Garenoxacin
- CAS NO.:194804-75-6
- Empirical Formula: C23H20F2N2O4
- Molecular Weight: 426.41
- MDL number: MFCD08141853
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-05-18 08:51:57
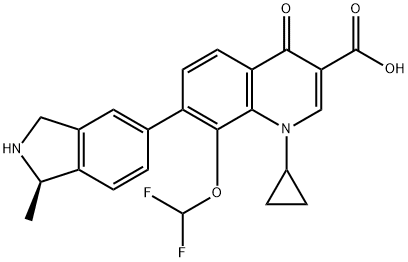
What is Garenoxacin?
Description
Garenoxacin is a new quinolone antimicrobial agent that exhibits a
broad spectrum of activity against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive
organisms, including the important community-acquired respiratory pathogens
S.pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis. In addition, it has
potent activity against several resistant strains such as multidrug-resistant
S.pneumoniae, methicillin-resistant S.aureus (MRSA), and vancomycin-resistant
enterococci (VRE). It was launched in Japan as an oral treatment for respiratory tract and otorhinolaryngological infections. As with other quinolone antibiotics marketed in recent years, the mechanism of action of garenoxacin involves dual inhibition of two essential bacterial enzymes, DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. The lack of 6-fluoro substituent does not adversely affect its potency of inhibiting DNA gyrase (Escherichia coli, IC50 0.17 mg/mL) or topoisomerase IV (S. aureus, IC50 2.19 mg/ mL).
In human pharmacokinetic studies, oral garenoxacin results in dose-proportionate increases of plasma Cmax and AUC values at doses ranging from 50 to 1,200 mg. Its oral bioavailability is about 95%, and the mean terminal half-life is 15.4 h.
The most common adverse events associated with garenoxacin were rash, dizziness, nausea, headache, and pruritus. Garenoxacin is chemically derived in a sequence of 14 steps, 12 of which entail the construction of a key quinolone intermediate, 7-bromo-1- cyclopropyl-8-(difluoromethoxy)-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester. Subsequently, Suzuki cross-coupling reaction of this intermediate with (R)-[1-methyl-2-(trityl)isoindolin-5-yl]boronic acid, followed by deprotection of the trityl group and ester hydrolysis with hydrochloric acid gives garenoxacin. The chiral isoindoline reagent is obtained from racemic 5-bromo-2-methylisoindoline via coupling with N-CBZ-L-phenylalanine, separation of diastereomers by chromatography, cleavage of the chiral auxiliary, N-tritylation, halogen-metal exchange with butyllithium, and boronation with triisopropyl borate.
Originator
Toyama (Japan)
The Uses of Garenoxacin
Des-F(6)-quinolone antibacterial; topoisomerase II inhibitor. Antibacterial.
What are the applications of Application
Garenoxacin is an antibacterial agent and a Topo II inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: A quinolinemonocarboxylic acid that is 1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid that is substituted by a cyclopropyl group at position 1, an oxo group at position 4, a (1R)-1-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindol-5-yl group at po ition 7, and a difluoromethoxy group at position 8.
brand name
Geninax
Properties of Garenoxacin
| Melting point: | 226-227°; mp 234-235° |
| Boiling point: | 581.5±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D27 -9.0° (c = 0.10 in N,N-dimethylformamide) |
| Density | 1.421±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Hygroscopic, -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | DMF (Slightly, Heated), DMSO (Slightly, Heated), Methanol (Slightly, Heated) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 6.44±0.50(Predicted) |
| color | Off-White to Pale Yellow |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for Garenoxacin
Computed Descriptors for Garenoxacin
Garenoxacin manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 194804-75-6 Garenoxacin 98%View Details
194804-75-6 Garenoxacin 98%View Details
194804-75-6 -
 194804-75-6 98%View Details
194804-75-6 98%View Details
194804-75-6 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8