gamma-Linolenic acid
- CAS NO.:506-26-3
- Empirical Formula: C18H30O2
- Molecular Weight: 278.43
- MDL number: MFCD00065718
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
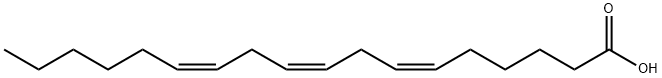
What is gamma-Linolenic acid?
Absorption
The findings from a pharmacokinetic study suggest that therapeutic levels of GLA can be achieved within a week. The fasting plasma GLA levels plateaued within seven days of beginning treatment, regardless of dose .
Toxicity
Oral TDLO reported in man is 3.14 mg/kg/42D (intermittent) . While limited cases of soft stool, belching, and abdominal bloating have been reported from dietary supplements containing gamolenic acid, daily doses up to 2.8 g were well tolerated .
Description
γ-Linolenic acid (gamma-linolenic acid or GLA, INN and USAN gamolenic acid) is a fatty acid found primarily in vegetable oils. It is sold as a dietary supplement for treating problems with inflammation and auto-immune diseases, although its efficacy is disputed.
Description
γ-
Chemical properties
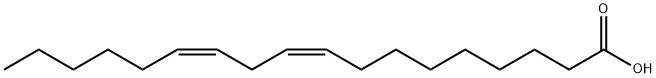
GLA is categorized as an n?6 (also called ω?6 or omega-6) fatty acid, meaning that the first double bond on the methyl end (designated with n or ω) is the sixth bond. In physiological literature, GLA is designated as 18:3 (n?6). GLA is a carboxylic acid with an 18-carbon chain and three cis double bonds. It is an isomer of α-linolenic acid, which is a polyunsaturated n?3 (omega-3) fatty acid, found in rapeseed canola oil, soy beans, walnuts, flax seed (linseed oil), perilla, chia, and hemp seed.
Occurrence
GLA is obtained from vegetable oils such as GLA safflower oil (Carthamus tinctorius), evening primrose (Oenothera biennis) oil, blackcurrant seed oil, borage oil, and hemp seed oil. GLA is also found in edible hemp seeds, oats, barley, and spirulina. Each contains varying amounts of the fatty acid, with GLA safflower oil at 40% GLA being a novel concentrated form. This is a new genetically modified oil and has been available in commercial quantities since 2011. It should be noted that conventional safflower oils have zero GLA. Borage oil ranges from 15 % to 20 % and evening primrose oil ranges from 8 % to 10 % GLA.
The human body produces GLA from linoleic acid (LA). This reaction is catalyzed by Δ6 - desaturase (D6D), an enzyme that allows the creation of a double bond on the sixth carbon counting from the carboxyl terminus. LA is consumed sufficiently in most diets, from such abundant sources as cooking oils and meats. However, a lack of GLA can occur when there is a reduction of the efficiency of the D6D conversion (for instance, as people grow older or when there are specific dietary deficiencies) or in disease states wherein there is excessive consumption of GLA metabolites.
History
GLA was first isolated from the seed oil of evening primrose. This herbal plant was grown by Native Americans to treat swelling in the body. In the 17th century, it was introduced to Europe and became a popular folk remedy, earning the name king's cure-all. in 1919, Heiduschka and Lüft extracted the oil from evening primrose seeds and described an unusual linolenic acid, which they name γ-. Later, the exact chemical structure was characterized by Riley.
Although there are α- and γ- forms of linolenic acid, there is no β- form. One was once identified, but it turned out to be an artifact of the original analytical process.
The Uses of gamma-Linolenic acid
γ-linolenic acid has been used as an analytical standard in gas chromatography. It may be used in nutritional studies regarding weight regain and as a possible tumor suppression agent. γ-linolenic acid is used in studies on the mechanisms and prevention of oxidation/peroxidation of unsaturated fatty acids.
