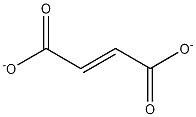
Ferrous fumarate
Synonym(s):Ferrous fumarate;Iron(II) fumarate
- CAS NO.:141-01-5
- Empirical Formula: C4H2FeO4
- Molecular Weight: 169.9
- MDL number: MFCD00058315
- EINECS: 205-447-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-24 14:33:46
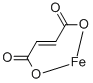
What is Ferrous fumarate?
Absorption
The efficiency of absorption depends on the salt form, the amount administered, the dosing regimen and the size of iron stores. Subjects with normal iron stores absorb 10% to 35% of an iron dose. Those who are iron deficient may absorb up to 95% of an iron dose.
Toxicity
Acute iron overdosage can be divided into four stages. In the first stage, which occurs up to six hours after ingestion, the principal symptoms are vomiting and diarrhea. Other symptoms include hypotension, tachycardia and CNS depression ranging from lethargy to coma. The second phase may occur at 6-24 hours after ingestion and is characterized by a temporary remission. In the third phase, gastrointestinal symptoms recur accompanied by shock, metabolic acidosis, coma, hepatic necrosis and jaundice, hypoglycemia, renal failure and pulmonary edema. The fourth phase may occur several weeks after ingestion and is characterized by gastrointestinal obstruction and liver damage. In a young child, 75 milligrams per kilogram is considered extremely dangerous. A dose of 30 milligrams per kilogram can lead to symptoms of toxicity. Estimates of a lethal dosage range from 180 milligrams per kilogram and upwards. A peak serum iron concentration of five micrograms or more per ml is associated with moderate to severe poisoning in many.
Description
Ferrous fumarate is the ferrous salt form of fumarate. One of its most important applications is being used as iron supplements for the treatment of iron deficiency and anemia. It has been demonstrated that application of ferrous sulfate drops or a single daily dose of microencapsulated ferrous fumarate sprinkles plus ascorbic acid both result in successful treatment of anemia without remarkable side effects. However, recent studies have also shown that compared to other iron supplements, ferrous fumarate has a highest rate of inducing adverse reactions such as erosive mucosal injury in the gastrointestinal tract as well as nausea, vomiting and epigastric discomfort.
Chemical properties
Ferrous fumarate (iron(II)fumarate, C4H2Fe04) is an odorless, reddish-orange to reddish-brown powder. It may contain soft lumps that produce a yellow streak when crushed. It is prepared by admixing hot solutions of ferrous sulfate and sodium fumarate.
Originator
Toleron,Mallinckrodt Inc.,US,1957
The Uses of Ferrous fumarate
Ferrous fumarate is available as a syrup and may be useful in small children for the treatment and prophylaxis of iron deficiency. Iron(II) Fumarate is a a chemical used in the treatment of iron deficiency. More commonly used for this treatment is Ferrous Sulfate however Iron(II) Fumarate does maintain similar absorption profiles.
The Uses of Ferrous fumarate
Ferrous Fumarate is a reddish orange to red-brown powder that is a source of iron. it has high bioavailability and can be used in foods where the red color can be masked. it contains approximately 33% iron. it is used as a dietary supplement in breakfast cereals, poultry stuffing, enriched flour, and instant drinks.
The Uses of Ferrous fumarate
Iron(II) fumarate is used as dietary Supplement, nutrient, iron source in foods and pharmaceuticals, as animal feed additive and in infant formulas.
Indications
Used in preventing and treating iron-deficiency anemia.
Background
Used in treatment of iron deficiency anemia.
Definition
Ferrous fumarate is a dicarboxylic acid. Anhydrous salt of a combination of ferrous iron and fumaric acid, stable, odorless, substantially tasteless. Reddish-brown, anhydrous powder, contains 33% iron by weight, does not melt at temperatures up to 280C, insoluble in alcohol, very slightly solubility. It is used in treatment of iron deficiency anemia.
