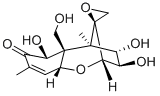
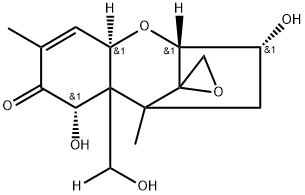
DEOXYNIVALENOL
Synonym(s):DON;Vomitoxin;DON solution;RD-toxon;(3α,7α)-3,7,15-trihydroxy-12,13-epoxytrichothec-9-en-8-one
- CAS NO.:51481-10-8
- Empirical Formula: C15H20O6
- Molecular Weight: 296.32
- MDL number: MFCD09039270
- EINECS: 610-668-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-29 15:43:00
What is DEOXYNIVALENOL?
Description
Vomitoxin or deoxynivalenol (DON) is one of the
trichothecenes (mycotoxins) which comprise a large
group (148 or more have been identified) of protein
synthesis inhibitors. These mycotoxins are also powerful
immunosuppressants which may predispose animals to
other diseases.
Vomitoxin is the most commonly found
trichothecene in moldy corn (maize), but a number of
other biologically active trichothecenes are produced by
species of the fungus Fusarium. These include nivalenol,
T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin, diacetoxyscirpenol (DAS), and
monoacetoxyscipenol (MAS). These mycotoxins are most
toxic when fed to swine and other monogastric animals
including humans. Poultry are generally more resistant
to trichothecenes than hogs, whereas T-2 toxin and DAS
appear to be more toxic to chickens than vomitoxin. Toxins
already present in corn at harvest may increase in stored
ear corn. Extended periods of warm, rainy, or damp
weather from flowering time onward promote infection
of corn by Fusarium species (1–7).
Description
4-deoxy Nivalenol is a trichothecene mycotoxin that has been found in Fusarium. It binds to eukaryotic ribosomes and inhibits protein synthesis in mice when administered at doses ranging from 5 to 25 mg/kg. 4-deoxy Nivalenol (0.1 and 0.2 mg/kg) induces emesis in pigs and decreases feed consumption in pigs when administered at a dose of 40 ppb in the diet. It induces lethality in mice (LD50 = 46-78 mg/kg). 4-deoxy Nivalenol has been found in F. graminearum-infected cereal grains such as wheat, barley, and corn.
Chemical properties
Off-White Solid
The Uses of DEOXYNIVALENOL
Deoxynivalenol is a tricothecene mycotoxin and potent protein synthesis inhibitor. Deoxynivalenol exhibits cytotoxic activity in vivo via the ribotoxic stress response. Deoxynivalenol induces p38-mediated gene expression and apoptosis in leukocytes; activity results in systemic expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and other proinflammatory cytokines. Also induces migration of NF-κB into the nucleus.
The Uses of DEOXYNIVALENOL
Deoxynivalenol is a natural type B trichothecene produced by certain species of the fungus Fusarium, particularly those found on cereal crops, including wheat, barley, oats, maize, and rye. This mycotoxin can induce vomiting, diarrhea, and weight loss as well as other physiological and toxicological effects. It inhibits protein biosynthesis, binds to peptidyl transferase, and inhibits the synthesis of RNA and DNA, contributing to immunotoxicity. It passes the blood-brain barrier at different rates in different animals and this may be related to anorexia.
The Uses of DEOXYNIVALENOL
Deoxynivalenol solution has been used as an analytical reference standard for the quantification of the analyte in cornmeal and wheat meal matrices using high-performance liquid chromatography with UV detection (HPLC-UV). It is used as an analytical standard in investigating its toxicity mechanism on human chondrocytes by microarray and bioinformatics analysis.
What are the applications of Application
Deoxynivalenol is Deoxynivalenol is a Fusarium mycotoxin, known for immunosuppressive characteristics and gene deregulation.
Definition
ChEBI: Deoxynivalenol is a trichothecene mycotoxin produced by Fusarium to which wheat, barley, maize (corn) and their products are susceptible to contamination. It has a role as a mycotoxin. It is a trichothecene, a cyclic ketone, a secondary alpha-hydroxy ketone, a primary alcohol, an enone and a triol.
General Description
Deoxynivalenol belongs to the class of type B trichothecene mycotoxins typically produced by the species of Fusarium genus. It is cytotoxic and is known to hinder the macromolecular synthesis.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Deoxynivalenol (DON) is a trichothecene mycotoxin that inhibits the synthesis of DNA and RNA as well as protein synthesis at the ribosomal level. DON induces IL-6 mediated serum hyperelevation of IgA, as well as phosphorylation of extracellular signal regulated protein kinases 1 and 2 (ERK 1,2) and c-Jun N-terminal kinases 1 and 2 (JNK 1,2) in mice. An in vitro study with porcine ovarian granulosa cells suggests a dose dependent association of DON on porcine ovarian functions. It was also shown that LPS and its downstream mediators can interact with DON to modulate proliferative, cytotoxic and apoptotic outcomes in leukocytes in a tissue specific manner.
