Glucagon
Synonym(s):GlucaGen;Glucagon;Glucagon peptide
- CAS NO.:16941-32-5
- Empirical Formula: C153H225N43O49S
- Molecular Weight: 3482.75
- MDL number: MFCD00167532
- EINECS: 685-611-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-15 19:19:13

What is Glucagon?
Chemical properties
White or almost white powder
The Uses of Glucagon
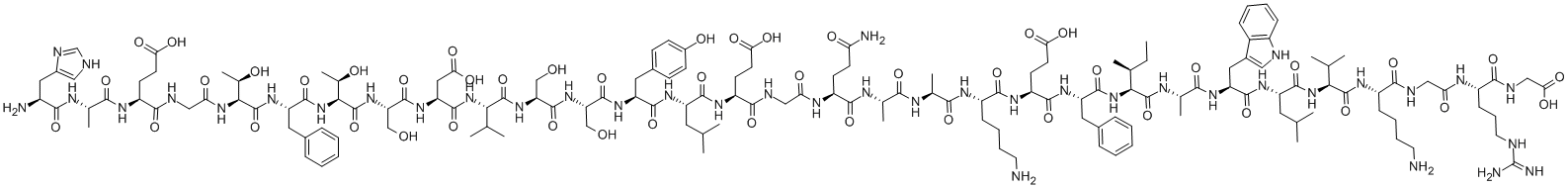
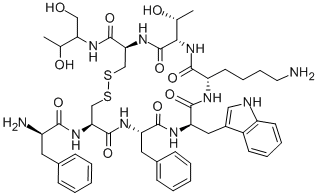
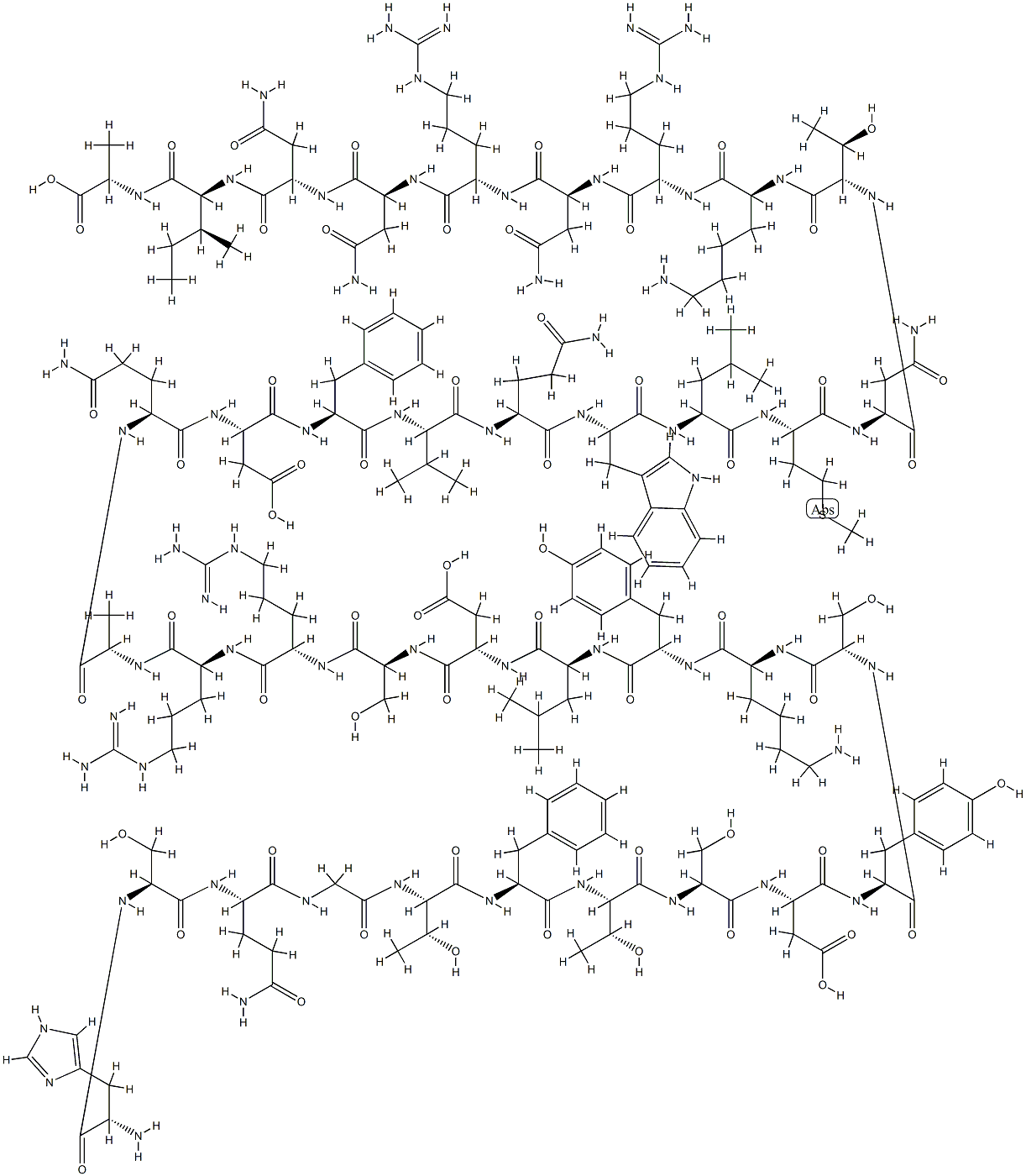
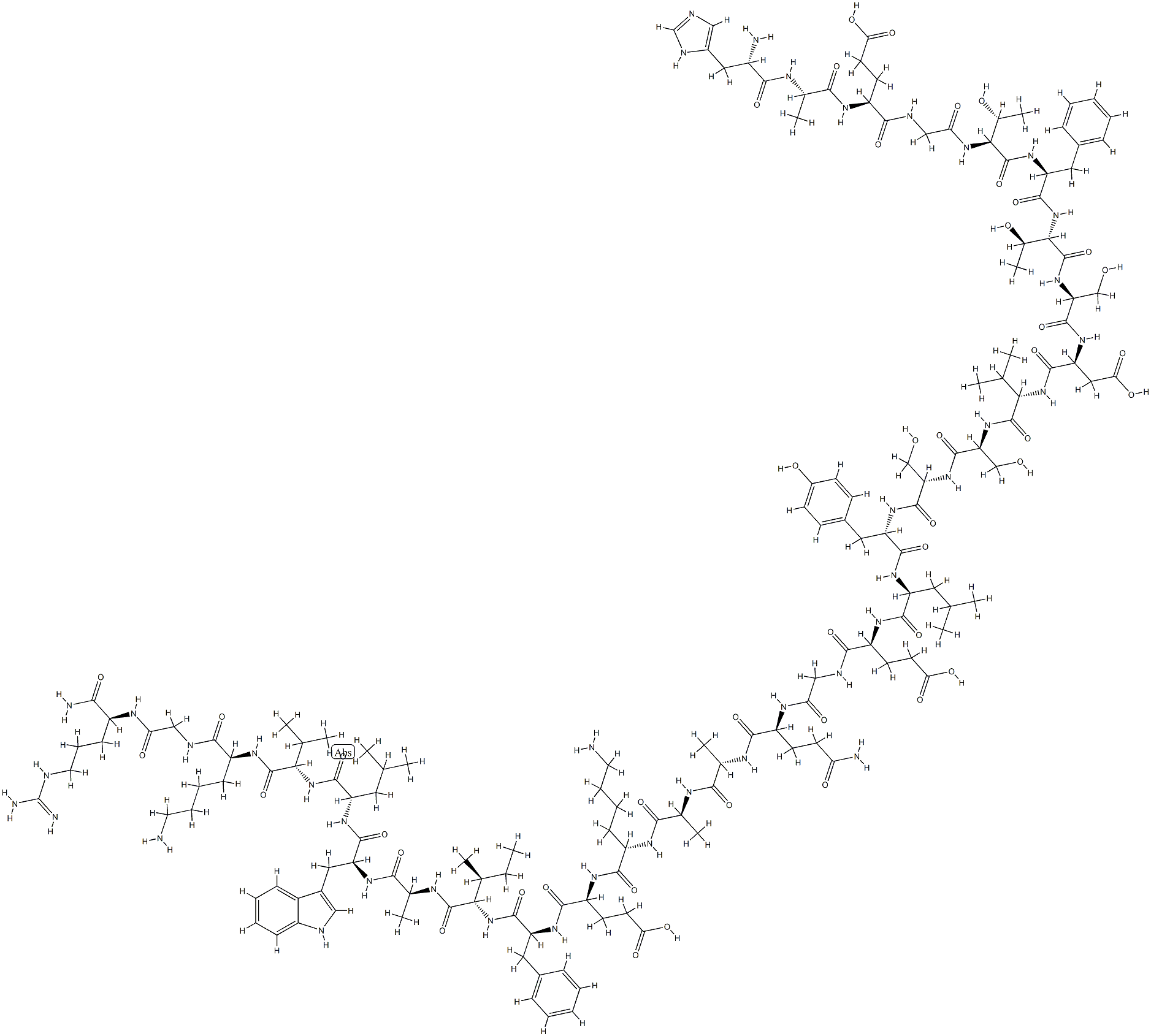
Glucagon is an Amino Acid sequence.
