Fosinopril
- CAS NO.:98048-97-6
- Empirical Formula: C30H46NO7P
- Molecular Weight: 563.66
- MDL number: MFCD21091258
- EINECS: 1806241-263-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-04-26 16:55:04
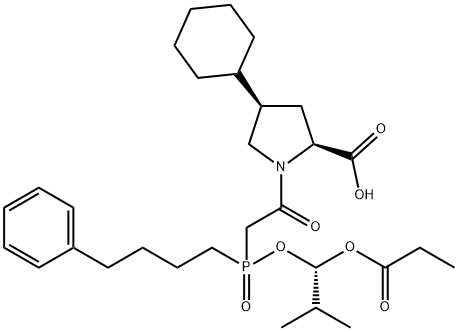
What is Fosinopril?
Absorption
Average absolute absorption is 36%. The primary site of absorption is the proximal small intestine (duodenum/jejunum). Food slows the rate of absorption with no effect on the extent of absorption.
Toxicity
Human overdoses of fosinopril have not been reported, but the most common manifestation of human fosinopril overdosage is likely to be hypotension. Oral doses of fosinopril at 2600 mg/kg in rats were associated with significant lethality. The most common adverse effects include dizzines, cough, fatigue, and headache.
Originator
Fosinopril Sodium,Bristol-Myers Squibb
The Uses of Fosinopril
mydriatic,
Background
Fosinopril is a phosphinic acid-containing ester prodrug that belongs to the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor class of medications. It is rapidly hydrolyzed to fosinoprilat, its principle active metabolite. Fosinoprilat inhibits ACE, the enzyme responsible for the conversion of angiotensin I (ATI) to angiotensin II (ATII). ATII regulates blood pressure and is a key component of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). Fosinopril may be used to treat mild to moderate hypertension, as an adjunct in the treatment of congestive heart failure, and to slow the rate of progression of renal disease in hypertensive individuals with diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria or overt nephropathy.
Indications
For treating mild to moderate hypertension, use as an adjunct in treating congestive heart failure, and may be used to slow the rate of progression of renal disease in hypertensive individuals with diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria or overt nephropathy.
Definition
ChEBI: A phosphinate ester-containing N-acyl derivative of (4S)-cyclohexyl-L-proline. It is used for the treatment of hypertension and heart failure. A pro-drug, it is hydrolysed in vivo to the corresponding phosphin nc acid, fosinoprilat, which is the active metabolite.
Manufacturing Process
To a solution of 4-phenylbutyl phosphinic acid (2.0 g, 0.01 mole) in
chloroform (40 ml) was added triethylamine (3.2 ml, 0.022 mole) and the
mixture was cooled in an ice bath to 0°C. Trimethylsilyl chloride (2.8 ml,
0.022 mole) was added to the above solution dropwise, followed by benzyl
bromoacetate (1.6 ml, 0.011 mole). The ice bath was removed and the
mixture stirred at room temperature for 5 hours and poured into 10%
aqueous HCl (30 ml) and crushed ice (20 g). After shaking the mixture in a
separatory funnel, the chloroform layer was separated and the aqueous layer
was extracted with dichloromethane. The combined organic phase was washed
with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and the solvents removed in
vacuum. The resulting crude thick oil (3.5 g) was dissolved in 30 ml ether,
hexane was added dropwise to get a turbid solution and the mixture was left
at room temperature overnight to complete the crystallization. It was cooled
in the freezer for 2 hours, filtered and the solid was washed very thoroughly
with hexane (50 ml), ether (50 ml) and again hexane (50 ml), ether (50 ml)
in that order. The solid was vacuum dried to get 2.48 g (71%) of [hydroxy-(4-phenylbutyl)-phosphinyl]acetic acid, phenylmethyl ester, m.p. 68-70°C. TLC
(Silica gel, CH2Cl2:MeOH:HOAc (20:1:1)) shows a single spot.
