Deoxycholic acid
Synonym(s):3α,12α-Dihydroxy-5β-cholanic acid;7-Deoxycholic acid;Deoxycholic acid;Desoxycholic acid
- CAS NO.:83-44-3
- Empirical Formula: C24H40O4
- Molecular Weight: 392.58
- MDL number: MFCD00003673
- EINECS: 201-478-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-25 11:31:46
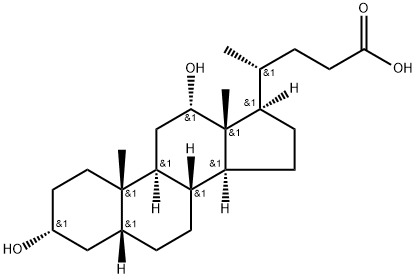
What is Deoxycholic acid?
Absorption
Deoxycholic acid is rapidly absorbed after subcutaneous administration. After maximum recommended single treatment dose, 100mg, the post-treatment plasma levels returned to endogenous levels within 24 hours. With the proposed treatment guideline, no accumulation is expected.
Description
Deoxycholic acid sodium salt, which is a secondary bile acid and the metabolite of intestinal bacteria, provides a nonsurgical treatment to significantly reduce submental fat in adults via injection directly into moderate-to-severe fatty tissue below the neck. When injected into fatty tissue, deoxycholic acid helps destroy fat cells. Although deoxycholic acid has many applications beyond human health, the application as a dyslipidemia drug was licensed to Kythera from Los Angeles Biomedical Institute at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center in 2007. Allergan acquired Kythera recently in 2015.
Chemical properties
white powder
The Uses of Deoxycholic acid
Deoxycholic acid has been used in a modified procedure to recover 40-80% of a protein from a 1 μg/mL solution. It forms complexes with fatty acid. Used as an emulsifying agent in food, a precursor in the synthesis of cortisone, and a gallbladder stimulant. It has been used to study assess how physiological concentrations of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) vs. deoxycholic acid (DCA) affect barrier function in mouse intestinal tissue. Deoxycholic acid has been used in a study to assess a pH-Responsive Mechanism of a Deoxycholic Acid and Folate Co-Modified Chitosan Micelle under Cancerous Environment. It has also been used in a study to investigate dose-dependent anti-inflammatory effect of ursodeoxycholic acid in experimental colitis.
The Uses of Deoxycholic acid
A Cholic Acid (C432600) derivative used as a component in cell lysis buffers.
The Uses of Deoxycholic acid
antiinflammatory, immunomodulator, antineoplastic
Background
Deoxycholic acid is a a bile acid which emulsifies and solubilizes dietary fats in the intestine, and when injected subcutaneously, it disrupts cell membranes in adipocytes and destroys fat cells in that tissue. In April 2015, deoxycholic acid was approved by the FDA for the treatment submental fat to improve aesthetic appearance and reduce facial fullness or convexity. It is marketed under the brand name Kybella by Kythera Biopharma and is the first pharmacological agent available for submental fat reduction, allowing for a safer and less invasive alternative than surgical procedures.
Indications
For improvement in appearance of moderate to severe fullness associated with submental fat in adults.
What are the applications of Application
Deoxycholic acid is a bile acid that may affect cellular signaling and gene expression
Definition
ChEBI: Deoxycholic acid is a bile acid that is 5beta-cholan-24-oic acid substituted by hydroxy groups at positions 3 and 12 respectively. It has a role as a human blood serum metabolite. It is a bile acid, a dihydroxy-5beta-cholanic acid and a C24-steroid. It is a conjugate acid of a deoxycholate.
General Description
This [TM="Certified Spiking Solution" is suitable for use as starting material in the preparation of linearity standards, calibrators, and controls in LC-MS/MS and GC/MS bile acid testing methods. Deoxycholic acid (DCA), also known as deoxycholate and cholanoic acid is a secondary bile acid that aids in the absorption of fats in the intestine. Mass spectrometry-based analysis of DCA is routinely performed in clinical diagnostic testing applications including neonatal testing of inborn errors of bile acid synthesis and differentiating among types of familial intrahepatic cholestasis.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Deoxycholic acid, due to its amphiphilicity, significantly helps to solubilize, emulsify, and absorb fat, vitamins, and cholesterol in the body. High levels of intestinal deoxycholic acid might cause colorectal cancer by inducing oxidative stress and leading to DNA damage. It acts as an oncogene and pro-tumor factor.
