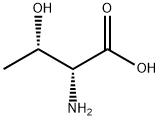
DL-Threonine
Synonym(s):(±)-2-Amino-3-hydroxybutyric acid
- CAS NO.:80-68-2
- Empirical Formula: C4H9NO3
- Molecular Weight: 119.12
- MDL number: MFCD00063722
- EINECS: 201-300-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
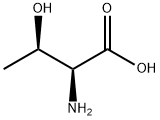
What is DL-Threonine?
Description
Threonine (abbreviated as Thr or T) is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH(OH)CH3. Its codons are ACU, ACA, ACC, and ACG. This essential amino acid is classified as polar. Together with serine, threonine is one of two proteinogenic amino acids bearing an alcohol group (tyrosine is not an alcohol but a phenol, since its hydroxyl group is bonded directly to an aromatic ring, giving it different acid/base and oxidative properties). It is also one of two common amino acids that bear a chiral side chain, along with isoleucine.
The threonine residue is susceptible to numerous posttr anslational modifications. The hydroxy side-chain can undergo Olinked glycosylation. In addition, threonine residues undergo phospho rylation through the action of a threonine kinase. In its phosphorylated form, it can be referred to as phospho threonine.
Chemical properties
White crystalline powder
Occurrence
Foods high in threonine include cottage cheese, poultry, fish, meat, lentils, Black turtle bean and Sesame seeds.
Racemic threonine can be prepared from crotonic acid by alphafunctionalization using mercury (II) acetate.
History
Threonine was discovered as the last of the 20 common proteinogenic amino acids in the 1930s by William Cumming Rose.
The Uses of DL-Threonine
DL-Threonine is used as a polar essential amino acid. It serves as a precursor of glycine as well as used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Further, it is used for biochemical research. In addition to this, it is used as a nutrition enhancer.
What are the applications of Application
DL-Threonine is a polar essential amino acid
Definition
ChEBI: 2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid is an alpha-amino acid that is butanoic acid substituted by an amino group at position 2 and a hydroxy group at position 3. It has a role as a plant metabolite.
brand name
L -Threonine is JAN.
Biosynthesis
As an essential amino acid, threonine is not synthesized in humans, hence we must ingest threonine in the form of threoninecontaining proteins. In plants and microorganisms, threonine is synthesized from aspartic acid via α-aspartyl-semialdehyde and homoserine. Homoserine undergoes O-phosphorylation; this phosphate ester undergoes hydrolysis concomitant with relocation of the OH group. Enzymes involved in a typical biosynthesis of threonine include :
aspartokinase
β-aspartate semialdehyde dehydrogenase
homoserine dehydrogenase
homoserine kinase
threonine synthase.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 32, p. 1031, 1991 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)74479-0
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 63, p. 3499, 1998 DOI: 10.1021/jo9722717
Metabolism
Threonine is metabolized in two ways:
It is converted to pyruvate via threonine dehydrogenase. An intermediate in this pathway can undergo thiolysis with CoA to produce acetyl-CoA and glycine.
In humans, it is converted to α-ketobutyrate in a less common pathway via the enzyme serine dehydratase, and thereby enters the pathway leading to succinyl-CoA.
.
Stereoisomerism
Threonine is one of two proteinogenic amino acids with two chiral centers. Threonine can exist in four possible stereo isomers with the following configurations: (2S,3R), (2R,3S), (2S,3S) and (2R,3R). However, the name L-threonine is used for one single diastereomer, (2S,3R)-2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid. The second stereoisomer (2S,3S), which is rarely present in nature, is called L-allo-threonine. The two stereo isomers (2R,3S)- and (2R,3R)-2-amino-3-hydroxy butanoic acid are only of minor importance.
Properties of DL-Threonine
| Melting point: | 244 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 222.38°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | [α]D20 0±1.0゜ (c=6, H2O) |
| Density | 1.3126 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4183 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Store at RT. |
| solubility | Soluble in water, Insoluble in absolute alcohol and oils |
| pka | 2.09(at 25℃) |
| form | Powder |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | 200 g/L (25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,9380 |
| BRN | 1721647 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 80-68-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | DL-Threonine(80-68-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Threonine (80-68-2) |
Safety information for DL-Threonine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for DL-Threonine
DL-Threonine manufacturer
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 80-68-2 DL-THREONINE 99%View Details
80-68-2 DL-THREONINE 99%View Details
80-68-2 -
 DL-Threonine CAS 80-68-2View Details
DL-Threonine CAS 80-68-2View Details
80-68-2 -
 DL-Threonine extrapure CHR CAS 80-68-2View Details
DL-Threonine extrapure CHR CAS 80-68-2View Details
80-68-2 -
 DL-Threonine CAS 80-68-2View Details
DL-Threonine CAS 80-68-2View Details
80-68-2 -
 DL-Threonine (contains DL-Allothreonine) CAS 80-68-2View Details
DL-Threonine (contains DL-Allothreonine) CAS 80-68-2View Details
80-68-2 -
 DL-THREONINE For Biochemistry CAS 80-68-2View Details
DL-THREONINE For Biochemistry CAS 80-68-2View Details
80-68-2 -
 DL-Threonine CAS 80-68-2View Details
DL-Threonine CAS 80-68-2View Details
80-68-2 -
 DL-Threonine CAS 80-68-2View Details
DL-Threonine CAS 80-68-2View Details
80-68-2