Flucloxacillin
- CAS NO.:5250-39-5
- Empirical Formula: C19H17ClFN3O5S
- Molecular Weight: 453.87
- MDL number: MFCD00864886
- EINECS: 226-051-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-15 10:43:31
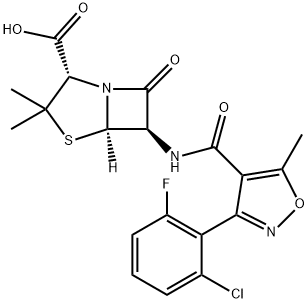
What is Flucloxacillin?
Absorption
Bioavailability is 50–70% following oral administration.
Description
Chemically this is 3(2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolyl penicillin; this differs from dicloxacillin only by the substitution of a fluorine for a chlorine atom (Sutherland et al., 1970). It comes as oral capsules of 250 and 500 mg, as a suspension of 25 and 50 mg/ml, and in an injectable formulation of 500 mg and 1 g.
Originator
Floxapen,Beecham,UK,1970
The Uses of Flucloxacillin
Antibacterial.
Indications
Used to treat bacterial infection by susceptible microorganisms.
Background
Antibiotic analog of cloxacillin.
Definition
ChEBI: A penicillin compound having a 6beta-[3-(2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazole-4-carboxamido] side-chain.
Manufacturing Process
3-(2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-carboxylicacid, MP 206° to
207°C, was obtained by chlorinating 2-chloro-6-fluorobenzaldoxime, then
condensing the resulting hydroxamoyl chloride with methyl acetoacetate in
methanolic sodium methoxide and hydrolyzing the resulting ester with hot
alkali. The acid chloride resulted from treatment of the acid with thionyl
chloride
A suspension of 6-aminopenicillanic acid (36.4 grams) in water was adjusted
to pH 7.2 by the addition of N aqueous sodium hydroxide and the resulting
solution was treated with a solution of 3-(2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl)-5-
methylisoxazole-4-carbonyl chloride (46.1 grams) in isobutyl methyl ketone.
The mixture was stirred vigorously for 1? hours and then filtered through Dicalite. The layers were separated and the isobutyl methyl ketone layer was
shaken with saturated brine. Then, precipitation of the sodium salt only took
place after dilution of the mixture with ether. In this way there was obtained
60.7 grams of the penicillin sodium salt having a purity of 88% as determined
by alkalimetric assay.
Therapeutic Function
Antibacterial
Antimicrobial activity
There is complete cross-resistance with other penicillinase-stable penicillins.
General Description
Flucloxacillin was synthesized by Beecham Research Laboratories in 1962 as a penicillinase-stable and orally active semisynthetic penicillin. It shows almost the same activity as dicloxacillin, and it has slightly higher serum and tissue concentrations than dicloxacillin. This drug has been used to treat pyoderma, sepsis, and postoperative infections as well as ear and nose, respiratory tract, and other infections caused by Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, including benzylpenicillin-resistant strains.
Pharmacokinetics
Flucloxacillin is a penicillin beta-lactam antibiotic used in the treatment of bacterial infections caused by susceptible, usually gram-positive, organisms. The name "penicillin" can either refer to several variants of penicillin available, or to the group of antibiotics derived from the penicillins. Flucloxacillin has in vitro activity against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. The bactericidal activity of Flucloxacillin results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis and is mediated through flucloxacillin binding to penicillin binding proteins (PBPs). Flucloxacillin is stable against hydrolysis by a variety of beta-lactamases, including penicillinases, and cephalosporinases and extended spectrum beta-lactamases.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: c. 80%
Cmax 250 mg (oral): 11 mg/L after 0.5–1 h
Plasma half-life: 2 h
Plasma protein binding: 95%
Absorption and distribution
It is well absorbed after oral administration and penetrates rapidly into extravascular exudates. Its high protein binding limits its diffusion, notably into the normal CSF.
Metabolism and excretion
Flucloxacillin is partly metabolized in the liver and about 10% of the plasma concentration is made up of metabolites. It is more slowly eliminated than cloxacillin. Some appears in the bile but about 50–80% of an oral dose is recovered from the urine, about 20% as metabolites.
Clinical Use
Uses are those of group 3 penicillins.
Side Effects
In patients treated by intravenous infusion, about 5% developed phlebitis by the first and 15% by the second day, after which the proportion rose dramatically. Side effects are otherwise those common to penicillins.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Reduces excretion of methotrexate.
Metabolism
Hepatic.
Metabolism
In normal subjects approximately 10% of the flucloxacillin administered is metabolised to penicilloic acid. Excretion occurs mainly through the kidney. Between 65.5% (oral route) and 76.1% (parenteral route) of the dose administered is recovered in unaltered active form in the urine within 8 hours. A small portion of the dose administered is excreted in the bile.
Properties of Flucloxacillin
| Boiling point: | 677.3±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.59±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| solubility | soluble in Methanol, Water |
| pka | pKa 2.7 (Uncertain) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 5250-39-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Flucloxacillin
Computed Descriptors for Flucloxacillin
Flucloxacillin manufacturer
PROTECH TELELINKS
Medec Dragon Private Limited
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 5250-39-5 Flucloxacillin 98%View Details
5250-39-5 Flucloxacillin 98%View Details
5250-39-5 -
 5250-39-5 99%View Details
5250-39-5 99%View Details
5250-39-5 -
 5250-39-5 98%View Details
5250-39-5 98%View Details
5250-39-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1