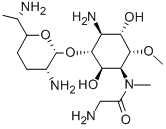
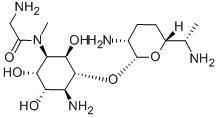
FORTIMICIN
- CAS NO.:55779-06-1
- Empirical Formula: C17H35N5O6
- Molecular Weight: 405.49
- MDL number: MFCD00864879
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2022-12-21 16:56:50
What is FORTIMICIN?
Originator
Fortimicin sulfate,Youngjin Pharma
Definition
ChEBI: An amino cyclitol glycoside that is L-chiro-inositol in which the hydroxy groups at positions 1, 4, and 6 are replaced by aminoacetyl)methylamino, amino, and methoxy groups, respectively, and in which the hydroxy group at posi ion 3 is converted to the corresponding 2,6-diamino-2,3,4,6,7-pentadeoxy-beta-L-lyxo-heptopyranoside. The major component of fortimicin, obtained from Micromonospora olivasterospora. It is adm nistered (as the sulfate salt) by intramuscular injection or intravenous infusion for the treatment of severe systemic infections due to sensitive Gram-negative organisms.
Manufacturing Process
Aminoglycoside antibiotic complex produced by Micromonospora used as a seed strain. One loopful of the seed strain is inoculated into 10 ml
of a seed medium containing 2% glucose, 0.5% peptone, 0.5% yeast extract
and 0.1% calcium carbonate (pH 7.5 before sterilization) in a 50 ml large test
tube. Culturing is carried out at 30°C for 5 days. 10 ml of the seed culture
broth is then inoculated into 30 ml of a second seed medium in a 250 ml
Erlenmeyer flask. The composition of the second seed medium is the same as
that of the first seed medium. The second seed culturing is carried out at
30°C for 2 days with shaking. Then 30 ml of the second seed culture broth is
inoculated into 300 ml of a third seed medium in a 2 L Erlenmeyer flask
provided with baffles. The composition of the third seed medium is the same
as that of the first seed medium. The third seed culturing is carried out at
30°C for 2 days with shaking and 1.5 L of the third seed culture broth
(corresponding to the content of five flasks) is inoculated into 15 L of a fourth
seed medium in a 30 L glass jar fermenter. The composition of the fourth seed
medium is the same as that of the first seed medium. Culturing in the jar
fermenter is carried out at 37°C for 2 days with aeration and stirring
(revolution: 350 r.p.m., aeration: 15 L/min). Thereafter, 15 L of the fourth
seed culture broth is inoculated into 150 L of a main fermentation medium in
a 300 L fermenter. The main fermentation medium comprises 4% soluble
starch, 2% soybean meal, 1% corn steep liquor, 0.05% K2HPO4, 0.05%
MgSO4·7H2O, 0.03% KCl and 0.1% CaCO3 (pH 7.5 before sterilization).
Culturing in the fermenter is carried out at 37°C for 4 days with aeration and
stirring (revolution: 150 r.p.m., aeration: 80 L/min).
After the completion of culturing, the resulting fermentation broth is adjusted
to a pH of 2.5 with concentrated sulfuric acid, and stirred for 30 minutes.
Then, about 7 kg of a filter aid, Radiolite No. 600 (product of Showa Kagaku
Kogyo Co., Ltd., Japan) is added thereto and the microbial cells are removed
by filtration. The filtrate is adjusted to a pH of 7.5 with 6 N sodium hydroxide
and passed through a column packed with about 20 L of a cation exchange
resin, Amberlite IRC-50 (ammonium form), and the effluent is discarded.
Active substances are adsorbed on the resin. After washing the resin with
water, the adsorbed active substances are eluted out with 1 N aqueous
ammonia. Activity of the eluate is determined by a paper disc method, using
an agar plate of Bacillus subtilis No. 10707. The active fractions are collected
and the mixture is concentrated to about 1 L under reduced pressure. The
concentrate is passed through a column packed with 500 ml of an anion
exchange resin, Dowex 1x2 (OH- form). Then, about 2 L of water is passed
through the column, whereby impurities are removed and active substances
are eluted out. The thus obtained active fractions are collected, and
concentrated to about 100 ml under reduced pressure, and the resulting
concentrate is passed through a column packed with about 50 ml of active
carbon powder. The active substances are adsorbed onto the carbon powders.
