DL-1-Phenethylalcohol
Synonym(s):(±)-α-Methylbenzyl alcohol;(±)-1-Phenylethanol;Methyl phenyl carbinol;Styrallyl alcohol;Styrene alcohol
- CAS NO.:98-85-1
- Empirical Formula: C8H10O
- Molecular Weight: 122.16
- MDL number: MFCD00004508
- EINECS: 202-707-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:44

What is DL-1-Phenethylalcohol?
Description
α-Methylbenzyl alcohol has a mild hyacinth-gardenia odor.
Chemical properties
colourless liquid
Chemical properties
DL-1-Phenethylalcohol has been identified as a volatile component of food (e.g., in tea aroma and mushrooms). The alcohol is a colorless liquid with a dry, rose-like odor, slightly reminiscent of hawthorn. It can be prepared by catalytic hydrogenation of acetophenone. 1- Phenylethyl alcohol is used in small quantities in perfumery and in larger amounts for the production of its esters, which are more important as fragrance materials.
Chemical properties
α-Methylbenzyl alcohol has a mild hyacinth–gardenia odor.
Occurrence
Two optically active isomers exist; the commercial product is the racemic form. Reported found in cranberry, grapes, chive, Scotch spearmint oil, cheeses, cognac, rum, white wine, cocoa, black tea, filbert, cloudberry, beans, mushroom and endive.
The Uses of DL-1-Phenethylalcohol
The Arthrobacter sp. is able to grow with (+ I-,(-)-1-phenylethanol or the racemic mixture as sole source of carbon. Growth is most rapid with the (-)-isomer, doubling time 12 h. Lipases show good activity and, in some cases, improved enantioselectivity when employed in pure ionic liquids for dynamic kinetic resolution of 1-phenylethanol by transesterification.
What are the applications of Application
1-Phenylethanol is an aromatic alcohol
Definition
ChEBI: An aromatic alcohol that is ethanol substituted by a phenyl group at position 1.
Preparation
By oxidation of ethylbenzene or by reduction of acetophenone.
Production Methods
1-Phenylethanol is coproduced with propylene oxide by reaction of a-peroxyethylbenzene (formed by the oxidation of ethylbenzene) with propylene. It is used as a fragrance additive in cosmetics such as perfumes, creams, and soaps and is an intermediate in styrene production. 1-Phenylethanol is also added to foods as a flavoring agent. Industrial exposure may occur from dermal contact and ingestion.
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 50 ppm: chemical, medicinal, with a balsamic vanilla woody nuance.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron Letters, 36, p. 3861, 1995 DOI: 10.1016/0040-4039(95)00679-7
General Description
A colorless liquid. Insoluble in water and less dense than water. Contact may slightly irritate skin, eyes and mucous membranes. May be slightly toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Used to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Attacks plastics. [Handling Chemicals Safely, 1980. p. 236]. Acetyl bromide reacts violently with alcohols or water [Merck 11th ed. 1989]. Mixtures of alcohols with concentrated sulfuric acid and strong hydrogen peroxide can cause explosions. Example: An explosion will occur if dimethylbenzylcarbinol is added to 90% hydrogen peroxide then acidified with concentrated sulfuric acid. Mixtures of ethyl alcohol with concentrated hydrogen peroxide form powerful explosives. Mixtures of hydrogen peroxide and 1-phenyl-2-methyl propyl alcohol tend to explode if acidified with 70% sulfuric acid [Chem. Eng. News 45(43):73. 1967; J, Org. Chem. 28:1893. 1963]. Alkyl hypochlorites are violently explosive. They are readily obtained by reacting hypochlorous acid and alcohols either in aqueous solution or mixed aqueous-carbon tetrachloride solutions. Chlorine plus alcohols would similarly yield alkyl hypochlorites. They decompose in the cold and explode on exposure to sunlight or heat. Tertiary hypochlorites are less unstable than secondary or primary hypochlorites [NFPA 491 M. 1991]. Base-catalysed reactions of isocyanates with alcohols should be carried out in inert solvents. Such reactions in the absence of solvents often occur with explosive violence [Wischmeyer 1969].
Health Hazard
Irritating to the skin, eyes, nose, throat, and upper respiratory tract.
Fire Hazard
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and subcutaneous routes. Moderately toxic by skin contact. A skin and severe eye irritant. Questionable carcinogen. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame; can react with oxidming materials. To fight fire, use alcohol foam, foam, CO2, dry chemical
Carcinogenicity
In an NTP study, both sexes of F344 rats were dosed by gavage with 0, 375, and 750 mg/kg 1-phenylethanol 5 days/week for 2 years. There was an increased incidence of neoplastic kidney tumors in the high-dose male rats but no evidence of carcinogenicity in the female rats . In the same NTP study, both sexes of B6C3F1 mice were dosed by oral gavage with 0, 375, and 750 mg/kg 1-phenylethanol 5 days/week for 2 years. There was no evidence that 1-phenylethanol was carcinogenic to mice in this study.
Purification Methods
Purify the alcohol via its hydrogen phthalate. [See Houssa & Kenyon J Chem Soc 2260 1930.] Shake it with a solution of ferrous sulfate, and th
Properties of DL-1-Phenethylalcohol
| Melting point: | 19-20 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 204 °C745 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 1.012 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 4.21 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.1 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 2685 | ALPHA-METHYLBENZYL ALCOHOL |
| Flash point: | 185 °F |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), Ethyl Acetate, Methanol (Sparingly) |
| pka | 14.43±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear colorless |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. fresh sweet acetophenone gardenia hyacinth |
| Water Solubility | 29 g/L (20 ºC) |
| JECFA Number | 799 |
| BRN | 1905149 |
| Dielectric constant | 7.6(90℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 98-85-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzenemethanol, «alpha»-methyl-(98-85-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | .alpha.-Methylbenzenemethanol (98-85-1) |
Safety information for DL-1-Phenethylalcohol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for DL-1-Phenethylalcohol
DL-1-Phenethylalcohol manufacturer
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![Isopropyl-α-[2-methylhydrazino]-p-toluamide](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/671-16-9.gif)
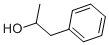
You may like
-
 98-85-1 STYRALLYL ALCOHOL 99%View Details
98-85-1 STYRALLYL ALCOHOL 99%View Details
98-85-1 -
 98-85-1 99%View Details
98-85-1 99%View Details
98-85-1 -
 1-Phenylethanol, 98% CAS 98-85-1View Details
1-Phenylethanol, 98% CAS 98-85-1View Details
98-85-1 -
 alpha-Phenethyl alcohol >99% (GC) CAS 98-85-1View Details
alpha-Phenethyl alcohol >99% (GC) CAS 98-85-1View Details
98-85-1 -
 (±)-1-Phenylethyl Alcohol CAS 98-85-1View Details
(±)-1-Phenylethyl Alcohol CAS 98-85-1View Details
98-85-1 -
 1-Phenylethanol CAS 98-85-1View Details
1-Phenylethanol CAS 98-85-1View Details
98-85-1 -
 Styrallyl Alcohol (98-85-1), 96-98%View Details
Styrallyl Alcohol (98-85-1), 96-98%View Details
98-85-1 -
 Styrallyl Alcohol (98-85-1 )View Details
Styrallyl Alcohol (98-85-1 )View Details
98-85-1
