SO4, then water, dry and fractionally distil it. [Beilstein 5 H 486, 5 I 234, 5 II 376, 5 III 1200, 5 IV 1371.]
Properties of Indan
| Melting point: | -51 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 176 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.965 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 1.5 at 25 °C (extrapolated, Ambrose and Sprake, 1975) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 50 °C |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Soluble in alcohol, ether (Weast, 1986), and many aliphatic hydrocarbons (hexane, pentane), and
aromatic hydrocarbons (benzene) |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | >14 (Schwarzenbach et al., 1993) |
| color | Clear colorless to yellow |
| Odor Threshold | 0.0037ppm |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, chloroform (slightly), and ether. Insoluble in water. |
| Merck | 14,4931 |
| BRN | 1904376 |
| Henry's Law Constant | (x 10-3 atm?m3/mol):
2.14 at 25 °C (approximate - calculated from water solubility and vapor pressure) |
| Stability: | Stable. Flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 496-11-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Indan (496-11-7) |
Safety information for Indan
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H304:Aspiration hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. |
Computed Descriptors for Indan
| InChIKey | PQNFLJBBNBOBRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 496-11-7 Indane 98%View Details
496-11-7 Indane 98%View Details
496-11-7 -
 Indan 95% CAS 496-11-7View Details
Indan 95% CAS 496-11-7View Details
496-11-7 -
 Indan CAS 496-11-7View Details
Indan CAS 496-11-7View Details
496-11-7 -
 Indan CAS 496-11-7View Details
Indan CAS 496-11-7View Details
496-11-7 -
 Indan CAS 496-11-7View Details
Indan CAS 496-11-7View Details
496-11-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
