Etodolac
Synonym(s):1,8-Diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano[3,4-b]indole-1-acetic acid;Etodolic acid;NSC 282126
- CAS NO.:41340-25-4
- Empirical Formula: C17H21NO3
- Molecular Weight: 287.35
- MDL number: MFCD00133313
- EINECS: 629-689-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
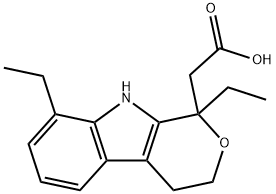
What is Etodolac?
Absorption
Based on mass balance studies, the systemic bioavailability of etodolac from either the tablet or capsule formulation is at least 80%.
Toxicity
Selective COX-2 inhibitors have been associated with increased risk of serious cardiovascular events (e.g. myocardial infarction, stroke) in some patients. Current data is insufficient to assess the cardiovascular risk of etodolac. Etodolac may increase blood pressure and/or cause fluid retention and edema. Risk of GI toxicity including bleeding, ulceration and perforation. Risk of direct renal injury, including renal papillary necrosis. Anaphylactoid and serious skin reactions (e.g. exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis) have been reported. Common adverse events include abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, GI bleeding, GI perforation, nausea, peptic ulcer, vomiting, renal function abnormalities, anemia, dizziness, edema, liver function test abnormalities, headache, prolonged bleeding time, pruritus, rash, tinnitus. Symptoms of overdose include lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain.
Description
Etodolac (etodolic acid) is a non-steroidal antiinflammatory/analgesic agent useful in the treatment of various inflammatory conditions, including rheumatoid and osteoarthritis.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Originator
Ayerst (USA)
The Uses of Etodolac
Etodolac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that selectively inhibits cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). Etodolac displays anti-inflammatory effects in both adjuvant arthritic and normal rats. E todolac is an anti-inflammatory; analgesic.
The Uses of Etodolac
Etodolac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Product Data Sheet
The Uses of Etodolac
betaadrenergic agonist
The Uses of Etodolac
For acute and long-term management of signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, as well as for the management of pain.
Background
Etodolac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic properties. Its therapeutic effects are due to its ability to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis. It is indicated for relief of signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
Indications
For acute and long-term management of signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, as well as for the management of pain.
What are the applications of Application
Etodolac is a Cox-2 inhibitor with anti-inflammatory activity
Definition
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid that is acetic acid in which one of the methyl hydrogens is substituted by a 1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano[3,4-b]indol-1-yl moiety. A preferential inhibitor of cyclo-oxygenase 2 and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, it is used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, and for the alleviation of postoperative pain. Administered as the racemate, only the (S)-enantiomer is active.
Indications
Etodolac (Lodine) is indicated for the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and acute pain. It inhibits COX-2 with slightly more selectivity than COX-1 and therefore produces less GI toxicity than many other NSAIDs. Common adverse effects include skin rashes and CNS effects.
brand name
Lodine(Wyeth).
General Description
Etodolac (Lodine, Ultradol), a chiral, COX-2 selectiveNSAID drug that is marketed as a racemate, possesses an indolering as the aryl portion of this group of NSAID drugs.It shares many similar properties of this group and is indicatedfor short- and long-term management of pain and OA.
Similar to ketorolac, etodolac exhibits several uniqueenantioselective pharmacokinetic properties. For example,the “inactive” (R)-enantiomer has approximately a 10-foldhigher plasma concentration than the active (S)-enantiomer.Furthermore, the active (S)-enantiomer is less protein boundthan its (R)-enantiomer and therefore has a very large volumeof distribution. It is well absorbed with an elimination halflifeof 6 to 8 hours. Etodolac is extensively metabolized intothree major inactive metabolites, 6-hydroxy etodolac (via aromatichydroxylation), 7-hydroxy-etodolac (via aromatic hydroxylation),and 8-(1'-hydroxylethyl) etodolac (via benzylichydroxylation), which are eliminated as the correspondingether glucuronides. Its unstable, acyl glucuronide, however,is subject to enterohepatic circulation and reactivation tothe parent drug, similar to other NSAIDS in this class.
Biological Activity
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that selectively inhibits cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) (IC 50 values are 53 and >100 μ M for COX-2 and COX-1 respectively). Displays anti-inflammatory effects in both adjuvant arthritic and normal rats.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory compound that is a non-selective inhibitor of COX-1 and COX-2.
Mechanism of action
The primary mechanism of action appears to be inhibition of the biosynthesis of prostaglandins at the cyclooxygenase step, with no inhibition of the lipoxygenase system. Etodolac, however, possesses a more favorable ratio of inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis in human rheumatoid synoviocytes and chondrocytes than by cultured human gastric mucosal cells compared to ibuprofen, indomethacin, naproxen, diclofenac, and piroxicam.
Pharmacokinetics
Etodolac is an anti-inflammatory agent with analgesic and antipyretic properties. It is used to treat osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and control acute pain. The therapeutic effects of etodolac are achieved via inhibition of the synthesis of prostaglandins involved in fever, pain, swelling and inflammation. Etodolac is administered as a racemate. As with other NSAIDs, the S-form has been shown to be active while the R-form is inactive. Both enantiomers are stable and there is no evidence of R- to S- conversion in vivo.
Pharmacokinetics
Etodolac is rapidly absorbed following oral administration, with maximum serum levels being achieved within 1 to 2 hours, and it is highly bound to plasma proteins (99%) with pKa 4.7. The penetration of etodolac into synovial fluid is greater than or equal to that of tolmetin, piroxicam, or ibuprofen. Only diclofenac appears to provide greater penetration.
