Dicyclohexylamine
Synonym(s):DCHA;Dicyclohexylamine
- CAS NO.:101-83-7
- Empirical Formula: C12H23N
- Molecular Weight: 181.32
- MDL number: MFCD00011658
- EINECS: 202-980-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
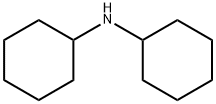
What is Dicyclohexylamine?
Description
Dicyclohexylamine is a combustible, colorlessliquid with a faint amine odor. Molecular weight=181.36;Boiling point=256℃; Flash point $99℃. HazardIdentification (based on NFPA-704 M Rating System): Health3, Flammability 1, Reactivity 0. Slightly soluble in water.
Chemical properties
Dicyclohexylamine is a combustible, colorless liquid with a faint amine odor.
Chemical properties
Dicyclohexylamine is strongly basic with reactive amine groups which readily form TV-substituted derivatives. It also forms salts with inorganic and organic acids. Dicyclohexylamine will also form crystalline hydrates and alcoholates.
The Uses of Dicyclohexylamine
Dicyclohexylamine (DCHA) is an aliphatic amine. As an intermediate, it can be used in a broad range of applications in different industries.
Dicyclohexylamine is used as a vulcanization accelerator.
In lubricants and cutting fluids it does function as a corrosion inhibitor. Here it should be mentioned that Dicyclohexylamine does not form Nitrosamines when being used.

Reagent for preparation of crystalline amino acid derivative salts.
Dicyclohexylamine was used to constitute ionic liquid matrices for bacterial analysis in matrix assisted laser desorption/ionisation mass spectrometry.
It was used to develop a new palladium catalyst for Suzuki coupling reaction of aryl bromides with boronic acids.
It was used as extractant in determination of gold(III) by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry.
The Uses of Dicyclohexylamine
Industrial solvent; corrosion inhibitor.
The Uses of Dicyclohexylamine
Dicyclohexylamine is manufactured by reacting equimolar quantities of cyclohexanone and cyclohexylamine or cyclohexanone and ammonia. It is used as a solvent and in organic syntheses. It is reportedly used as a chemical intermediate for the synthesis of corrosion inhibitors, rubber vulcanization accelerators, textiles, and varnishes.
Production Methods
Several methods are employed for the manufacture of dicyclohexylamine. It can be manufactured by hydrogenation of equimolar amounts of cyclohexanone and cyclohexylamine. Alternatively, dicyclohexylamine can be prepared by vapor phase catalytic hydrogenation of aniline at elevated temperature and pressure. Fractionation of the crude reaction product yields cyclohexylamine, unreacted aniline, and a high boiling residue comprised of N-phenylcyclohexylamine and dicyclohexylamine (Windholz et al 1983).
Definition
ChEBI: Dicyclohexylamine is a primary aliphatic amine.
General Description
A colorless liquid with a faint fishlike odor. Less dense than water. May be toxic by ingestion. Severely irritates skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Used to make paints, varnishes and detergents.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly soluble in water. May be sensitive to air.
Reactivity Profile
DCHA reacts with oxidizing agents. Forms crystalline salts with many N-protected amino acids . Neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Health Hazard
Dicyclohexylamine is a strong irritant to skin and mucous membranes. Direct skin contact with the liquid or vapor should be avoided. Its systemic effects in man include nausea and vomiting, anxiety, restlessness and drowsiness. Individuals repeatedly exposed to this chemical may develop sensitivity to it (HSDB 1988).
Fire Hazard
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Industrial uses
Dicyclohexylamine is a widely used chemical intermediate. It can be used to absorb acidic gases, to preserve rubber latex, to plasticize casein, and to neutralize plant and insect poisons. Metal complexes of dicyclohexylamine are catalysts used in the paint, varnish, and ink industries. Dicyclohexylamine salts of fatty acids and sulfuric acid have soap and detergent properties used in the printing and textile industries. One of the most important uses of dicyclohexylamine is as a vapor phase corrosion inhibitor. It is used to protect packaged or stored ferrous metals from atmospheric corrosion (Schweizer et al 1978).
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and subcutaneous routes. Corrosive. A severe skin and eye irritant. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Human mutation data reported. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame; can react with oxidizing materials. To fight fue, use alcohol foam, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also CYCLOHEXYLAMINE.
Potential Exposure
Dicyclohexylamine salts of fatty acids and sulfuric acid have soap and detergent properties useful to the printing and textile industries. Metal complexes of DI-CHA are used as catalysts in the paint, varnish, the ink industries. Several vapor-phase corrosion inhibitors are solid DI-CHA derivatives. These compounds are slightly volatile at normal temperatures and are used to protect packaged or stored ferrous metals from atmospheric corrosion. Dicyclohexylamine is also used for a number of other purposes: plasticizers, insecticidal formulations; antioxidant in lubricating oils, fuels, and rubber; and as an extractant. Incompatibilities: Contact with strong oxidizers can cause fire and explosion hazard
First aid
Skin Contact: Flood all areas of body thathave contacted the substance with water. Do not wait toremove contaminated clothing; do it under the water stream.Use soap to help assure removal. Isolate contaminatedclothing when removed to prevent contact by others.Eye Contact: Remove any contact lenses at once. Flusheyes well with copious quantities of water or normal salinefor at lest 20-30 min. Seek medical attention.
Metabolism
The extensive use of cyclamates as artificial sweeteners a number of years ago led to extensive study on the metabolism and carcinogenicity of cyclohexylamine, a metabolic product of cyclamate. However, there is little such information available concerning dicyclohexylamine. Filov (1968) investigated the metabolism of cyclohexylamine and dicyclohexylamine. Both amines were readily absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract. In addition, they rapidly entered the bloodstream following inhalation and penetrated intact skin. In rats, it was determined that 26-44% of dicyclohexylamine present in the stomach was eliminated unchanged, mostly in the urine. The clearance rate of the amines was also quite high, particularly for dicyclohexylamine.
Storage
(1) Color Code—White: Corrosive or ContactHazard; Store separately in a corrosion-resistant location.(2) Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Store in asecure poison location. Prior to working with Di-Cha youshould be trained on its proper handling and storage. Storein tightly closed containers in a refrigerator away from oxidizers. Where possible, automatically pump liquid fromdrums or other storage containers to process containers.Protection from air is recommended for long-term storage.
Shipping
UN2565 Dicyclohexylamine, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material
Incompatibilities
Dicyclohexylamine salts of fatty acids and sulfuric acid have soap and detergent properties useful to the printing and textile industries. Metal complexes of DI-CHA are used as catalysts in the paint, varnish, the ink industries. Several vapor-phase corrosion inhibitors are solid DI-CHA derivatives. These compounds are slightly volatile at normal temperatures and are used to protect packaged or stored ferrous metals from atmospheric corrosion. Dicyclohexylamine is also used for a number of other purposes: plasticizers, insecticidal formulations; antioxidant in lubricating oils, fuels, and rubber; and as an extractant. Incompatibilities: Contact with strong oxidizers can cause fire and explosion hazard
Waste Disposal
Incineration; incinerator equipped with a scrubber or thermal unit to reduce nitrogen oxides emissions.
Properties of Dicyclohexylamine
| Melting point: | -2 °C |
| Boiling point: | 256 °C |
| Density | 0.912 g/mL at 20 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 6 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 12 mm Hg ( 37.7 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 205 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | organic solvents: soluble |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| appearance | Pale yellow liquid 0.912 g/mL at 20 C |
| pka | 10.4(at 25℃) |
| color | White to off-white |
| PH | 11 (1g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | amine odor |
| explosive limit | 0.8-4.6%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 1 g/L (20 ºC) |
| FreezingPoint | -2℃ |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,3095 |
| BRN | 605923 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 101-83-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Cyclohexanamine, N-cyclohexyl-(101-83-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dicyclohexylamine (101-83-7) |
Safety information for Dicyclohexylamine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Dicyclohexylamine
| InChIKey | XBPCUCUWBYBCDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Dicyclohexylamine manufacturer
GVSK Pharma Private Limited
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


