DIMETHYLCYANAMIDE
- CAS NO.:1467-79-4
- Empirical Formula: C3H6N2
- Molecular Weight: 70.09
- MDL number: MFCD00001767
- EINECS: 215-991-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-11-28 16:31:44
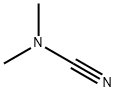
What is DIMETHYLCYANAMIDE?
Chemical properties
CLEAR COLORLESS TO YELLOWISH LIQUID
The Uses of DIMETHYLCYANAMIDE
Dimethylcyanamide in the presence of tetrachlorosilane and zinc chloride is used as a promoter for one-pot, three component synthesis of a novel series of 1,3-oxazines. Being a dialkylcyanamide, it has been proved to be a more reactive substrate toward metal-mediated nucleophilic addition than alkylcyanides.
Production Methods
Dimethyl cyanamide is made by the reaction of nitromethane with tris(dimethylamino) arsine.
General Description
Clear liquid.
Air & Water Reactions
Reacts with water to form cyanide gas
Reactivity Profile
Nitriles, such as DIMETHYLCYANAMIDE, may polymerize in the presence of metals and some metal compounds. They are incompatible with acids; mixing nitriles with strong oxidizing acids can lead to extremely violent reactions. Nitriles are generally incompatible with other oxidizing agents such as peroxides and epoxides. The combination of bases and nitriles can produce hydrogen cyanide. Nitriles are hydrolyzed in both aqueous acid and base to give carboxylic acids (or salts of carboxylic acids). These reactions generate heat. Peroxides convert nitriles to amides. Nitriles can react vigorously with reducing agents. Acetonitrile and propionitrile are soluble in water, but nitriles higher than propionitrile have low aqueous solubility. They are also insoluble in aqueous acids. DIMETHYLCYANAMIDE reacts with oxidizers, water, or steam.
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: DIMETHYLCYANAMIDE is an irritant. It reacts with water to produce toxic and flammable vapors.
Fire Hazard
DIMETHYLCYANAMIDE is combustible.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, skin contact, and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by inhalation. Flammable when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidzers. Can react with oxidzing materials. To fight fire, use foam, CO2, or dry chemical. When heated to decomposition or in reaction with water or steam it produces toxic fumes of NOx, and CNand flammable vapors. See also CYANIDE
Properties of DIMETHYLCYANAMIDE
| Melting point: | -41 °C |
| Boiling point: | 161-163 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.867 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 137 °F |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), Hexane (Slightly) |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | -4.76±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | Clear colorless to yellow |
| Dielectric constant | 37.229999999999997 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dimethylcyanamide (1467-79-4) |
Safety information for DIMETHYLCYANAMIDE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H227:Flammable liquids H301:Acute toxicity,oral H310:Acute toxicity,dermal H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P370+P378:In case of fire: Use … for extinction. P405:Store locked up. P403+P235:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep cool. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for DIMETHYLCYANAMIDE
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![5-Cyano-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/42787-75-7.gif)
![N-Cyano-N-[2-(5-methylimidazole-4-methylthio)ethyl]-S-methyl isothiourea](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/52378-40-2.gif)

![[(6-CHLOROPYRIDAZIN-3-YL)(METHYL)AMINO]METHANENITRILE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB1161526.gif)
You may like
-
 Dimethylcyanamide CAS 1467-79-4View Details
Dimethylcyanamide CAS 1467-79-4View Details
1467-79-4 -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4