Guar gum
Synonym(s):Gum guar
- CAS NO.:9000-30-0
- Empirical Formula: C10H14N5Na2O12P3
- Molecular Weight: 535.145283
- MDL number: MFCD00131250
- EINECS: 232-536-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:51
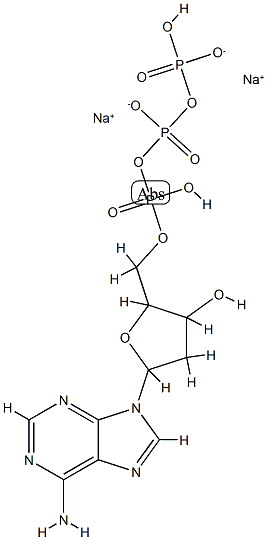
What is Guar gum?
Description
Background. Guar gum, like locust bean gum, is a galactomannan
derived from the seed of a leguminous plant. The source of guar,
Cyamopsis tetragonolobus, is widely grown in Pakistan and India
as cattle feed, and was introduced to the United States as a cover
crop in 1903. The U.S. is now also a producer. It was not until
1953, however, that guar gum was produced on a commercial
scale, primarily as a replacement for locus bean gum in the paper,
textile and food industries. The most important property of guar
is the ability to hydrate rapidly in cold water to attain a very high
viscosity. In addition to the food industry, guar is used in the
mining, paper, textile, ceramic, paint, cosmetic, pharmaceutical,
explosive, and other industries.
Sources, Harvesting, and Producing Areas. The guar is a hardy
and drought-resistant plant which grows three to six feet high with
vertical stalks. The guar pods, which grow in clusters along the
vertical stems, are about six inches long and contain 6 to 9 seeds,
which are considerably smaller than locus bean seeds. As in the
case of locust bean gum, the endosperm, which comprises 35-42%.
Chemical properties
Yellowish-white free-flowing powder. Completely soluble in hot or cold water. Practically insoluble in oils, greases, hydrocarbons, ketones, esters. Water solutions are tasteless, odorless, nontoxic. Has 5-8 times the thickening power of starch. Reduces the friction drag of water on metals.
Chemical properties
The USP32–NF27 describes guar gum as a gum obtained from the
ground endosperms of Cyamopsis tetragonolobus (L.) Taub. (Fam.
Leguminosae). It consists chiefly of a high-molecular-weight
hydrocolloidal polysaccharide, composed of galactan and mannan
units combined through glycoside linkages, which may be described
chemically as a galactomannan. The PhEur 6.3 similarly describes
guar galactomannan as being obtained from the seeds of Cyamopsis
tetragonolobus (L.) Taub. by grinding the endosperms and
subsequent partial hydrolysis.
The main components are polysaccharides composed of Dgalactose
and D-mannose in molecular ratios of 1 : 1.4 to 1 : 2. The
molecule consists of a linear chain of b-(1!4)-glycosidically linked
manno-pyranoses and single a-(1→6)-glycosidically linked galactopyranoses.
Guar gum occurs as an odorless or nearly odorless, white to
yellowish-white powder with a bland taste.
Chemical properties
Guar gum is the endosperm of the seed of the Indian cluster bean, Cyamopsis tetragonolobus. It has been grown for several thousand years in India and Pakistan as a vegetable and a forage crop. The guar is a hardy and drought-resistant plant, which grows 1 to 2 m high with vertical stalks and resembles the soybean plant in general appearance. The guar pods, which grow in clusters along the vertical stems, are about 30 cm long and contain six to nine seeds, which are considerably smaller than locust bean seeds Guar gum is odorless. As in the case of locust bean gum, the endosperm, which comprises 35 to 42% of the seed, is the source of the gum Typically, guar gum is around 80% of the endosperm of the guar seed. As the endosperm is about 40% of the seed, guar gum is roughly 30% of the guar plant seed. It is harvested before the frst rain following the frst frost to obtain maximum yield and purity (Burdock, 1997).
Physical properties
Guar gum is a white to yellowish-white powder It is dispersible in either hot or cold water, forming a solution having a pH between 5.4 and 7.0 that may be converted to gel by the addition of a small amount of sodium borate.