The Uses of gamma-Linolenic acid
γ-Linolenic Acid is a fatty acid found mainly in vegetable oil. Studies suggest that γ-Linolenic Acid may have immune regulating and anti-inflammatory effects. γ-Linolenic Acid has also been used in the treatment of atopic eczeme although its efficacy is
Definition
ChEBI: A C18, omega-6 acid fatty acid comprising a linolenic acid having cis- double bonds at positions 6, 9 and 12.
Indications
Indicated as a dietary supplement for over-the-counter uses.
Background
Gamolenic acid, or gamma-linolenic acid (γ-Linolenic acid) or GLA, is an essential fatty acid (EFA) comprised of 18 carbon atoms with three double bonds that is most commonly found in human milk and other botanical sources . It is an omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) also referred to as 18:3n-6; 6,9,12-octadecatrienoic acid; and cis-6, cis-9, cis-12- octadecatrienoic acid . Gamolenic acid is produced minimally in the body as the delta 6-desaturase metabolite of Linolenic acid. It is converted to Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid, a biosynthetic precursor of monoenoic prostaglandins such as PGE1. While Gamolenic acid is found naturally in the fatty acid fractions of some plant seed oils , Evening primrose oil and Borage oil are rich sources of gamolenic acid. Evening primrose oil has been investigated for clinical use in menopausal syndrome, diabetic neuropathy, and breast pain, where gamolenic acid is present at concentrations of 7-14% . Gamolenic acid may be found in over-the-counter dietary supplements. Gamolenic acid is also found in some fungal sources and also present naturally in the form of triglycerides . Various clinical indications of gamolenic acid have been studied, including rheumatoid arthritis, atopic eczema, acute respiratory distress syndrome, asthma, premenstrual syndrome, cardiovascular disease, ulcerative colitis, ADHD, cancer, osteoporosis, diabetic neuropathy, and insomnia.
What are the applications of Application
γ-Linolenic Acid (18:3, n-6) is an antitumor agent
Biochem/physiol Actions
Gamma-linolenate (C18:6,9,12) differs from α-linolenate (C18:9,12,15) in the positions of the double bonds.
Pharmacokinetics
Gamolenic acid is converted to PGE1, which exhibits anti-inflammatory, antithrombotic, antiproliferative, and lipid-lowering effects . PGE1 also induces smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation. Gamolenic acid is an essential component of membrane phospholipids, including the mitochondrial membrane, where it enhances the the integrity and the fluidity of the membrane .
Bone and joint health: In a pilot study of women with a mean age of 79.5 years and senile osteoporosis, the use of gamolenic acid in combination with calcium and eicosapentaenoic acid was associated with an increase in femoral bone density and lumbar spine density in comparison to placebo, where there were no observable changes . In clinical studies of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, treatment with gamolenic acid-containing oils resulted in an improvement in symptoms, measured by joint tenderness counts and scores, joint swelling scores, physician global assessment, and pain .
Inflammation: A study demonstrated that oral administration of gamolenic acid suppressed human T-cell proliferation and activation by interfering with early events in the TcR/CD3-receptor–mediated signal transduction cascade .
Atherosclerosis: In ApoE genetic knock-out mice, dietary gamolenic acid was shown to reduce the average medial layer thickness of the vessel wall and reduces the size of atherosclerotic lesions .
Diabetic complications: In a clinical trial of patients with mild diabetic neuropathy or distal diabetic neuropathy, treatment with gamolenic acid was associated with improved symptoms in hot and cold threshold, sensation, tendon reflexes, and muscle strength . GLA ameliorated the inflammatory profile in diabetic nephropathy in rat studies .
Cancer: In three human tumor cell lines (the neuroblastoma CHP-212, the tubal carcinoma TG, and the colon carcinoma SW-620), gamolenic acid elicited cytotoxic effects in tumours by blocking cell proliferation following incorporation into malignant cells . In both clinical and animal studies of breast cancer, gamolenic acid, in combination with tamoxifen, down-regulated the expression of estrogen receptors .
