HYDROCODONE
- CAS NO.:125-29-1
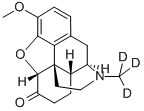
- Empirical Formula: C18H21NO3
- Molecular Weight: 299.37
- MDL number: MFCD00661056
- EINECS: 204-733-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
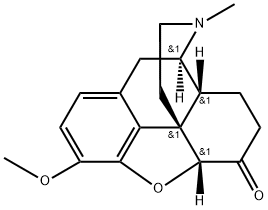
What is HYDROCODONE?
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of hydrocodone has not been characterized due to lack of an IV formulation. The liquid formulations of hydrocodone have a Tmax of 0.83-1.33 h. The extended release tablet formulations have a Tmax of 14-16 h. The Cmax remains dose proportional over the range of 2.5-10 mg in liquid formulations and 20-120 mg in extended release formulations. Administration with food increases Cmax by about 27% while Tmax and AUC remain the same. Administration with 40% ethanol has been observed to increase Cmax 2-fold with an approximate 20% increase in AUC with no change in Tmax. 20% alcohol produces no significant effect.
Toxicity
Overdosage with hydrocodone presents as opioid intoxication including respiratory depression, somnolence, coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin, constricted pupils, pulmonary edema, bradycardia, hypotension, partial or complete airway obstruction, atypical snoring, and death.
In case of oversdosage the foremost priority is the maintenance of a patent and protected airway with the provision of assisted ventilation if necessary. Supportive measures such as IV fluids, supplemental oxygen, and vasopressors may be used to manage circulatory shock. Advanced life support may be necessary in the case of cardiac arrest or arrhythmias. Opioid antagonists such as naloxone may be used to reverse the respiratory and circulatory effects of hydrocodone. Emergency monitoring is still required after naloxone administration as the opioid effects may reappear. Additionally, if used in an opioid tolerant patient, naloxone may produce opioid withdrawal symptoms.
Chemical properties
Beige Solid
Originator
Dicodid,Knoll,Belgium
The Uses of HYDROCODONE
Hydrocodone is a powerful anticough drug that is widely used for suppressing the cough reflex. It is widely used in effective commercial anticough drugs in combination with guaiphenesin (entuss), with homatropine (hycodan), with phenylpropanolamine (hycomine), phenyltoloxamine (tussionex), and pseudoephedrine and guaiphenesin (tussened).
The Uses of HYDROCODONE
Analgesic (narcotic); antitussive. Controlled substance (opiate).
Indications
Hydrocodone is indicated for the management of acute pain, sometimes in combination with acetaminophen or ibuprofen, as well as the symptomatic treatment of the common cold and allergic rhinitis in combination with decongestants, antihistamines, and expectorants.
Background
Hydrocodone is a synthetic opioid derivative of codeine. It is commonly used in combination with acetaminophen to control moderate to severe pain. Historically, hydrocodone has been used as a cough suppressant although this has largely been replaced by dextromethorphan in current cough and cold formulations. Hydrocodone's more potent metabolite, hydromorphone has also found wide use as an analgesic and is frequently used in cases of severe pain. The FDA first approved Hydrocodone for use as part of the cough suppressant syrup Hycodan in March of 1943.
Definition
ChEBI: A morphinane-like compound that is a semi-synthetic opioid synthesized from codeine.
Manufacturing Process
60 g of codeine about 94.5% (anhydrous codeine alkaloid basis) was dissolved in a solution made from 10 ml concentrated sulfuric acid and 390 ml water The mixture was refluxed for one hour with 25.0 g of 5% Pd on charcoal. The hot solution was immediately filtered and the catalyst was washed with 400 ml of dilute sulfuric acid of the same strength as was used in the rearrangement described above. To the combined cooled filtrate and wash, 750 ml if benzene was added, after which the mixture was cooled to 15°C, stirred, and made alkaline to pH 10 by addition of 80 ml of 40% NaOH. After shaking and separating the aqueous layer was extracted twice with 500 ml benzene. The combined benzene extracts are then extracted three times with 500 ml and twice with 400 ml portions of fresh 10% sodium bisulfite solution. Crude dihydrocodeinone was precipitated from bisulfite solution by eddition of 180 ml 40% NaOH at 15°C (to pH 10). The product was filtered, washed well and air-dried at room temperature. The melting point was about 184°C and yield about 35-38 g or 58-59%. The product was darken and the rest of Pd on charcoal and the original alkaloid were removed with column of Al2O3 (eluent - dry ethylene chloride) to give the dihyrocodeinone.
Therapeutic Function
Narcotic analgesic, Antitussive
General Description
Hydrocodone is the 3 methoxy version of hydromorphone.The loss of the 3-OH group yields a compound that is approximately4 to 5 times less potent than hydromorphone, thusabout equal to morphine. Unlike codeine, the agonist activityof hydrocodone does not require 3-O-demethylation, althoughit does occur via CYP2D6 representing 4.6% of totalclearance. The protected 3-position has better brain penetration,and the 7,8-dihydro-6-keto C ring contributes to the increasedbinding of the compound to the μ-receptor.
There are no pure hydrocodone products available on theU.S. market. All FDA-approved products containing hydrocodoneare combination products. Like codeine, hydrocodoneis marketed as an antitussive agent. It is availablecombined with the anticholinergic agent homatropineas a syrup and a tablet. The addition of the anticholinergicagent is to discourage abuse. It is also available in a delayedrelease suspension form (Tussionex). This formulation usesa sulfonated styrene divinylbenzene copolymer complexedwith hydromorphone and chlorpheniramine that acts as acation-exchange resin slowly releasing the drugs over a 12-hour period. Hydrocodone is also marketed in combinationwith acetaminophen (Vicodin, Lortab) or aspirin (LortabASA) for the treatment of pain. The dose of acetaminophenconsumed by the patient must be closely monitored, andprescriptions that allow for greater than 4 grams of acetaminophenper 24-hour period should not be dispensed.
Pharmacokinetics
Hydrocodone inhibits pain signaling in both the spinal cord and brain . Its actions in the brain also produce euphoria, respiratory depression, and sedation.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous and subcutaneous routes. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Metabolism
Hydrocodone undergoes oxidative O-demethylation to form hydromorphone, a more potent active metabolite. Though hydromorphone is active it is not present in sufficient quantities to contribute significantly to hydrocodone's therapeutic effects. Both hydrocodone and hydromorphone form 6-α- and 6-β-hydroxy metabolites through 6-ketoreduction. The hydroxy metabolites and hydromorphone can form glucuronide conjugates. Hydrocodone also undergoes oxidative N-demthylation to norhydrocodone. O-demethylation is primarily catalyzed by CYP2D6 while N-demethylation is primarily CYP3A4.
Properties of HYDROCODONE
| Melting point: | 194-197°C |
| Boiling point: | 440.69°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1613 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5500 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | Controlled Substance, -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 6.61(50% aq EtOH) (Uncertain) |
| color | Prisms from EtOH |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Morphinan-6-one, 4,5-epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methyl-, (5.alpha.)- (125-29-1) |
Safety information for HYDROCODONE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P311:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for HYDROCODONE
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