Occurrence
Guar gum is an annual found in India, the United States, and the tropics of Asia.
The Uses of Guar gum
guar gum has a coating action on the skin that allows for moisture retention. often used as a thickener and emulsifier in cosmetic formulations, guar gum is a polysaccharide found in the seeds of the guar plant. It is the nutrient material required by the developing plant embryo during germination. When the endosperm, once separated from the hull and embryo, is ground to a powder form, it is marketed as guar gum.
The Uses of Guar gum
low calorie, soluble dietery fiber
The Uses of Guar gum
In paper sizing; as a protective colloid, stabilizer, thickening and film forming agent for cheese, salad dressings, ice cream, soups; as a binding and disintegrating agent in tablet formulations; in pharmaceutical jelly formulations; in suspensions, emulsions, lotions, creams, toothpastes; in the mining industry as a flocculant, as a filtering agent; in water treatment as a coagulant aid.
Food additives, emulsifying stabilizer, thickener and gelling agent.
The Uses of Guar gum
Guar gum is obtained from the seed kernel of the plant cyamopsis tetragonoloba. It has a mannose:galactose ratio of approximately 2:1. It is dispersible in cold water to form viscous sols which upon heating will develop additional viscosity. A 1% solution has a viscosity range of 2,000–3,500 cp at 25°c. It is a versatile thickener and stabilizer used in ice cream, baked goods, sauces, and beverages at use levels ranging from 0.1 to 1.0%. It is scientifically termed guaran.
Definition
A water-soluble plant mucilage obtained from the ground endosperms of Cyanopsis tetragonoloba, cultivated in India and Pakistan as livestock feed, as well as in southwestern U.S. The water-soluble portion of the flour (85%) is called guaran and consists o
Production Methods
Guar gum is obtained from the ground endosperm of the guar plant,
Cyamopsis tetragonolobus (L.) Taub. (Fam. Leguminosae), which is
grown in India, Pakistan, and the semiarid southwestern region of
the USA.
The seed hull can be removed by grinding, after soaking in
sulfuric acid or water, or by charring. The embryo (germ) is
removed by differential grinding, since each component possesses a
different hardness. The separated endosperm, containing 80%
galactomannan is then ground to different particle sizes depending
upon final application.
General Description
Off-white to yellowish-white powder. Five to eight times the thickening power of starch. Water solutions are tasteless, odorless, and nontoxic and have a pale translucent gray color with neutral pH. Water solutions converted to gel by small amounts of borax.
Air & Water Reactions
The organic dusts can react violently when suspended in air in the presence of an ignitable source. . Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Guar gum is a ether-alcohol derivative, the ether being relatively unreactive. Flammable and/or toxic gases are generated by the combination of alcohols with alkali metals, nitrides, and strong reducing agents. They react with oxoacids and carboxylic acids to form esters plus water. Oxidizing agents convert alcohols to aldehydes or ketones. Alcohols exhibit both weak acid and weak base behavior. They may initiate the polymerization of isocyanates and epoxides.
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: When heated to decomposition Guar gum emits irritating fumes and smoke.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Guar gum are not available. However, Guar gum is probably combustible.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Guar gum is a galactomannan, commonly used in cosmetics, food
products, and pharmaceutical formulations. It has also been
investigated in the preparation of sustained-release matrix tablets
in the place of cellulose derivatives such as methylcellulose.
In pharmaceuticals, guar gum is used in solid-dosage forms as a
binder and disintegrant; in oral and topical products
as a suspending, thickening, and stabilizing agent; and also as a
controlled-release carrier. Guar gum has also been examined for use
in colonic drug delivery. Guar-gum-based three-layer matrix
tablets have been used experimentally in oral controlled-release
formulations.
Therapeutically, guar gum has been used as part of the diet of
patients with diabetes mellitus. It has also been used as an
appetite suppressant, although its use for this purpose, in tablet
form, is now banned in the UK.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Guar gum has been shown to have numerous beneficial effects including improved glucose tolerance and attenuation of diabetic nephropathy.
Safety
Guar gum is widely used in foods, and oral and topical
pharmaceutical formulations. Excessive consumption may cause
gastrointestinal disturbance such as flatulence, diarrhea, or nausea.