Storage
Store at +4°C
Properties of DEOXYNIVALENOL
| Melting point: | 151-153 C |
| Boiling point: | 357.92°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D25+6.35° (c = 0.07 in ethanol) |
| Density | 1.48 |
| refractive index | 1.4359 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | -3 °C |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMF: 30 mg/ml; DMSO: 25 mg/ml; Ethanol: 30 mg/ml; PBS (pH 7.2): 10 mg/ml |
| pka | 11.91±0.70(Predicted) |
| form | solution (ethanol: 2-propanol 95:5) |
| color | White to off-white |
| Merck | 13,10092 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| InChI | InChI=1/C15H20O6/c1-7-3-9-14(5-16,11(19)10(7)18)13(2)4-8(17)12(21-9)15(13)6-20-15/h3,8-9,11-12,16-17,19H,4-6H2,1-2H3/t8-,9-,11-,12-,13-,14-,15+/s3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 51481-10-8 |
Safety information for DEOXYNIVALENOL
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects H371:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for DEOXYNIVALENOL
| InChIKey | LINOMUASTDIRTM-QUKTVYMZNA-N |
| SMILES | [C@@]12(CO1)[C@@]1([H])[C@H](O)C[C@]2(C)[C@@]2(CO)[C@H](O)C(C(C)=C[C@@]2([H])O1)=O |&1:0,3,5,8,10,13,19,r| |
New Products
BOC-L-4-HYDROXYPROLINE 2-nitro 3-hydroxy pyridine 2,6-Dichloropyridin-4-amine 2,3 Diamino pyridine 5-Iodo-2-(1-methylethyl)-3(2H)-pyridazinone 1-Azetidinecarboxylic acid, 3-[(3S)-1-(trans-3-carboxy-3-methylcyclobutyl)-3-piperidinyl]-, 1-(1,1-dimethylethyl) ester Tert-Butyl N-[3-(dimethylcarbamoyl)prop-2-en-1-yl]carbamate 1-(difluoromethyl)-N-methylcyclobutan-1-amine 2-(4-Methyl-1,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl)-1H-benzimidazole 6-(4-iodophenyl)-1-oxa-6-azaspiro[3.3]he Trimethyl(phenylthio)silane Polycaprolactone(2000)-PEG(20000)-Polycaprolactone(2000) Diacrylate Diethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether, PolyoxyethyleneOleylCetylEtherSulfosuccinate Ascorbyl Tetraisopalmitate or Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate Castor Oil, Ethoxylated, Cremophor EL or PEG-35 Castor Oil Tween 20 or Polysorbate 20 Acetone-d6 (R)-2-Mercaptobutanoic acid 3-iodo-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine 3-(naphthalen-1-ylsulfonyl)-1H-indazol-5-amine methyl 5-amino-3-(1,1-dioxidotetrahydro-2H-1,2-thiazin-2-yl)-2-fluorobenzoate 7-methoxy-8-(2-morpholinoethoxy)-4-((3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)amino)benzo[g]quinoline-3-carbonitrile Dimethylaluminum isopropoxideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
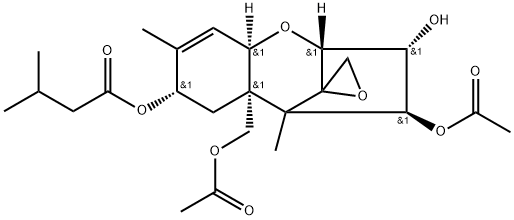
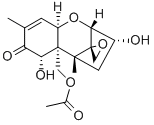

You may like
-
 Deoxynivalenol solution CAS 51481-10-8View Details
Deoxynivalenol solution CAS 51481-10-8View Details
51481-10-8 -
 Deoxynivalenol solution CAS 51481-10-8View Details
Deoxynivalenol solution CAS 51481-10-8View Details
51481-10-8 -
 4-Deoxynivalenol in acetonitrile CAS 51481-10-8View Details
4-Deoxynivalenol in acetonitrile CAS 51481-10-8View Details
51481-10-8 -
 Deoxynivalenol CAS 51481-10-8View Details
Deoxynivalenol CAS 51481-10-8View Details
51481-10-8 -
 5721-91-5 98%View Details
5721-91-5 98%View Details
5721-91-5 -
 Calcium 11% clear solution 98%View Details
Calcium 11% clear solution 98%View Details -
 Sodium Croscarmellose 98%View Details
Sodium Croscarmellose 98%View Details
74811-65-7 -
 16455-61-1 98%View Details
16455-61-1 98%View Details
16455-61-1