A solution of 50 g (0.14 mole) of [hydroxy-(4-phenylbutyl)-phosphinyl]acetic
acid, phenylmethyl ester in 300 ml of dry CHCl3 was treated with 28.6 g (0.28
mole) of Et3N, 35.6 g (0.21 mole) of 1-chloroisobutyl propionate, 12.0 g
(0.035 mole) of (n-Bu)4NHSO4 and 5.3 g (0.035 mole) of NaI. The above
mixture was stirred and heated to mild reflux for 20 hours, then cooled and
the solvent evaporated in vacuo. The oil residue was dissolved in 150 ml of
ether and washed with 150 ml of water. The aqueous wash was extracted with
150 ml of ether. The combined ether solutions were washed with 5% NaHCO3,
10% NaHSO3 and brine. After drying (MgSO4) the ether was evaporated in
vacuo to give 57.0 g (83%) of crude [[2-methyl-1-(1-oxopropoxy)propoxy](4-
phenylbutyl)phosphinyl]acetic acid, phenyl methyl ester as an oil product.
A solution of 57.0 g (0.12 mole) of [[2-methyl-1-(1-oxopropoxy)propoxy](4-
phenylbutyl)phosphinyl]acetic acid, phenyl methyl ester in 300 ml of ethyl
acetate was treated with 3.0 g of 10% Pd/C and hydrogenated on the Parr
apparatus (45 psi) for 4 hours. The mixture was filtered through Hyflo and the
solution was extracted with 5% NaHCO3. The aqueous extracts were washed
with ether, cooled to 5°C and treated with 36 ml of HOAc. The product was
extracted into ethyl acetate, dried (MgSO4) and the solvent was evaporated in
vacuo. The residue was dissolved in 300 ml of toluene and the solvent was
evaporated in vacuo to remove last traces of acetic acid. The oil residue
became semi-solid on standing at room temperature. The yield of the product
of debenzoylation - 2-[carboxymethyl)-(4-phenylbutyl)-phosphinoyloxy]-2-
methylpropionic acid ethyl ester (racemic mixtures) was 39.8 g (72%).
A suspension of 10.0 g (0.026 mole) of [[2-methyl-1-(1-oxopropoxy)propoxy]
(4-phenylbutyl)phosphinyl]acetic acid in 50 ml of isopropyl ether was stirred
vigorously for 15 min, then kept at 5°C for 20 hours. The colorless product
was filtered, washed with a small amount of cold isopropyl ether to give 5.0 g
of [[2-methyl-1-(1-oxopropoxy)propoxy](4-phenylbutyl)phosphinyl]acetic acid
(A/B isomer, racemic mixture) , m.p. 87-89°C. The filtrate was evaporated in
vacuo and retained for isolation of isomer C/D. A solution of the above
material in 110 ml of hot isopropyl ether was filtered through a hot glass
funnel (glass wool). The cooled solution gave 4.6 g (92%) of desired product,
m.p. 90-92°C.
To a vigorously stirred suspension of 980 g (3.33 mol) of l-cinchonidine in 6 L
of ethyl acetate maintained at 45°C was gradually added 1275.5 g (3.33 mol)
of A/B isomer mixture and stirring then continued for an additional 2.5 hours
while the resulting suspension of salt was gradually heated to 70°C when
complete solution was obtained. After filtration (Hyflo) from a small amount of
insoluble material, the solution was seeded and cooled. The crystalline product
which separated was then filtered, washed with 1200 ml of 1:1 ethyl
acetate/isopropyl ether, and dried in vacuo to give 1897.2 g of cinchonidine
salt enriched in the B-isomer, m.p. 106-109°C, [α]D = -59.3° (c = 1,
methanol). This material was combined with 136.8 g of similarly prepared
material (from 0.412 mol of A/B isomer) and the total quantity (2014 g)
recrystallized from 10.18 L of boiling ethyl acetate to afford after filtration,
washing with 1500 ml of the same solvent mixture used before, and drying in
vacuo 1162 g (92%) of [[2-methyl-1-(1-oxopropoxy)propoxy](4-phenylbutyl) phosphinyl]acetic acid (Resolution; isomer B), cinchonidine salt (1:1), m.p.
120-122°C (dec.), [α]D= -45° (c = 1, methanol), [α]365 = -185.5° (c = 1,
methanol). A sample (10 g) was recrystallized twice from acetonitirle and
three times from ethyl acetate additionally to give salt of m.p. 125-126°C
(dec.), [α]D= -42.2°.
