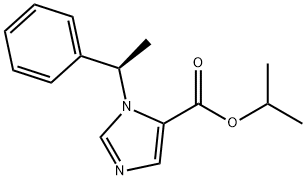
Etomidate
Synonym(s):(R)-1-(α-Methylbenzyl)imidazole-5-carboxylic acid ethyl ester;Amidate;R16659
- CAS NO.:33125-97-2
- Empirical Formula: C14H16N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 244.29
- MDL number: MFCD00869295
- EINECS: 251-385-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
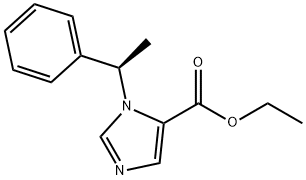
What is Etomidate?
Toxicity
Undesirable side effects of etomidate that may limit its use include pain on injection, myoclonus and adrenocortical suppression lasting 4-6 hours following an induction dose.
Description
Etomidate , ethyl (R)-(+)-1(α- methylbenzyl)-imidazole-5-carboxylate, Mr 224.28, is a white to yellowish crystalline or amorphous powder. It is insoluble in water at pH 7, but soluble in acidic aqueous solutions at pH<3. Etomidate is soluble in propylene glycol and readily soluble in alcohol.
Chemical properties
Etomidate is a white crystalline powder. easily soluble in water, methanol, ethanol and propylene glycol, soluble in chloroform, insoluble in acetone, insoluble in ether. Its effects on the central nervous system is similar to barbiturates.
Originator
Hypnomidate,Janssen,W. Germany,1977
The Uses of Etomidate
Etomidate is a GABAA receptors agonist with short-acting sedative, hypnotic, and general anesthetic properties. It is a unique drug used for induction of general anesthesia and sedation. It is also a hypnotic. Hypnotic effect of Etomidate is strong , and its efficacy is about 12 times higher than thiopental, it has no analgesic effect.
Indications
Used in the induction of general anesthesia.
Background
Imidazole derivative anesthetic and hypnotic with little effect on blood gases, ventilation, or the cardiovascular system. It has been proposed as an induction anesthetic.
What are the applications of Application
Etomidate is a GABAA receptors agonist
Definition
ChEBI: Etomidate is the ethyl ester of 1-[(1R)-1-phenylethyl]-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylic acid. It is an intravenous general anaesthetic with no analgesic activity. It has a role as an intravenous anaesthetic and a sedative. It is a member of imidazoles and an ethyl ester. It derives from a 1-[(1R)-1-phenylethyl]-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylic acid.
Indications
Etomidate is administered intravenously as a short-acting anesthetic for the induction of lengthy anesthesia, especially for the induction of neuroleptanalgesia and inhalation anesthesia . Etomidate produces 3 – 5 min of sleep.
brand name
Amidate (Hospira);Hypnomidate concentrate;Hypnomidate injection;Hypromidate;Nalgol;Sibu.
Therapeutic Function
Hypnotic
World Health Organization (WHO)
Etomidate, a potent hypnotic agent, was introduced in 1977 for use as an intravenous anaesthetic. Its prolonged use can inhibit adrenal steroidogenesis and, following reports of reduced serum cortisol levels unresponsive to ACTH injection, the manufacturer suspended promotion of etomidate for sedation in intensive care in 1983. In 1985 regulatory action taken only in the United Kingdom further restricted use of the drug to induction of anaesthesia. Etomidate remains widely available and is currently registered for induction of anaesthesia in 34 countries and for maintenance of anaesthesia in 17 countries. It has never been registered for sedation.
Biological Functions
The pharmacological properties of etomidate (Amidate) are similar to those of the barbiturates, although its use may provide a greater margin of safety because of its limited effects on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Since it has a relatively short elimination halflife (t1/2β = 2.9 hours), in addition to its use as an induction agent, etomidate has been used as a supplement to maintain anesthesia in some critically ill patients. Etomidate is rapidly hydrolyzed in the liver.
General Description
Etomidate is a carboxylated imidazole intended for the inductionof general anesthesia. It is marketed as the morepotent R (+) isomer. It is believed to exert its anestheticeffect via positive modulation of the GABAA receptor. Itis not water soluble and is available in the United States as a2-mg/mL solution containing 35% v/v propylene glycol andin Europe as a soybean oil and medium-chain triglyceridesformulation. The propylene glycol has been associatedwith moderate-to-severe pain on injection and irritation ofthe vascular tissue. A high incidence of skeletal musclemovements were noted in about 32% of patients followingetomidate injection. Case reports of seizures are also foundin the literature.
Biological Activity
Etomidate is a general anesthetic with GABA modulatory and GABA-mimetic actions; selectively interacts with β 2- and β 3-subunit containing GABAA receptors. Short acting and potent hypnotic, with low toxicity.The possible neuroprotective effect of etomidate against streptozotocin-induced (STZ-induced) hyperglycaemia were investigated in the rat brain and spinal cord. Etomidate treatment demonstrated neuroprotective effect on the neuronal tissue against the diabetic oxidative damage.
