DBCO-NHS Ester
- CAS NO.:1353016-71-3
- Empirical Formula: C23H18N2O5
- Molecular Weight: 402.4
- MDL number: MFCD24386367
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
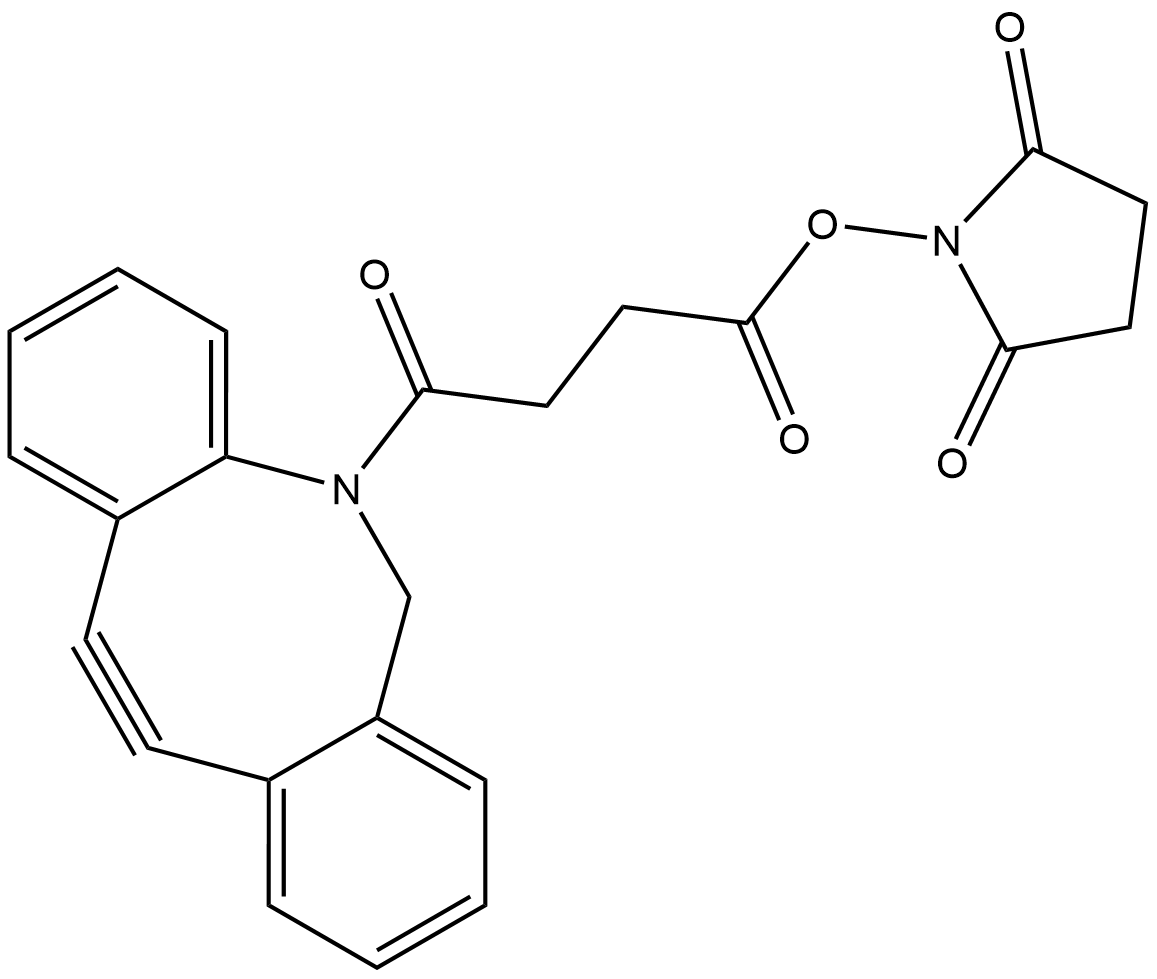
What is DBCO-NHS Ester?
Description
DBCO-NHS Ester is a very popular amine-reactive click chemistry reagent. It can be used to modify an amine-containing molecule in organic solvents (limited solubility in aqueous media). It reacts with primary amines such as the side chain of lysine residues or aminosilane-coated surfaces at neutral or slightly basic pH to form covalent bonds. The low mass weight will add minimal spacer to modified molecules. DBCO is commonly used for copper-free Click Chemistry reactions.
The Uses of DBCO-NHS Ester
DBCO-NHS Ester is a derivative of DBCO (Dibenzylcyclooctyne), used in Cu-free click chemistry. It useful in strain-promoted copper-free azide-alkyne cycloaddition reactions. Used in DNA-Assisted protein analysis such as proximity ligation and extention assays. Intracellular Imaging.
The Uses of DBCO-NHS Ester
DBCO NHS ester contains an NHS carbonate group and a DBCO group. The spacer contains a photocleavable nitrobenzyloxyl group, which can be efficiently cleaved under UV to release the conjugated molecules. DBCO on the other hand readily react with azide bearing biomolecule through a copper-free click reaction instantly and in high yield.
DBCO-NHS Ester is a very popular amine-reactive click chemistry reagent. It can be used to modify an amine-containing molecule in organic solvents (limited solubility in aqueous media). It reacts with primary amines such as the side chain of lysine residues or aminosilane-coated surfaces at neutral or slightly basic pH to form covalent bonds. The low mass weight will add minimal spacer to modified molecules. DBCO is commonly used for copper-free Click Chemistry reactions.
What are the applications of Application
Dibenzocyclooctyne-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl ester is an amine reactive crosslinker for incorporation of the cyclooctyne moiety
Properties of DBCO-NHS Ester
| Boiling point: | 670.2±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.43±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO, DCM, DMF |
| pka | -0.23±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Stability: | Moisture Sensitive |
Safety information for DBCO-NHS Ester
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for DBCO-NHS Ester
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium 3-Bromopyrazole (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-hexahydro-5-Triethyl silyloxy-4-((E)-3-oxo-5-phenylpent-1- enyl)cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one. 1-Chlorocarbonyl-4-piperidinopiperidine 1-Bromo-4-phenyl-2-Butanone 4-Amino-2-fluoro-N-methylbenzamide 1,1'-Carbonyldiimidazole SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTIONRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Dbco-nhs ester 95% CAS 1353016-71-3View Details
Dbco-nhs ester 95% CAS 1353016-71-3View Details
1353016-71-3 -
![Dimethyl [2-oxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propyl]phosphonate 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) Dimethyl [2-oxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propyl]phosphonate 99%View Details
Dimethyl [2-oxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propyl]phosphonate 99%View Details
54094-19-8 -
 85-81-4 99%View Details
85-81-4 99%View Details
85-81-4 -
![208111-98-2 (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-5-(Benzoyloxy)hexahydro-4-[(1E)-3-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-1-buten- 1-yl]-2H-cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 208111-98-2 (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-5-(Benzoyloxy)hexahydro-4-[(1E)-3-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-1-buten- 1-yl]-2H-cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one 99%View Details
208111-98-2 (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-5-(Benzoyloxy)hexahydro-4-[(1E)-3-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-1-buten- 1-yl]-2H-cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one 99%View Details
208111-98-2 -
 2033-24-1 99%View Details
2033-24-1 99%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 Meldrums acid 2033-24-1 99%View Details
Meldrums acid 2033-24-1 99%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 Cyaclopentane carboxylic acid 99%View Details
Cyaclopentane carboxylic acid 99%View Details
3400-45-1 -
 2-Aminopyridine 504-29-0 99%View Details
2-Aminopyridine 504-29-0 99%View Details
504-29-0