Skin disorders: In an open study of patients with atopic dermatitis, which is a disorder related to a deficiency of delta-6-desaturase and inefficient conversion of linoleic acid to gamolenic acid, daily administration of gamolenic acid was associated with a significant increase in plasma GLA and DGLA levels in combination with an improvement of clinical signs of atopic dermatitis .
Respiratory disorders: In patients with acute lung injury or acute respiratory distress syndrome, gamolenic acid was shown to reduce cytokine production and neutrophil recruitment into the lung . In patients with atopic asthma, gamolenic acid blocked ex vivo synthesis of leukotrienes from whole blood and isolated neutrophils compared to the placebo group .
Metabolism
Via elongation mediated by elongase (ELOVL5), gamolenic acid is rapidly converted to dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid (DGLA), which is further cyclooxygenated to prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) via COX-1 or COX-2 enzymatic activity depending on the cell type . PGE1 may be metabolized to smaller prostaglandin remnants, primarily dicarboxylic acids, which undergo renal excretion . DGLA may be converted to 15-(S)-hydroxy-8,11,13-eicosatrienoic acid (15-HETrE) by 15-lipoxygenase enzyme .
Although the enzymatic pathway is less predominant relative to ELOVL5 in most cells, DGLA may also be converted to arachidonic acid (AA) via delta-5-desaturate activity , where hydrogen atoms are selectively removed to create new double bonds F27]. Arachidonic acid is a precursor in the biosynthesis of prostaglandin E2, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes, which are potent inflammatory mediators and play an important role in inflammatory pathways.
References
[1] yagaloff k a, franco l, simko b, et al. essential fatty acids are antagonists of the leukotriene b4 receptor[j]. prostaglandins, leukotrienes and essential fatty acids, 1995, 52(5): 293-297.
[2] crooks s w, stockley r a. leukotriene b4[j]. the international journal of biochemistry & cell biology, 1998, 30(2): 173-178.
[3] tasset-cuevas i, fernández-bedmar z, lozano-baena m d, et al. protective effect of borage seed oil and gamma linolenic acid on dna: in vivo and in vitro studies[j]. plos one, 2013, 8(2): e56986.
[4] jamal g a, carmichael h. the effect of γ‐linolenic acid on human diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial[j]. diabetic medicine, 1990, 7(4): 319-323.
[5] andreassi m, forleo p, dilohjo a, et al. efficacy of γ-linolenic acid in the treatment of patients with atopic dermatitis[j]. journal of international medical research, 1997, 25(5): 266-274.
Properties of gamma-Linolenic acid
| Melting point: | -12~-11℃ |
| Boiling point: | 379.5±11.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 0.92 |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 110 °C |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | liquid |
| pka | 4.74±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | Colourless |
| Merck | 14,5507 |
| BRN | 1712253 |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 506-26-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Gamolenic acid(506-26-3) |
Safety information for gamma-Linolenic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for gamma-Linolenic acid
| InChIKey | VZCCETWTMQHEPK-QNEBEIHSSA-N |
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Gamma-linolenic acid 95% CAS 506-26-3View Details
Gamma-linolenic acid 95% CAS 506-26-3View Details
506-26-3 -
 γ-Linolenic Acid CAS 506-26-3View Details
γ-Linolenic Acid CAS 506-26-3View Details
506-26-3 -
 gamma-Linolenic acid 95.00% CAS 506-26-3View Details
gamma-Linolenic acid 95.00% CAS 506-26-3View Details
506-26-3 -
 γ-Linolenic acid CAS 506-26-3View Details
γ-Linolenic acid CAS 506-26-3View Details
506-26-3 -
 γ-Linolenic acid CAS 506-26-3View Details
γ-Linolenic acid CAS 506-26-3View Details
506-26-3 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0