Pharmacokinetics
Etomidate is a non-barbiturate hypnotic that acts at the level of the reticular-activating system to produce anesthesia. Etomidate is an imidazole compound that appears to depress CNS function via GABA. Duration of action is intermediate between thiopental and methohexital, and recovery from a single dose is rapid with little residual depression. Like the barbiturates and propofol, etomidate is does not induce analgesia. Etomidate induces unconsciousness within one circulation time. Recovery is rapid as a result of extensive redistribution and rapid metabolism.
Clinical Use
Etomidate should only beused for induction of anesthesia when the cardiac benefitsoutweigh the risks associated with adrenal insufficiency.Etomidate is quickly distributed throughout most organsin the body after intravenous administration and the tissueconcentrations equal and sometimes exceed the plasmaconcentrations. The lipid solubility of the drug allows it torapidly penetrate into the brain with peak concentrationsoccurring within 1 minute of administration. Etomidate israpidly metabolized in the plasma and liver via esterases.About 75% of the drug is eliminated in the urine as the inactiveester hydrolyzed carboxylic acid.
Side Effects
Etomidate may cause pain on injection and may produce myoclonic muscle movements in approximately 40% of patients during its use as an induction anesthetic. In addition, etomidate can suppress the adrenocortical response to stress, an effect that may last up to 10 hours.
Synthesis
The preparation of etomidate involves
a modification of Jones’ synthesis: α-
phenylethylamine is alkylated with ethyl chloroacetate
to the N-(α-phenylethyl)-glycine ester,
whose NH group is formylated. This product
is condensed with methyl formate and cyclized
withHCl-KSCNto yield ethyl 2-mercapto-1-(α-
methylbenzyl)-5-imidazolecarboxylate, which
is then oxidatively desulfurized . The (R)
isomer is obtained by separating the racemic
acid with (R)-(+)-1-phenylethylamine.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Etomidate may be useful as an alternative to thiopental or propofol for anesthetic induction in small animals, particularly in patients with preexisting cardiac dysfunction, head trauma, or that are critically ill.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Adrenergic neurone blockers: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Antidepressants: avoid MAOIs for 2 weeks before surgery; increased risk of arrhythmias and hypotension with tricyclics.
Antipsychotics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Metabolism
Hepatic. Metabolized rapidly by ester hydrolysis to inactive metabolites.
Metabolism
Etomidate is hydrolyzed by hepatic esterases to the corresponding inactive carboxylic acid, with subsequent renal and biliary excretion terminating its action. Its apparent elimination half-life is approximately 5 to 6 hours, with a volume of distribution of 5 to 7 L/kg. Changes in hepatic blood flow or hepatic metabolism will have only moderate effects on etomidate disposition. Concerns regarding the ability of etomidate to precipitate myoclonic jerks and inhibit adrenal steroid synthesis have been reported.
Storage
Room temperature
Mode of action
The exact mechanism of action of etomidate is unknown. It is felt to induce sedation by interaction with GABA receptors. and likely enhances the activity of a-aminobutyric acid. However, it is not structurally related to benzodiazepines or to barbiturates. Of significantnote, etomidate exhibits no analgesic properties.
Properties of Etomidate
| Melting point: | 72-74°C |
| Boiling point: | 160-162 °C(Press: 1 Torr) |
| alpha | D20 +66° (c = 1 in ethanol) |
| Density | 1.11±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: >10 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | pKa 4.24(H2O t=25.0) (Uncertain) |
| color | white |
| Merck | 14,3881 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 33125-97-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Etomidate(33125-97-2) |
Safety information for Etomidate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
Computed Descriptors for Etomidate
Etomidate manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Etomidate 98%View Details
Etomidate 98%View Details
33125-97-2 -
 Etomidate 33125-97-2 98%View Details
Etomidate 33125-97-2 98%View Details
33125-97-2 -
 33125-97-2 Etomidate Reference Standard 98%View Details
33125-97-2 Etomidate Reference Standard 98%View Details
33125-97-2 -
 Etomidate 33125-97-2 95-99%View Details
Etomidate 33125-97-2 95-99%View Details
33125-97-2 -
 Etomidate 95% CAS 33125-97-2View Details
Etomidate 95% CAS 33125-97-2View Details
33125-97-2 -
 Etomidate CAS 33125-97-2View Details
Etomidate CAS 33125-97-2View Details
33125-97-2 -
 Etomidate (CAS 33125-97-2)View Details
Etomidate (CAS 33125-97-2)View Details
33125-97-2 -
 Etomidate Powder, Cas 33125-97-2, USPView Details
Etomidate Powder, Cas 33125-97-2, USPView Details
33125-97-2