The Uses of Glucagon
Hypoglycemia?(diabetes?mellitus)
The Uses of Glucagon
Glucagon has been used:
- in the stimulation of human primary hepatocytes for cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) production
- for measuring glucagon response in mice
- to induce gluconeogenic stimuli in primary hepatocytes
The Uses of Glucagon
Glucagon is a polypeptide secreted by the α cells of the pancreatic islets. Its physiological actions include stimulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis in response to hypoglycaemia and amino acids and as part of the stress response. These effects are mediated by increasing adenylate cyclase activity and intracellular cAMP by a mechanism independent of the β-adrenergic receptor. It increases cAMP in myocardial cells and so increases cardiac contractility. Glucagon causes nausea and vomiting, hyperglycaemia and hyperkalaemia and is not used as an inotrope except in the management of β-blocker poisoning.
Definition
Produced by the α cells of the islands of Langerhans and also by the gastric mucosa. It is opposite in effect to insulin. It appears to be a straight-chain polypeptide with a molecular weight of approximately 3500. Small amounts have been detected in comm
Biological Functions
Glucagon, a 29-amino-acid, straight-chain polypeptide of α-cell pancreatic origin, triggers liver glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, thereby elevating glucose levels. The principal action of glucagon is the liver-mediated release into the blood of abnormally high concentrations of glucose, which causes hyperglycemia. This means that glucagon has an effect on blood glucose levels that is opposite to what occurs with insulin.
General Description
produced by recombinant DNA technology ismarketed by Novo Nordisk (glucagon [recombinant] hydrochloride,GlucaGen HypoKit, GlucaGen Diagnostic Kit)and by Eli Lilly (glucagon [recombinant] Emergency Kit).
General Description
The hyperglycemic–glycogenolytic hormone elaborated by the α-cells of the pancreas is known as glucagon. It contains 29 amino acid residues. Glucagon has been isolated from the amorphous fraction of a commercial insulin sample (4% glucagon).
It is soluble, 1 to 10 mg/mL, in the pH ranges 2.5 to 3.0 and 9.0 to 9.5. Solutions of 200 μg/mL at pH 2.5 to 3.0 are stable for at least several months at 4°C if sterile. Loss of activity by fibril formation occurs readily at high concentrations of glucagon at room temperature, or above, at pH 2.5. The isoelectric point appears to be at pH 7.5 to 8.5. Because it has been isolated from commercial insulin, its stability properties should be comparable to those of insulin.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Glucagon functions to elevate glucose by activating GCGR in liver mediating the glucose circulation in blood. The hyperglucagonemia elevated levels of glucagon is observed in diabetes and in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, post gastric bypass surgery and glucagon based tumors.
Clinical Use
Endogenous glucagon isproduced from the gene-derived protein PG in the cells ofthe islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. The core functionof this hormone is to renormalize blood glucose levels whenthey fall too low, by stimulating production from glycogen stores in liver and muscle, and stimulating hepatic gluconeogenesis.Glucagon also elicits biochemical processes (suchas fatty acid oxidation) that supply the needed precursors forgluconeogenesis. Glucagon supplied exogenously (i.e., injected)in response to emergency hypoglycemia acts rapidlyto elicit these same responses. Clinically, glucagon also providesan alternative to cholinergic antagonists for reducingGI motility and secretory activity during radiologic imagingprocedures.
Clinical Use
The glucagon test is performed to identify glucagonoma. It is also performed clinically to measure glucose control in patients who have developed type 2 diabetes, or in patients who may be insulin-resistant. Glucagon administration is used in the treatment of hypoglycemia, in anaphylactic reaction in patients on beta-blocker therapy, in beta-blocker- or calcium channel blocker-induced myocardial depression unresponsive to standard measures, and in the temporary inhibition of gastrointestinal movement during radiologic examinations.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
In small animals, the primary use for glucagon is to increase blood
glucose in patients with excessive insulin levels, either endogenously
produced (insulinoma) or exogenously administered (insulin
overdose). Glucagon has potential in the treatment of fatty liver
syndrome in dairy cattle.
In human medicine, glucagon is used in treating the cardiac
manifestations of beta-blocker and calcium-channel blocker overdoses.
One study (Kerns, D et al. 1997) in dogs, however, demonstrated
insulin to be superior to glucagon in treating experimental
propranolol overdoses in dogs.
storage
Store at -20°C
Properties of Glucagon
| Density | 1.53±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water and in most organic solvents. It is soluble in dilute mineral acids and in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides. |
| form | powder |
| color | White to off-white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble to 1 mg/ml in water |
Safety information for Glucagon
Computed Descriptors for Glucagon
| InChIKey | MASNOZXLGMXCHN-SXVMFYJYNA-N |
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 7-Bromo-1H-indazole N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid Electrolytic Iron Powder Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 1-(4-Methylphenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,3-benzotriazole 1-(2-Chlorobenzyl)-4-nitro-1H-pyrazole 1-(2-Nitrophenyl)-4-phenylpiperazineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 rGlucagon, recombinant glucagon (human) CAS 16941-32-5View Details
rGlucagon, recombinant glucagon (human) CAS 16941-32-5View Details
16941-32-5 -
 55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
1169630-40-3 -
 1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 -
 127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5