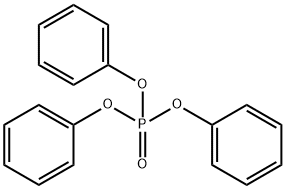
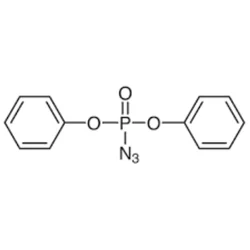
Diphenylphosphoryl azide
Synonym(s):DPPA;12-Deoxyphorbol 13-phenylacetate 20-acetate;DPPA polymer-bound;Phosphoric acid diphenyl ester azide;PS-DPPA
- CAS NO.:26386-88-9
- Empirical Formula: C12H10N3O3P
- Molecular Weight: 275.2
- MDL number: MFCD00001987
- EINECS: 247-644-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
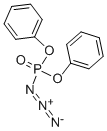
What is Diphenylphosphoryl azide?
Chemical properties
Diphenylphosphoryl azide (DPPA) is a colorless or pale yellow liquid which boils at 134-136 °C/0.2 mmHg, and it will be stable at room temperature under shading. It is non-explosive just like the other phosphorazidate. When DPPA is stored at room temperature for a long time, it might be slowly and partially hydrolyzed with moisture in air to produce diphenyl phosphate and toxic explosive hydrazoic acid. In this case, it will be recommended to use after washing DPPA with aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate followed by drying.
The Uses of Diphenylphosphoryl azide
Diphenylphosphoryl azide (DPPA or diphenyl phosphorazidate, (PhO)2P(O)N3) is a very toxic and potentially explosive organic compound. DPPA has been found to be effective for a variety of organic reactions as a versatile synthetic reagent. It is widely used in synthesis of other organic compounds especially as a reagent for the synthesis of peptides by virtue of its reactions with carboxylic acids leading to either the urethane or the amide.
The Uses of Diphenylphosphoryl azide

To a solution of the SM (48 g, 384 mmol) and PPh3 (121 g, 461 mmol) in THF (1.8 L) was added DIAD ( 93.1 g, 461 mmol). The reaction mixture was cooled to 10 C and treated with DPPA (98.8 g, 461 mmol). The mixture was stirred at RT for 16 h, and then was concentrated in vacuo. The crude was purified by column chromatography (eluting with 33% EtOAc/pentane). The product fractions were concentrated to ~150 mL and diluted with EtOH (1.0 L). 10% Pd/C was added and the mixture was hydrogenated under 1 atm of H2. The mixture was filtered and the filtrate was concentrated in vacuo to a volume of ~500 mL.10M HCl in EtOH (50 mL) was added dropwise and the resulting solid was filtered and washed with EtOH to provide the product as a solid. [30 g, 44%]
What are the applications of Application
Diphenyl phosphoryl azide is a hydroazidation catalyst for facile preparation of organoazides
What are the applications of Application
Diphenylphosphoryl azide (DPPA) is a well-known azide reagent used in peptide couplings, Curtius rearrangements, and Mitsunobu inversions—is often encountered in pharmaceutical process development because it enables the most direct route to a desired product. Diphenylphosphonic azide acts as a reagent for the synthesis of peptides and phosphoramidates by reacting with amines. It is also used in the preparation of oligosaccharides linked with carbamate and urea bonds utilizing modified Curtis rearrangement. It is involved in pseudohalogen replacement of the azido group by treatment with nucleophilic reagents, such as water, butanol, ammonia, and various amines. Further, it is used as a hydroazidation catalyst for preparation of organoazides.
Preparation
Diphenylphosphoryl azide (DPPA) is easily prepared in high yield by the reaction of the corresponding chloride with sodium azide in acetone. Combination of sodium azide and 18-crown-6 in the same reaction was reported, and the use of a quaternary ammonium salt as a phase-transfer catalyst in a biphasic phase of water and an organic solvent was also reported to be effective, as shown in Scheme 3.
Diphenyl Phosphorazidate (DPPA) - More Than Three Decades Later
Takayuki Shioiri
Graduate School of Environmental and Human Sciences, Meijo University
Reactions
Diphenylphosphoryl azide, originally developed by Yamada in 1972, has shown significant synthetic versatility, being used in isocyanate synthesis, especially in the Curtius rearrangement, stereospecific conversion of alcohol into azide, as a coupling reagent in macrolactamization[4], in allylic amine synthesis, and in aziridination reactions. Diphenylphosphoryl azide, also called DPPA, diphenyl phosphorazidate or phosphoric acid diphenyl ester azide, is a colorless liquid with high boiling point (157 ??C/0.17 mmHg), and can be easily prepared by the reaction between diphenylphosphoryl chloride and sodium azide in acetone in high yield. The Waldvogel group developed a reliable protocol for the large-scale (100 g) synthesis of DPPA, including purification by reduced-pressure distillation (Picture 1). A polymer-supported form of the reagent has also been developed using phenol resin by the Taylor group.

Mechanism of action
Diphenyl phosphoryl azide is used in the aziridination of olefins catalyzed by colbalt-tetraphenylporphyrin. It is also used as the activating agent in the preparation of macrocyclic lactams and of an aldose reductase inhibitor.
Properties of Diphenylphosphoryl azide
| Boiling point: | 157 °C/0.17 mmHg (lit.) |
| Density | 1.277 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Acetonitrile (Slightly), Chloroform (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Sparingly) |
| form | Liquid |
| appearance | Colorless to light yellow liquid |
| color | slightly yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 1.277 |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 7: reacts slowly with moisture/water |
| BRN | 2058967 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with acids, strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 26386-88-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Diphenylphosphoryl azide(26386-88-9) |
Safety information for Diphenylphosphoryl azide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Diphenylphosphoryl azide
| InChIKey | SORGEQQSQGNZFI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Diphenylphosphoryl azide manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
NSR Amino Organics
ASM Organics
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 26386-88-9 Diphenyl Phophoryl Azide(DPPA) 99%View Details
26386-88-9 Diphenyl Phophoryl Azide(DPPA) 99%View Details
26386-88-9 -
 26386-88-9 DI PHENYL PHOSPHORYL AZIDE 98%View Details
26386-88-9 DI PHENYL PHOSPHORYL AZIDE 98%View Details
26386-88-9 -
 Diphenylphosphonic azide, 95% 26386-88-9 99%View Details
Diphenylphosphonic azide, 95% 26386-88-9 99%View Details
26386-88-9 -
 Diphenylphosphoryl Azide CAS 26386-88-9View Details
Diphenylphosphoryl Azide CAS 26386-88-9View Details
26386-88-9 -
 Diphenylphosphoryl azide 98% CAS 26386-88-9View Details
Diphenylphosphoryl azide 98% CAS 26386-88-9View Details
26386-88-9 -
 Diphenyl phosphoryl azide CAS 26386-88-9View Details
Diphenyl phosphoryl azide CAS 26386-88-9View Details
26386-88-9 -
 Diphenylphosphoryl Azide Cas 26386-88-9View Details
Diphenylphosphoryl Azide Cas 26386-88-9View Details
26386-88-9 -
 26386-88-9 98%View Details
26386-88-9 98%View Details
26386-88-9