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by ingestion and intravenous routes. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Synthesis
The synthesis started from the commercially available 9- hydroxyandrost-4-ene-3,17-dione (114).85 Hydrogenation of 114 gave the saturated 5|?-dione 115 in 85% yield. Alcohol 115 was then dehydrated with H2SO4 in CH2Cl2 to provide 5|?-androst-9(11)-ene-3,17-dione 116 in 95% yield as off-white solid, and this was followed by selective reduction with LiAlH(O-t-Bu)3 to afford (3|á,5|?)-3-hydroxyandrost- 9(11)-en-17-one (117). The crude ketone 117 was submitted to a Wittig reaction with triphenylethylphosphonium bromide in the presence of potassium t-butoxide in THF to yield (3|á,5|?,17E)-pregna-9(11),17-dien-3-ol (118). The crude alcohol 118 was acetylated with Ac2O in the presence of DMAP and Et3N to yield prenyl acetate 119 in 64% across the threestep sequence. Compound 119 was reacted with methyl acrylate in the presence of EtAlCl2 to facilitate conjugate addition and subsequent tertiary carbocation elimination to afford adduct 120, and this resulting olefin was hydrogenated to selectively saturate the cyclopentenyl double bond, resulting in steroid 121 in 85% yield from 119. The remaining alkene 121 then underwent allylic oxidation with tert-butyl hydrogen peroxide and 10% NaOCl aqueous solution in EtOAc to give enone 122, and this material was then hydrogenated over 10% Pd/C in EtOAc to afford the saturated ketone 123. Next, the ketone within 123 was selectively reduced with LiAlH(O-t-Bu)3 in THF to give the 12|á-hydroxy precursor 124 in excellent yield. Finally the remaining methyl ester 124 was hydrolyzed with 20% NaOH aqueous solution in THF/MeOH and acidified with 4 M HCl to give deoxycholic acid (XV) in 99% yield as a white solid.

Metabolism
Deoxycholic acid is not metabolized to any significant extent under normal conditions.
Purification Methods
Reflux the acid with CCl4 (50mL/g), filter, evaporate under vacuum at 25o, recrystallise the residue from acetone and dry it under vacuum at 155o [Trenner et al. J Am Chem Soc 76 1196 1954]. A solution of (cholic acid-free) material (100mL) in 500mL of hot EtOH is filtered, evaporate it to less than 500mL on a hot plate, and pour it into 1500mL of cold diethyl ether. The precipitate, filtered off by suction, is crystallised twice from 1-2 parts of absolute EtOH, to give an alcoholate, m 118-120o, which is dissolved in EtOH (100mL for 60g) and poured into boiling water. After boiling until free of the EtOH, the precipitate is filtered off, dried, ground and dried to constant weight in vacuo [Sobotka & Goldberg Biochem J 26 555 1932]. Deoxycholic acid is also freed from fatty acids and cholic acid by silica gel chromatography and elution with 0.5% acetic acid in ethyl acetate [Tang et al. J Am Chem Soc 107 4058 1985]. It can also be recrystallised from butanone. Its solubility in H2O at 15o is 0.24g/L, but in EtOH it is 22.07g/L. [Beilstein 10 IV 1608.]
Properties of Deoxycholic acid
| Melting point: | 171-174 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 437.26°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 55 º (c=1, EtOH) |
| Density | 0.9985 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 0.004Pa at 20℃ |
| refractive index | 1.4460 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | 0.24 g/L (15°C) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 5.15(at 20℃) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +54±1°, c = 1% in ethanol |
| Water Solubility | 0.24 g/L (15 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,2899 |
| BRN | 3219882 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 83-44-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cholan-24-oic acid, 3,12-dihydroxy-, (3.alpha.,5.beta.,12.alpha.)- (83-44-3) |
Safety information for Deoxycholic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Deoxycholic acid
Deoxycholic acid manufacturer
Clickchem Research LLP
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![(2S)-2-[[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)diphenylsilyl]oxy]methyl]-1,3-oxathiolan-5-ol 5-Acetate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180601/GIF/202532-88-5.gif)
You may like
-
 83-44-3 Deoxycholic acid 98%View Details
83-44-3 Deoxycholic acid 98%View Details
83-44-3 -
 Deoxycholicac Id 99%View Details
Deoxycholicac Id 99%View Details -
 Deoxycholic Acid CAS 83-44-3View Details
Deoxycholic Acid CAS 83-44-3View Details
83-44-3 -
 Deoxycholic Acid extrapure CAS 83-44-3View Details
Deoxycholic Acid extrapure CAS 83-44-3View Details
83-44-3 -
 Deoxycholic acid CAS 83-44-3View Details
Deoxycholic acid CAS 83-44-3View Details
83-44-3 -
 Deoxycholic Acid CAS 83-44-3View Details
Deoxycholic Acid CAS 83-44-3View Details
83-44-3 -
 Deoxycholic Acid (Desoxycholic Acid) CAS 83-44-3View Details
Deoxycholic Acid (Desoxycholic Acid) CAS 83-44-3View Details
83-44-3 -
 DEOXYCHOLIC ACID 90 % AboveView Details
DEOXYCHOLIC ACID 90 % AboveView Details
83-44-3
