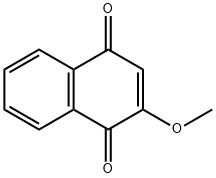
DMNQ
Synonym(s):DMNQ
- CAS NO.:6956-96-3
- Empirical Formula: C12H10O4
- Molecular Weight: 218.21
- MDL number: MFCD00184331
- EINECS: 604-604-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
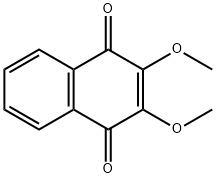
What is DMNQ?
Description
DMNQ is a 1,4-naphthoquinone that acts as a redox-cycling agent, typically increasing intracellular superoxide and hydrogen peroxide formation. The amount of oxidative stress is proportional to the amount of DMNQ applied and can alter diverse cellular parameters, including signal transduction, mitochondrial function, and gene expression.
The Uses of DMNQ
DMNQ is a non-alkylating redox cycling quinone.
The Uses of DMNQ
2,3-Dimethoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone has been used to investigate the effects of ethanol on podocyte apoptosis under hypoxic and hyperoxic conditions.
What are the applications of Application
DMNQ is a non-alkylating redox cycling quinone
Definition
ChEBI: A naphthoquinone that is 1,4-naphthoquinone bearing two methoxy substituents at positions 2 and 3. Redox-cycling agent that induces intracellular superoxide anion formation and, depending on the concentration, induces cell proliferation, apoptosis or necro is. Used to study the role of ROS in cell toxicity, apoptosis, and necrosis.
Biochem/physiol Actions
2,3-dimethoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (DMNQ) has the ability to produce H2O2?through redox cycling but fails to conjugate with glutathione (GSH).
storage
+4°C
References
References/Citations 1) Gant?et al. (1988)?Redox Cycling and Sulphydryl Arylation; Their Relative Importance in the Mechanism of Quinone Cytotoxicity to Isolated Hepatocytes; Chem. Biol. Interactions;?65?157 2) Stubberfield and Cohen (1989)?Interconversion of NAD(H) to NADP(H). A cellular response to quinone-induced oxidative stress in isolated hepatocytes; Biochem. Pharmacol.,?38?2631 3) Dypbukt?et al?(1994)?Different prooxidant levels stimulate growth, trigger apoptosis or produce necreosis of insulin-secreting RINm5F cells. The role of intracellular polyamines; J. Biol. Chem.,?269?30553 4) Henry and Wallace (1996)?Differential mechanisms of cell killing by redox cycling and arylating quinones; Arch. Toxicol.,?70?482
Properties of DMNQ
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 10 mg/ml) or in Ethanol (up to 5 mg/ml). |
| form | solid |
| color | Yellow |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20° for up to 3 months. |
Safety information for DMNQ
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for DMNQ
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 7-Bromo-1H-indazole N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid Electrolytic Iron Powder Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 1-(4-Methylphenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,3-benzotriazole 1-(2-Chlorobenzyl)-4-nitro-1H-pyrazole 1-(2-Nitrophenyl)-4-phenylpiperazineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![1-Chloro-3-methanesulfonyl-6,6-dimethyl-6,7-dihydro-5H-benzo[c]thiophen-4-one](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180601/GIF/882288-28-0.gif)



You may like
-
 2,3-Dimethoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone CAS 6956-96-3View Details
2,3-Dimethoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone CAS 6956-96-3View Details
6956-96-3 -
 55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
1169630-40-3 -
 1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 -
 127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5