Glycerol phenylbutyrate
- CAS NO.:611168-24-2
- Empirical Formula: C33H38O6
- Molecular Weight: 530.65
- MDL number: MFCD28016960
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
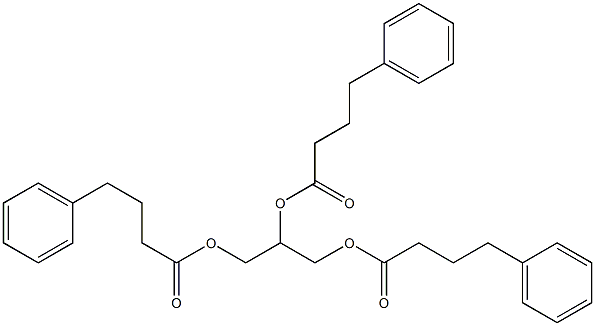
What is Glycerol phenylbutyrate?
Absorption
Glycerol phenylbutyrate is a prodrug in which phenylbutyrate (PBA) is released from the glycerol backbone by lipases in the gastrointestinal tract. PBA then undergoes beta-oxidtion to form PAA. When a single oral dose of 2.9 mL/m2 of Glycerol phenylbutyrate is given to fasting adult subjects, the pharmacokinetic parameters are as follows: Tmax: PBA = 2 hours; PAA = 4 hours; PAGN = 4 hours. Cmax: PBA = 37.0 μg/mL; PAA = 14.9 μg/mL; PAGN = 30.2 μg/mL. In healthy subjects, the hydrolysis of glycerol phenylbutyrate is incomplete, but to what extent is unknown. When glycerol phenylbutyrate is given to adult UCD patients, maximum plasma concentrations at steady state (Cmaxss) of PBA, PAA, and PAGN occurred at 8 h, 12 h, and 10 h, respectively, after the first dose in the day. Intact glycerol phenylbutyrate was not detectable in plasma in UCD patients.
Toxicity
Most common adverse reactions in ≥10% of patients are diarrhea, flatulence, and headache.
The Uses of Glycerol phenylbutyrate
Tri(4-phenylbutyryl)glycerol is a drug that is currently under development for treatment of urea cyclic disorders (UCDs). It works by preventing the harmful buildup of ammonia in the body.
Background
Glycerol phenylbutyrate is a nitrogen-binding agent. Chemically, it is a triglyceride in which three molecules of phenylbutyrate are linked to a glycerol backbone. FDA approved on February 1, 2013.
Indications
Glycerol phenylbutyrate is a nitrogen-binding agent for the chronic management of adult and pediatric patients ≥2 years of age with urea cycle disorders (UCDs) who cannot be managed by dietary protein restriction and/or amino acid supplementation alone.
Definition
ChEBI: Glycerol phenylbutyrate is a triglyceride.
Pharmacokinetics
Glycerol phenylbutyrate prolongs the QTc interval.
Metabolism
Pancreatic lipases hydrolyze glycerol phenylbutyrate to release PBA from the glycerol backbone. PBA undergoes β-oxidation to PAA, which is conjugated with glutamine in the liver and in the kidney through the enzyme phenylacetyl-CoA: L-glutamine-N-acetyltransferase to form PAGN.
Properties of Glycerol phenylbutyrate
| Boiling point: | 621.2±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.131±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO:150.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);282.67(Max Conc. mM) Ethanol:50.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);94.22(Max Conc. mM) |
| form | Oil |
| color | Colourless |
Safety information for Glycerol phenylbutyrate
Computed Descriptors for Glycerol phenylbutyrate
Abamectin manufacturer
Nuray Chemicals Pvt Ltd
Stereokem Pvt Ltd
Aruvi Labs
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid 4-Fluorophenylacetic acid tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid N,N-DIMETHYLFORMAMIDE DIMETHYL ACETAL 2-Bromo-4-fluorothioanisole Para Fluoro Aniline (PFA) 2-HYDROXYPYRIDINE 4-CYANO-2-FLUORO BENZYL ALCOHOL Para Chloro Aniline (PCA) Benzamidine.HCl 5-Cyano indole 2-Methyl resorcinol Formalin; Methanal 3-Cyclopentyl-1-propanol 2-Acetylcyclohexanone 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 5-Fluoro-2-iodo-3-methylanilineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Glycerol phenylbutyrate 98%View Details
Glycerol phenylbutyrate 98%View Details -
 Glycerol phenylbutyrate 98%View Details
Glycerol phenylbutyrate 98%View Details -
 Glycerol phenylbutyrate 98%View Details
Glycerol phenylbutyrate 98%View Details
611168-24-2 -
 Glycerol phenylbutyrate CAS 611168-24-2View Details
Glycerol phenylbutyrate CAS 611168-24-2View Details
611168-24-2 -
 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 98%+View Details
2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 98%+View Details -
 tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate 98%+View Details
tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate 98%+View Details -
 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 98%+View Details
1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 98%+View Details -
 diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate 98%+View Details
diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate 98%+View Details