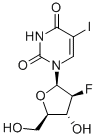
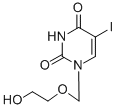
Fialuridine
Synonym(s):1-(2-Deoxy-2-fluoro-β-D-arabinofuranosyl)-5-iodo-2,4(1H,3H)-Pyrimidinedione;FIAU
- CAS NO.:69123-98-4
- Empirical Formula: C9H10FIN2O5
- Molecular Weight: 372.09
- MDL number: MFCD00866922
- EINECS: 1312995-182-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
What is Fialuridine?
Description
Fialuridine (FIAU) is one of a series of 2'-fluoro-substituted arabinosyl pyrimidine nucleosides that have demonstrated potent antiviral activities against a number of clinically important viruses, including hepatitis B virus (HBV). Analogs of FIAU have been shown to inhibit viral replication in the woodchuck and duck models of HBV infection. Although the mechanism of the anti-HBV activity is not well understood, evidence suggests that the triphosphate analog of FIAU is a potent inhibitor of HBV DNA polymerase activity. During early clinical investigation FIAU showed much promise as an antiHBV drug because it markedly reduced the level of HBV DNA in the serum of patients with chronic hepatitis B. However, clinical trials were terminated after adverse events occurred following oral administration of FIAU (0.1 and 0.25 mg/kg of body weight per day) for more than 2 months. The mechanism of the unexpected delayed toxicity is unresolved.
Chemical properties
Colourless crystals
The Uses of Fialuridine
Fialuridine has been used in the selection of clones.
The Uses of Fialuridine
An antiviral agent; nucleoside analog with antihepatitis B activity
What are the applications of Application
Fialuridine is a nucleoside analog with antiviral and antihepatitis B activity
General Description
Fialuridine (1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-d-arabinofuranosyl)-5-iodouracil, or FIAU) is an antiviral agent. It is a thymidine-based nucleoside analogue.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Fialuridine (1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-d-arabinofuranosyl)-5-iodouracil, or FIAU) and its metabolites blocks DNA polymerase at sites of multiple adjacent analog incorporation, reduces the presence of mtDNA (mitochondrial DNA) and results in mitochondrial structural defects in cultured hepatoblasts. It is considered as an efficient drug against hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.
Clinical Use
Fialuridine, a nucleoside analog designed for the treatment of hepatitis B virus infection, failed in clinical trials due to fatal hepatotoxicity, occuring after 13 weeks of 0.25 mg/kg qd dosing in HBV infected patients. Both in vitro assays as well as preclinical in vivo tests in mice, rats, dogs, and primates could not predict its hepatotoxic potential. Fialuridine toxicity is thought to be mediated by human-specific impaired mitochondrial function after long-term exposure. We used the micropatterned primary hepatocyte coculture model, HepatoPac™, to assess fialuridine-mediated toxicity in vitro. To confirm the human specific toxicity, also rat, dog and monkey HepatoPac™ were exposed to fialuridine.
Another nucleoside analog, sofosbuvir, which is on the market for the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection and shows no signs of hepatotoxicity in the clinic, was used to study whether this approach would be able to distinguish a nucleoside analog with clinical chronic DILI finding from a nucleoside analog without DILI findings.
in vitro
previous in-vitro data showed that 1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl)-5-ethyluracil (feau) had activity against herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 comparable to that of 1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl)-5-methyluracil (fmau), fialuridine (fiau), and acyclovir (acv). the cellular toxicity of feau was found to be much lower than that of fiau. biochemical experiments indicated that feau had similar affinity toward thymidine kinases encoded by hsv 1 and 2 and a much lower affinity for cellular thymidine kinase than thymidine [1].
in vivo
the in-vivo antiviral efficiency of feau was compared with that of fiau and acv by using the herpes encephalitis mode. moreover, acv and feau could significantly increase the number of survivors at doses of 50 and 100 mg/kg per day, respectively, and fiau showed significant activity at 25 mg/kg per day in the animal model [1].
References
[1] mansuri, m. m.,ghazzouli, i.,chen, m.s., et al. 1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-d-arabinofuranosyl)-5-ethyluracil. a highly selective antiherpes simplex agent. journal of medicinal chemistry 30(5), 867-871 (1987).
[2] mckenzie r et al. hepatic failure and lactic acidosis due to fialuridine (fiau), an investigational nucleoside analogue for chronic hepatitis b. n engl j med. 1995 oct 26;333(17):1099-105.
Properties of Fialuridine
| Melting point: | 216-217°C |
| Density | 2.18±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble5mg/mL, clear (warmed) |
| form | powder |
| pka | 7.94±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | white to beige |
| Merck | 14,4069 |
Safety information for Fialuridine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Fialuridine
| InChIKey | IPVFGAYTKQKGBM-BYPJNBLXSA-N |
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![1-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-3-Fluoro-4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-5-methylpyrimidine-2,4-dione](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/69256-17-3.gif)


![2'-FLUORO 2'-DEOXY-5-IODOURACIL-BETA-D-ARABINOFURANOSIDE, [2-14C]-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure4/GIF/CB0757911.gif)
You may like
-
 Fialuridine CAS 69123-98-4View Details
Fialuridine CAS 69123-98-4View Details
69123-98-4 -
 Fialuridine 98.00% CAS 69123-98-4View Details
Fialuridine 98.00% CAS 69123-98-4View Details
69123-98-4 -
 Fialuridine CAS 69123-98-4View Details
Fialuridine CAS 69123-98-4View Details
69123-98-4 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1