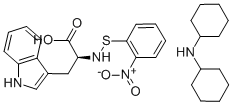
![N-[(1-[1,1-biphenyl]-4-ylisopropyloxycarbonyl]glycine, compound with N-dicyclohexylamine (1:1)](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/18701-38-7.gif)

You may like
-
 Dicyclohexylamine 99%View Details
Dicyclohexylamine 99%View Details -
 Dicyclohexylamine pure CAS 101-83-7View Details
Dicyclohexylamine pure CAS 101-83-7View Details
101-83-7 -
 Dicyclohexylamine CASView Details
Dicyclohexylamine CASView Details -
 Dicyclohexylamine 98% CAS 101-83-7View Details
Dicyclohexylamine 98% CAS 101-83-7View Details
101-83-7 -
 Lab Grade Dicyclohexylamine(101-83-7), 1 Ltr, 99%View Details
Lab Grade Dicyclohexylamine(101-83-7), 1 Ltr, 99%View Details
101-83-7 -
 DicyclohexylamineView Details
DicyclohexylamineView Details
101-83-7 -
 Dicyclohexylamine ( D C H A )View Details
Dicyclohexylamine ( D C H A )View Details
101-83-7 -
 Analytical Grade Dicyclohexylamine Powder, 99%, 101-83-7View Details
Analytical Grade Dicyclohexylamine Powder, 99%, 101-83-7View Details
101-83-7