A slurry of methyl-1-(1-oxopropoxy)propoxy](4-phenylbutyl)phosphinyl]acetic
acid (B-isomer), dried in vacuo at room temperature for 72 hours, (230.4 g,
0.6 moles) and hydroxybenzotriazole hydrate, dried, in vacuo at 80°C for 24
hours, (101.1 g, 0.66 mole) dichloromethane (sieved dried) (6 L) was chilled
in an ice/acetone bath and treated with N,N-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (136 g,
0.66 mole). The mixture was warmed to room temperature and stirred for 3
hours. The mixture was then chilled in ice/acetone and treated with (trans)-4-
cyclohexyl-L-proline, hydrochloride (154.2 g, 0.66 mole) followed by
diisopropylethylamine (170.7 g, 1.32 mole). The reaction mixture was stirred
at room temperature for 18 hours. The mixture was then chilled, treated with
water (1 L) and concentrated in vacuo to remove dichloromethane. The
residue was diluted with ether (3600 ml) and water (3600 ml) and filtered.
The filtrate was brought to pH = 1.8 with 10% hydrochloric acid. The ether
layer was separated and the aqueous layer washed with ethyl acetate (3 x 2
L). The combined organic layers were washed with 5% KHSO4 (3 x 1 L), water
(3 x 1 L) and brine (1 L), dried over magnesium sulfate and concentrated in
vacuo to yield 398.9 g of crude [R,1S,4S]-4-Cyclohexyl-1-[[[2-methyl-1-(1-
oxopropoxy)propoxy](4-phenylbutyl)phosphinyl]acetyl]-L-proline, monosodium
salt (isomer B). The crude product was dissolved in acetone (4393 ml),
treated with a solution of 2-ethyl hexanoic acid, sodium salt (117.3 g) in
acetone (1468 ml), then stirred at room temperature overnight. The resultant
precipitate was collected by filtration, washed with acetone (3 x 400 ml) and
hexane (1 L) then dried in vacuo. Yield 277 g, m.p. 195-196°C, [α]D= -5.1°
(MeOH, c = 2), HI = 99.8%. Isomer "A" was not detectable.
brand name
Monopril (Bristol-Myers Squibb).
Therapeutic Function
Antihypertensive
Pharmacokinetics
Following oral administration, fosinopril is rapidly and completely hydrolyzed to its principle active metabolite, fosinoprilat. Hydrolysis is thought to occur in the gastrointestinal mucosa and liver. Fosinoprilat is a competitive inhibitor of ACE, a peptidyl dipeptidase that is part of the RAAS. The RAAS is a homeostatic mechanism for regulating hemodynamics, water and electrolyte balance. During sympathetic stimulation or when renal blood pressure or blood flow is reduced, renin is released from the granular cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatus in the kidneys. In the blood stream, renin cleaves circulating angiotensinogen to ATI, which is subsequently cleaved to ATII by ACE. ATII increases blood pressure using a number of mechanisms. First, it stimulates the secretion of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex. Aldosterone travels to the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and collecting tubule of nephrons where it increases sodium and water reabsorption by increasing the number of sodium channels and sodium-potassium ATPases on cell membranes. Second, ATII stimulates the secretion of vasopressin (also known as antidiuretic hormone or ADH) from the posterior pituitary gland. ADH stimulates further water reabsorption from the kidneys via insertion of aquaporin-2 channels on the apical surface of cells of the DCT and collecting tubules. Third, ATII increases blood pressure through direct arterial vasoconstriction. Stimulation of the Type 1 ATII receptor on vascular smooth muscle cells leads to a cascade of events resulting in myocyte contraction and vasoconstriction. In addition to these major effects, ATII induces the thirst response via stimulation of hypothalamic neurons. ACE inhibitors inhibit the rapid conversion of ATI to ATII and antagonize RAAS-induced increases in blood pressure. ACE (also known as kininase II) is also involved in the enzymatic deactivation of bradykinin, a vasodilator. Inhibiting the deactivation of bradykinin increases bradykinin levels and may further sustain the effects of fosinoprilat by causing increased vasodilation and decreased blood pressure.
Metabolism
Since fosinoprilat is not biotransformed after intravenous administration, fosinopril, not fosinoprilat, appears to be the precursor for the glucuronide and p-hydroxy metabolites.
Properties of Fosinopril
| Melting point: | 149-153°C |
| Boiling point: | 705.7±70.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.173±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 3.38±0.40(Predicted) |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 98048-97-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Fosinopril
Computed Descriptors for Fosinopril
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4