Therapeutically, daily oral doses of up to 25 g of guar gum have
been administered to patients with diabetes mellitus.
Although it is generally regarded as a nontoxic and nonirritant
material, the safety of guar gum when used as an appetite
suppressant has been questioned. When consumed, the gum swells
in the stomach to promote a feeling of fullness. However, it is
claimed that premature swelling of guar gum tablets may occur and
cause obstruction of, or damage to, the esophagus. Consequently,
appetite suppressants containing guar gum in tablet form have been
banned in the UK. However, appetite suppressants containing
microgranules of guar gum are claimed to be safe. The use of
guar gum for pharmaceutical purposes is unaffected by the ban.
In food applications, an acceptable daily intake of guar gum has
not been specified by the WHO.
LD50 (hamster, oral): 6.0 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, oral): 8.1 g/kg
LD50 (rabbit, oral): 7.0 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 6.77 g/kg
Storage
Aqueous guar gum dispersions have a buffering action and are
stable at pH 4.0–10.5. However, prolonged heating reduces the
viscosity of dispersions.
The bacteriological stability of guar gum dispersions may be
improved by the addition of a mixture of 0.15% methylparaben
and 0.02% propylparaben as a preservative. In food applications,
benzoic acid, citric acid, sodium benzoate, or sorbic acid may be
used.
Guar gum powder should be stored in a well-closed container in
a cool, dry place.
Properties and Applications
|
Items |
Standard |
|
Appearance |
Light yellow free flow powder |
|
120mesh residue |
1% max |
|
200mesh residue |
10% max |
|
Moisture |
10% max |
|
pH |
6.5-7.5 |
|
Apparent viscosity (30oC,170s,0.6%)mpa.s |
110 min |
|
Water insolubles |
4% max |
|
Crosslinking property |
Can be picked up by glass rod |
|
Fluidity |
Good |
|
Hydroxypropyl degree of substitution |
0.30 min |
Incompatibilities
Guar gum is compatible with most other plant hydrocolloids such
as tragacanth. It is incompatible with acetone, ethanol (95%),
tannins, strong acids, and alkalis. Borate ions, if present in the
dispersing water, will prevent the hydration of guar gum. However,
the addition of borate ions to hydrated guar gum produces cohesive
structural gels and further hydration is then prevented. The gel
formed can be liquefied by reducing the pH to below 7, or by
heating.
Guar gum may reduce the absorption of penicillin V from some
formulations by a quarter.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral suspensions, syrups, and tablets; topical preparations; vaginal tablets). Also included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Guar gum
| Melting point: | >220°C (dec.) |
| alpha | D25 +53° (1N NaOH) |
| FEMA | 2537 | GUAR GUM (CYAMOPSIS TETRAGONOLOBUS (L.)) |
| storage temp. | Hygroscopic, -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | It yields a mucilage of variable viscosity when dissolved in water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent). |
| form | Free Flowing Powder |
| color | Yellow-white |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Merck | 13,4588 / 13,4587 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. A mixture of air and finely-divided powder is potentially explosive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Guar gum (9000-30-0) |
Safety information for Guar gum
Computed Descriptors for Guar gum
Guar gum manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Guar Gum 99%View Details
Guar Gum 99%View Details -
 Gum Guar 98%View Details
Gum Guar 98%View Details
9000-30-0 -
 Gum Guar 9000-30-0 98%View Details
Gum Guar 9000-30-0 98%View Details
9000-30-0 -
 Guar gum powder CAS 9000-30-0View Details
Guar gum powder CAS 9000-30-0View Details
9000-30-0 -
 Guar sum, spazial CAS 9000-30-0View Details
Guar sum, spazial CAS 9000-30-0View Details
9000-30-0 -
 Guar gum CAS 9000-30-0View Details
Guar gum CAS 9000-30-0View Details
9000-30-0 -
 POTASSIUM IODIDE (7681-11-0)View Details
POTASSIUM IODIDE (7681-11-0)View Details
7681-11-0 -
 Food Grade Powder Guar GumView Details
Food Grade Powder Guar GumView Details
9000-30-0
