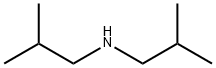
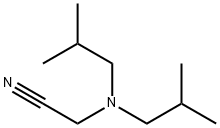
Diisobutylamine
- CAS NO.:110-96-3
- Empirical Formula: C8H19N
- Molecular Weight: 129.24
- MDL number: MFCD00008930
- EINECS: 203-819-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
What is Diisobutylamine?
Chemical properties
The chemical reactivity of diisobutylamine is similar to other aliphatic amines and is governed by the unshared electron pair on the nitrogen atom. It is a strong base tending to form salts with acids. As with other secondary amines, diisobutylamine can be nitrosated, especially under acidic conditions, by nitrite ion or by nitrogen oxides from the air to form the carcinogenic and mutagenic N-nitrosodiisobutylamine (Olah et al 1975).
The Uses of Diisobutylamine
Diisobutylamine was used to study the effect of achiral amine on hydrogenation of ethyl pyruvate over cinchonidine-Pt/Al2O3 catalyst system.
Production Methods
Diisobutylamine can be produced by the reaction of ammonia and butanol over a
dehydration catalyst at high temperature and pressure (Hawley 1977). Alternatively,
ammonia, butanol, and hydrogen can be passed over a dehydrogenation
catalyst. In 1976, 18,000 tons of diisobutylamine were produced (Schweizer et al
1978). Diisobutylamine is also naturally present in foods and soil.
As with other secondary amines, diisobutylamine can be nitrosated to form the
highly toxic (Olah 1975) N-nitrosodiisobutylamine (Guttenplan 1987; Vlasenko et
al 1981; Spiegeholder et al 1978). Thus, nitrosation of commercial preparations of
diisobutylamine occurs on standing, presumably by reaction with nitrogen oxides
in the air (Spiegelhalder et al 1978) and N-nitrosodiisobutylamine has been found
in various fishery products (Kawabata et al 1974) and other foods (Osborne 1972;
Telling 1972).
General Description
Diisobutylamine appears as a clear colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Insoluble in water and less dense than water. Hence floats on water. Vapors heavier than air. Toxic oxides of nitrogen produced during combustion.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Sensitive to heat and air. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Diisobutylamine can react vigorously with oxidizing materials . Neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of high concentrations of vapor will cause irritation of the respiratory tract and the lungs. Contact with liquid may result in severe skin and eye irritation. Exposure to concentrated vapors may result in corneal edema. Poisonous if swallowed.
Health Hazard
Diisobutylamine is a relatively strong base and is therefore irritating to the eyes, respiratory tract, and skin. Inhalation of vapors can result in pulmonary edema following prolonged exposure. Ingestion of liquid can cause severe burning of the esophagus.
Industrial uses
Diisobutylamine is used as a chemical intermediate in the manufacture of several agricultural and pharmaceutical products.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion. A dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heator flame; can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. To fight fire, use alcohol foam, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Nox
Metabolism
There is little information available on the metabolism of diisobutylamine.
Properties of Diisobutylamine
| Melting point: | -77 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 137-139 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.74 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 85 °F |
| storage temp. | Flammables area |
| solubility | insoluble to slightly soluble in water; soluble in ethanol, methanol,
ethyl ether, ethyl acetate, acetone, benzene, aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons,
fixed oils, mineral oil, oleic and stearic acids |
| pka | 11.07±0.28(Predicted) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear |
| Odor | amine odor |
| Water Solubility | 5 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| BRN | 1209251 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.7(22℃) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 110-96-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1-Propanamine, 2-methyl-N-(2-methylpropyl)-(110-96-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Diisobutylamine (110-96-3) |
Safety information for Diisobutylamine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H301:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Diisobutylamine
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Diisobutylamine, 99% CAS 110-96-3View Details
Diisobutylamine, 99% CAS 110-96-3View Details
110-96-3 -
 Diisobutylamine CAS 110-96-3View Details
Diisobutylamine CAS 110-96-3View Details
110-96-3 -
 Diisobutylamine CAS 110-96-3View Details
Diisobutylamine CAS 110-96-3View Details
110-96-3 -
 Diisobutylamine CAS 110-96-3View Details
Diisobutylamine CAS 110-96-3View Details
110-96-3 -
 17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 -
 Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
67967-07-1 -
 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
1878-69-9 -
 132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6
