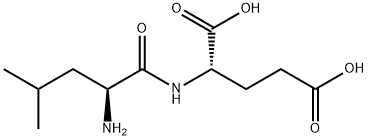
DIFOPEIN
- CAS NO.:396834-58-5
- Empirical Formula: C273H424N76O89S6
- Molecular Weight: 6387.13
- MDL number: MFCD06798321
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-21 10:59:17
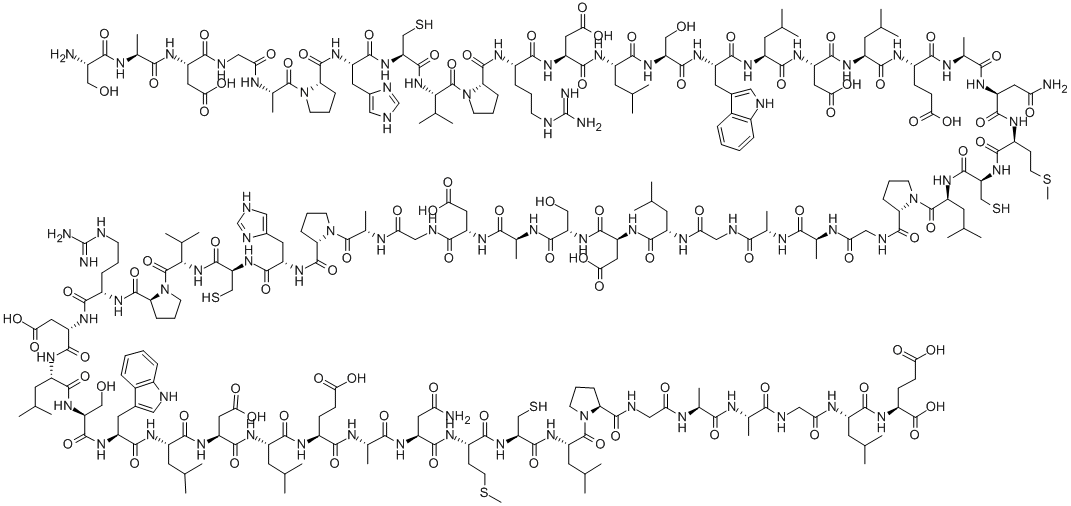
What is DIFOPEIN?
Description
Difopein is an inhibitor of 14-3-3 protein.
14-3-3 protein has been involved in a wide range of biologic processes such as signal transduction, vesicular transport, cell cycle control, DNA replication, DNA repair and apoptosis. 14-3-3 protein has been associated with tumor genesis. 14-3-3 protein correlates with reduced tumor cell apoptosis and abbreviated patient survival. Up-regulation of 14-3-3 protein provides a survival advantage to tumor cells. Inhibition of 14-3-3 protein might trigger apoptosis, inhibit growth of established tumors, suppress de novo tumor formation, and promise a novel therapeutic approach for glioma treatment [1].
In human glioma U251 and U87 cells, difopein resulted in apoptosis characteristics, such as nuclear fragmentation, DNA laddering fragment and appearance of membrane-enclosed apoptotic bodies. Difopein induced apoptosis in a time-dependent manner [1]. Difopein induced glioma cell apoptosis through down-regulating Bcl-2, up-regulating Bax and activating caspase-9 and caspase-3. In vivo, difopein effectively hindered proliferation and triggered apoptosis of tumor cells implanted into nude mice [1].
References
[1] Cao W, Yang X, Zhou J, et al. Targeting 14-3-3 protein, difopein induces apoptosis of human glioma cells and suppresses tumor growth in mice[J]. Apoptosis, 2010, 15(2): 230-241.
Properties of DIFOPEIN
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| Water Solubility | Soluble to 5 mg/ml in Water |
Safety information for DIFOPEIN
Computed Descriptors for DIFOPEIN
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1