Clinical Use
Etodolac is promoted as the first of a new chemical class of anti-inflammatory drugs, the pyranocarboxylic acids. Although not strictly an arylacetic acid derivative (because there is a two-carbon atom separation between the carboxylic acid function and the hetero-aromatic ring), it still possesses structural characteristics similar to those of the heteroarylacetic acids and is classified here. It was introduced in the United States in 1991 for acute and long-term use in the management of osteoarthritis and as an analgetic. It also possesses antipyretic activity. Etodolac is marketed as a racemic mixture, although only the S-(+)-enantiomer possesses anti-inflammatory activity in animal models. Etodolac also displays a high degree of enantioselectivity in its inhibitory effects on the arachidonic acid cyclooxygenase system.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Etodolac is labeled for the management of pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis in dogs. It may find uses, however, for a variety of conditions where pain and/or inflammation should be treated.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-II antagonists: antagonism of hypotensive effect, increased risk of nephrotoxicity and hyperkalaemiaAnalgesics: avoid concomitant use of 2 or more NSAIDs, including aspirin (increased side effects); avoid with ketorolac, increased risk of side effects and haemorrhage.Antibacterials: possibly increased risk of convulsions with quinolones.Anticoagulants: effects of coumarins and phenindione enhanced; possibly increased risk of bleeding with heparin, dabigatran and edoxaban - avoid long term use with edoxaban.Antidepressants: increased risk of bleeding with SSRIs and venlafaxine.Antidiabetic agents: effects of sulphonylureas enhanced.Antiepileptics: possibly increased phenytoin concentration.Antivirals: increased risk of haematological toxicity with zidovudine; concentration possibly increased by ritonavirCiclosporin: may potentiate nephrotoxicityCytotoxic agents: reduced excretion of methotrexate; increased risk of bleeding with erlotinib.Diuretics: increased risk of nephrotoxicity; antagonism of diuretic effect; hyperkalaemia with potassium-sparing diuretics.Lithium: excretion decreased.Pentoxifylline: increased risk of bleedingTacrolimus: increased risk of nephrotoxicity.
Metabolism
Etodolac is extensively metabolized in the liver. Renal elimination of etodolac and its metabolites is the primary route of excretion (72%). Metabolites found in urine (with percents of the administered dose) are: unchanged etodolac (1%), etodolac glucuronide (13%), hydroxylated metabolites (6-, 7-, and 8-OH; 5%), hydroxylated metabolite glucuronides (20%), and unidentified metabolites (33%). Fecal excretion accounts for 16% of its elimination.
Metabolism
Etodolac is metabolized to three hydroxylated metabolites and to glucuronide conjugates, none of which possesses important pharmacological activity. Metabolism appears to be the same in the elderly as in the general population, so no dosage adjustment appears necessary. Etodolac is indicated for the management of the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis and for the management of pain.
References
[1] kumagai k1, kubo m, imai s, toyoda f, maeda t, okumura n, matsuura h, matsusue y.the cox-2 selective blocker etodolac inhibits tnfα-induced apoptosis in isolated rabbit articular chondrocytes. int j mol sci. 2013 sep 30;14(10):19705-15.
[2] hakozaki m1, hojo h, kikuchi s, abe m. etodolac, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, induces apoptosis by activating caspases in human malignant rhabdoid tumor cells (frtk-1). oncol rep. 2007 jan;17(1):169-73.
Properties of Etodolac
| Melting point: | 145-1480C |
| Boiling point: | 507.9±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.193±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in acetone and in ethanol (96 per cent) |
| form | neat |
| pka | 4.65(at 25℃) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Orange to Green |
| Water Solubility | 40mg/L(37 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,3874 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 41340-25-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Pyrano[3,4-b]indole-1-acetic acid, 1,8-diethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro- (41340-25-4) |
Safety information for Etodolac
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Etodolac
| InChIKey | NNYBQONXHNTVIJ-QGZVFWFLSA-N |
Etodolac manufacturer
Synaptics Labs Private Limited
Sam Fine O Chem Limited
Shamrock Medicaments Ltd.
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

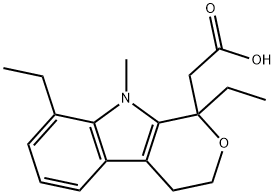
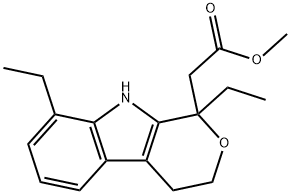
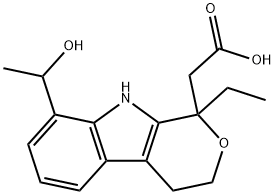

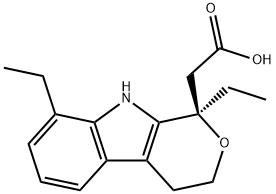
![ETODOLAC RELATED COMPOUND A (25 MG) ((+/-)-8-ETHYL-1-METHYL-1,3,4,9-TETRAHYDROPYRANO [3,4-B]-INDOLE-1-ACETIC ACID)](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/109518-50-5.gif)
You may like
-
 lodine 99%View Details
lodine 99%View Details -
 ETODOLAC 98%View Details
ETODOLAC 98%View Details -
 41340-25-4 98%View Details
41340-25-4 98%View Details
41340-25-4 -
 41340-25-4 Etodolac 98%View Details
41340-25-4 Etodolac 98%View Details
41340-25-4 -
 41340-25-4 98%View Details
41340-25-4 98%View Details
41340-25-4 -
 41340-25-4 Etodolac 99%View Details
41340-25-4 Etodolac 99%View Details
41340-25-4 -
 Etodolac 98% CAS 41340-25-4View Details
Etodolac 98% CAS 41340-25-4View Details
41340-25-4 -
 Etodolac CAS 41340-25-4View Details
Etodolac CAS 41340-25-4View Details
41340-25-4