Gilenia
- CAS NO.:162359-55-9
- Empirical Formula: C19H33NO2
- Molecular Weight: 307.47
- MDL number: MFCD14705150
- EINECS: 1308068-626-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-25 11:31:46
What is Gilenia?
Absorption
Fingolimod is slowly but efficiently absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. AUC varies greatly, depending on the patient, and pharmacokinetic studies demonstrate a range of AUC values for fingolimod. The Tmax of fingolimod ranges between 12-16 hours and its bioavailability is 90-93%. Steady-state concentrations of fingolimod are achieved within 1-2 months after initiation when it is administered in a single daily dose.
Toxicity
The LD50 of fingolimod in rats ranges from 300-600 mg/kg.
Prescribing information for fingolimod does not mention symptoms or management of an overdose , however, a case report of an intentional overdose with 14mg of fingolimod and 2g phenoxymethylpenicillin resulted in hypotension in bradycardia, resolved by administering atropine. Since fingolimod has been associated with cardiotoxicity, it would be reasonable to expect cardiac effects such as bradycardia and heart block in the case of an overdose.
Chemical properties
white solid
The Uses of Gilenia
Prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients receiving allogenic renal transplants (sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor).
The Uses of Gilenia
Fingolimod is a novel immune modulator that prolongs allograft transplant survival in numerous models by inhibiting lymphocyte emigration from lymphoid organs.
Background
Multiple sclerosis, or MS, is a devastating inflammatory disease that often progresses and causes severe neurological, physical, and cognitive effects. Fingolimod is a sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator for the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. It was developed by Novartis and initially approved by the FDA in 2010. Fingolimod was also studied for the treatment of COVID-19, the disease caused by infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Indications
Fingolimod is indicated for the treatment of patients aged 10 and above with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis, which may include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, as well as active secondary progressive disease.
Definition
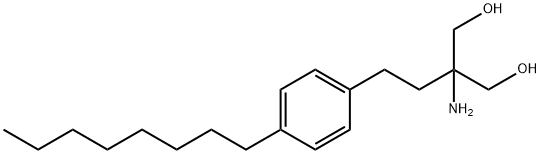
ChEBI: An aminodiol that consists of propane-1,3-diol having amino and 2-(4-octylphenyl)ethyl substituents at the 2-position. It is a sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator used for the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. A prodrug, fingolimo is phosphorylated by sphingosine kinase to active metabolite fingolimod-phosphate, a structural analogue of sphingosine 1-phosphate.
Pharmacokinetics
In multiple sclerosis, fingolimod binds to sphingosine receptors, reducing its associated neuroinflammation.In COVID-19, it may reduce lung inflammation and improve the clinical outcomes of patients with this disease.
Fingolimod causes a transient reduction in heart rate and AV conduction during treatment initiation. It has the potential to prolong the QT interval.
Clinical Use
Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator:Treatment of highly active relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Anti-arrhythmics: possible increased risk of bradycardia with amiodarone, disopyramide and dronedarone. Antifungals: concentration increased by ketoconazole. Beta-blockers: possibly increased risk of bradycardia. Calcium channel blockers: possible increased risk of bradycardia with diltiazem and verapamil.
Metabolism
Sphingosine kinase metabolizes fingolimod to an active metabolite, fingolimod phosphate. Fingolimod metabolism occurs via 3 major metabolic pathways: firstly, phosphorylation of the (S)-enantiomer of fingolimod-phosphate (pharmacologically active), secondly, oxidation by cytochrome P450 4F2 (CYP4F2), and thirdly, fatty acid-like metabolism to various inactive metabolites. The formation of inactive non-polar ceramide analogs of fingolimod also occurs during its metabolism.
Metabolism
Transformed by reversible stereoselective phosphorylation to the pharmacologically active (S)-enantiomer of fingolimod phosphate. It is eliminated by oxidative biotransformation mainly via the cytochrome P450 4F2 isoenzyme and subsequent fatty acid-like degradation to inactive metabolites, and by formation of pharmacologically inactive non-polar ceramide analogues of fingolimod. The main enzyme involved in the metabolism of fingolimod is partially identified and may be either CYP4F2 or CYP3A4. 81% excreted as inactive metabolites in the urine and <2.5% in the faeces as metabolites and unchanged drug.
Properties of Gilenia
| Melting point: | 103-105° |
| Boiling point: | 479.5±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.016 |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Very Slightly, Heated), DMSO (Slightly, Heated), Methanol (Slightly, |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 12.20±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | Off-White |
Safety information for Gilenia
Computed Descriptors for Gilenia
Gilenia manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
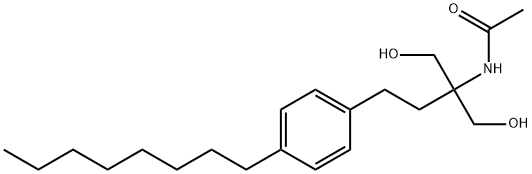
![N-[1,1-Bis[(acetyloxy)methyl]-3-(4-octylphenyl)propyl]acetamide](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/162358-09-0.gif)
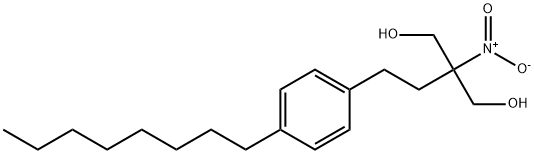
![2-(Acetylamino)-2-[2-(4-octylphenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-propanedioic acid 1,3-diethyl ester](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20150408/GIF/268557-49-9.gif)
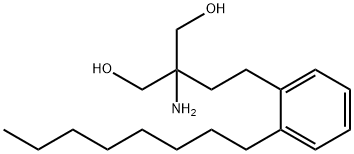

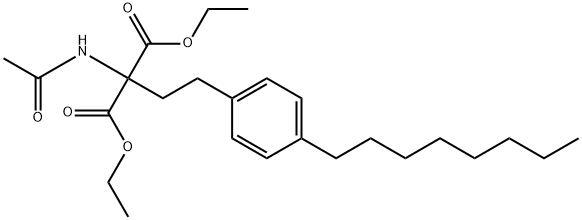
You may like
-
 162359-55-9 Fingolimod 98%View Details
162359-55-9 Fingolimod 98%View Details
162359-55-9 -
 162359-55-9 98%View Details
162359-55-9 98%View Details
162359-55-9 -
 Fingolimod 98%View Details
Fingolimod 98%View Details
162359-55-9 -
 Fingolimod 162359-55-9 98%View Details
Fingolimod 162359-55-9 98%View Details
162359-55-9 -
 162359-55-9 Fingolimod 98%View Details
162359-55-9 Fingolimod 98%View Details
162359-55-9 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
