EC 3.4.15.1
Synonym(s):ACE;Peptidyl-dipeptidase A;Peptidyldipeptide Hydrolase
- CAS NO.:9015-82-1
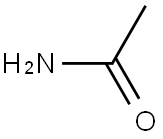
- Empirical Formula: C2H5NO
- Molecular Weight: 59.0672
- MDL number: MFCD00130325
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-23 13:36:13
What is EC 3.4.15.1?
Description
ACE possesses dual actions to convert Ang I to Ang II, and degrade bradykinin. The development of an ACE inhibitor was the first effective drug for hypertension caused by high renin activity. ACE2 was identified as the receptor for the SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) coronavirus, which caused an epidemic in 2002–2003. ACE was discovered in the mid-1950s through the observation that the dialysis of plasma and kidney extract with water and saline before incubation produced two separate pressor substances, Ang I and Ang II, respectively. It was discovered for a second time in 1966 during the characterization of a bradykinin (BK)-degrading enzyme from the kidney. This was named kininase II, which later was found to be the same enzyme as ACE. ACE2 was discovered in 2000 when two independent research groups cloned homologous ACE that could convert Ang I to Ang1–9 and yet also be captopril-insensitive.
The Uses of EC 3.4.15.1
Angiotensin converting enzyme from rabbit lung has been used:
- for measuring inhibitory effect of egg white protein hydrolysates on ACE activity by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
- to measure the ACE inhibition by litchi pericarp and cooked chicken breast using hippuryl-L-histidyl-L-leucine (HHL) as substrate by reverse phase-HPLC (RP-HPLC)3 and HPLC respectively
- in releasing GPI anchored protein in vitro in few cell lines like HeLa, HEK293 and in vivo in mice sperm.
General Description
The angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) is a dipeptidyl-carboxypeptidase which exists in somatic and testicular isoforms with zinc binding motif HEXXH in their active site. ACE regulates blood pressure through renin-angiotensin system. ACE elevates blood pressure by converting angiotensin I to a key vasoconstrictor angiotensin II and inhibiting a potent vasodilator bradykinin. Inhibition of ACE is a targeted therapeutic strategy for high blood pressure. Several ACE synthetic inhibitory peptides available for clinical use include captopril, enalapril and lisinopril. Currently, developing inhibitory peptides from natural food sources, or phenolic compounds from plant sources to inhibit ACE is underway. ACE plays a critical role in fertilization by releasing the proteins anchored to glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) in sperm membrane.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Removes C-terminal dipeptides from susceptible substrates, e.g., angiotensin I and bradykinin.
Clinical Use
ACE has been the target of hypertension control since the 1970s. ACE inhibitors are prescribed as the sole or combinational treatment for high blood pressure, for its dual effects of lowering Ang II and slowing down BK degradation. In human hypertensive patients, ACE2 levels are lower in both the kidney and heart compared to normotensive volunteers.
Purification Methods
Purify ACE by fractionation on DEAE-cellulose, Ca phosphate gel chromatography, elution from Sephadex G-200 and lectin affinity chromatography. The MW varied with glycosidation and is higher by gel filtration. It contains one atom of Zn/mol and has Km values for hydrolysis of hippurylhistidinylleucine and angiotensin I of 2.3 and 0.07 mM, and turnover of 15,430 and 792 mol/min/mol at 37o, respectively. The activity is inhibited by EDTA and increased amounts of Ca ions but required Ca ions. [Das & Soffer J Biol Chem 250 6762 1975, Reviewed by Ehlers & Riordan Biochemistry 28 5311 1989.]
Properties of EC 3.4.15.1
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| form | lyophilized powder |
| color | Off-white to light yellow |
Safety information for EC 3.4.15.1
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H334:Sensitisation, respiratory |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P284:Wear respiratory protection. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for EC 3.4.15.1
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Angiotensin Converting Enzyme from porcine kidney CAS 9015-82-1View Details
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme from porcine kidney CAS 9015-82-1View Details
9015-82-1 -
 Angiotensin Converting Enzyme from rabbit lung CAS 9015-82-1View Details
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme from rabbit lung CAS 9015-82-1View Details
9015-82-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1