Manufacturing Process
Sodium carbonate (53.5 pounds of Na2CO3-H2O) was dissolved in water (40 to 45 gallons) and fumaric acid (50 pounds) was added slowly. During the addition the solution was stirred and heated. The resulting solution of sodium fumarate, having a pH of 6.8, was added slowly with mixing to a solution of ferrous sulfate (118 pounds FeSO4-7H2O in 33 gallons of water) having a pH of 3.3, both solutions being maintained at or near boiling temperature during the mixing. The resulting slurry of reddish-brown anhydrous ferrous fumarate was filtered and washed in a centrifuge and dried in a tray drier (15 hours at 110°C). Yield: 63 pounds, 86% of theory. Calculated for FeC4H2O4: Fe, 32.9%. Found: Fe, 32.6%. Only 0.2% of ferric iron (Fe+++) was found.
Therapeutic Function
Hematinic
General Description
Ferrous fumarate is a commonly used inexpensive substitute for other forms of iron, that is employed as a food iron fortificant.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Pharmacokinetics
The major activity of supplemental iron is in the prevention and treatment of iron deficiency anemia. Iron has putative immune-enhancing, anticarcinogenic and cognition-enhancing activities.
Clinical Use
Iron deficiency anaemia
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by ingestion and subcutaneous routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: dyspnea, nausea or vomiting, somnolence. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also FUMRIC ACID.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Antibacterials: reduced absorption of 4-quinolones and tetracyclines. Dimercaprol: avoid concomitant use. Mycophenolate: may significantly reduce absorption of mycophenolate.
Metabolism
Not Available
Metabolism
Following absorption, the majority of iron is bound to transferrin and transported to the bone marrow where it is incorporated into haemoglobin. The remainder is stored within ferritin or haemosiderin or is incorporated into myoglobin with smaller amounts occurring in haemcontaining enzymes or in plasma bound to transferrin. Only very small amounts are excreted as the body reabsorbs the iron after the haemoglobin has broken down.
References
Zlotkin, Stanley, et al. "Treatment of anemia with microencapsulated ferrous fumarate plus ascorbic acid supplied as sprinkles to complementary (weaning) foods." The American journal of clinical nutrition 74.6 (2001): 791-795.Cancelo-Hidalgo, María Jesús, et al. "Tolerability of different oral iron supplements: a systematic review." Current medical research and opinion 29.4 (2013): 291-303.
Properties of Ferrous fumarate
| Melting point: | >280°C |
| Density | 2.435 |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | Slightly soluble in water, very slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). |
| form | solid |
| color | Dark Red to Dark Brown |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water (0.14 g/100 ml at 25°C). |
| Merck | 14,4046 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stability |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 141-01-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Butenedioic acid (2E)-, iron(2+) salt (1:1) (141-01-5) |
Safety information for Ferrous fumarate
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Ferrous fumarate
| InChIKey | PMVSDNDAUGGCCE-TYYBGVCCSA-L |
Ferrous fumarate manufacturer
Shanpar Industries Private Limited
Panchamrut Chemicals
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Ferrous Fumarate 99%View Details
Ferrous Fumarate 99%View Details -
 Ferrous fumarate 98%View Details
Ferrous fumarate 98%View Details -
 Ferrous fumarate 98%View Details
Ferrous fumarate 98%View Details -
 141-01-5 Ferrous fumarate 98%View Details
141-01-5 Ferrous fumarate 98%View Details
141-01-5 -
 Ferrous fumarate CAS 141-01-5View Details
Ferrous fumarate CAS 141-01-5View Details
141-01-5 -
 Ferrous Fumarate IP/EP/BP/USP/FCC, Packaging Type: Bag, Packaging Size: 25 kgView Details
Ferrous Fumarate IP/EP/BP/USP/FCC, Packaging Type: Bag, Packaging Size: 25 kgView Details
141-01-5 -
 Ferrous Fumarate C4H2FeO4, Packaging Type: Hdpe Bag, Packaging Size: 50 kgView Details
Ferrous Fumarate C4H2FeO4, Packaging Type: Hdpe Bag, Packaging Size: 50 kgView Details
141-01-5 -
 Ferrous Fumarate, Packaging Type: Bag, Packaging Size: 25 kgView Details
Ferrous Fumarate, Packaging Type: Bag, Packaging Size: 25 kgView Details
141-01-5