Then, the column is washed with water and the effluent and the washing
water are discarded. Then, the adsorbed active substances are eluted out with
0.2 N sulfuric acid. Activity of the eluate is determined by the paper disc
method using Bacillus subtilis, and the active fractions are collected. The thus
obtained fractions are passed through a column of Dowex 44 (OH- form), and
active substances are eluted out with water. The active fractions are again
collected and concentrated to about 50 ml. The thus obtained concentrate is
lyophilized, whereby about 32 g of a crude powder containing Fortimicin A is obtained. The crude powder exhibits an activity of 575 unit/mg (the activity of
1 mg of a pure product corresponds to 1000 units).
Then 10 g of the crude powder is placed as a thin and uniform layer on 500
ml of silica gel packed in a glass column. The glass column is prepared by
suspending the silica gel in a solvent of the lower layer of a mixture
comprising chloroform, isopropanol and 17% aqueous ammonia (2:1:1 by
volume), and then packing the suspension tightly in the column as a uniform
layer, and thereafter washing with the same solvent. After placing the crude
powder at the head of the column, elution is carried out with the abovedescribed
solvent by gradually pouring into the column from its top, and
thereafter elution is carried out at a flow rate of about 50 ml/hour. The eluate
is obtained as fractions of 20 ml each, and the activity of each fraction is
determined by a paper disc method. Fortimicin B is eluted out at first.
Thereafter, fractions containing Fortimicin A are obtained. The active fractions
are subjected to paper chromatography, and the fractions containing
Fortimicin A are collected and concentrated under reduced pressure to
completely remove the solvent. The concentrate is then dissolved in a small
amount of water. After freeze-drying the solution, about 1.8 g of purified
preparate of the free base of Fortimicin A is obtained. The activity of the
preparate is about 970 unit/mg. White amorphous powder, MP: >200° (dec.).
[α] D
25 +87.5° (c = 0.1 in water), solves in water and lower alcohols,
insoluble in organic solvents.
Therapeutic Function
Antibiotic
Antimicrobial activity
A pseudodisaccharide aminoglycoside produced by
Micromonospora olivoasterospora. Formulated as the sulfate.
Intrinsic activity is similar to that of amikacin for most
groups of organisms, but activity against Ps. aeruginosa is relatively
poor. It is resistant to many aminoglycoside-modifying
enzymes, but is sensitive to AAC(3) and the APH(2″)/AAC(6′)
bifunctional enzyme.
Peak concentrations of 10–12 mg/L were found in the
blood following 200 mg intravenous or intramuscular administration
to volunteers. The plasma half-life was 1.5–2 h. Over
85% of the drug was recovered in urine during the 8 h following
administration.
Toxicity and side effects are similar to those observed with
other aminoglycosides. Where the drug is available it is used
instead of amikacin in the treatment of infections caused by
susceptible organisms.
Properties of FORTIMICIN
| Melting point: | >200° (dec) |
| Boiling point: | 526.82°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D25 +87.5° (c = 0.1 in water) |
| Density | 1.0897 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.7600 (estimate) |
| pka | 13.16±0.70(Predicted) |
Safety information for FORTIMICIN
Computed Descriptors for FORTIMICIN
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid Electrolytic Iron Powder 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine N-Boc-L-proline methyl ester 2-(BOC-Amino)4-picoline 1-(4-Methylphenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,3-benzotriazole 1-(2-Chlorobenzyl)-4-nitro-1H-pyrazoleRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 181228-33-1 99%View Details
181228-33-1 99%View Details
181228-33-1 -
 Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
1169630-40-3 -
 1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 -
 127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5