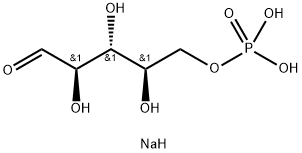
D-Ribose
Synonym(s):D -Ribofuranose
- CAS NO.:50-69-1
- Empirical Formula: C5H10O5
- Molecular Weight: 150.13
- MDL number: MFCD00135453
- EINECS: 200-059-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18
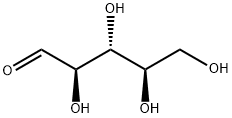
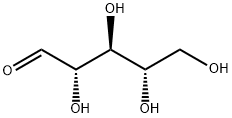
What is D-Ribose?
Description
D-ribose is an important five-carbon monosaccharide with the chemical formula C5H10O5. It is an important constituent of ribonucleic acid (RNA) and ATP, and plays an important role in the formation of life. It is also an important pharmaceutical intermediate for the production of various nucleic acid drugs.
Chemical properties
D-Ribose is a five-carbon sugar with strong water solubility and sweet taste, also known as D-ribofuranose. It is used by all living cells and is an essential component in living organisms for energy production. It is widely present in the furan form.
Occurrence
Reported found in boiled crab, hen egg, catfish, whitefish, haddock, stored beef, stored veal, milk, applesauce, potato, rapeseed, roasted coffee, fresh coffee and shrimp.
The Uses of D-Ribose
D-Ribose is produced by microorganism fermentation of glucose in a fermentation culture medium without adding calcium carbonate.
Definition
ChEBI: D-ribose is a ribofuranose having D-configuration. It is a naturally occurring monosaccharide found in the cells and particularly in the mitochondria is essential in energy production.
Preparation
D-Ribose is obtained by using D-glucose as a raw material, inserting bacteria or Bacillus subtilis for fermentation, and separating and refining the fermentation product.(By fermentation technology)
Biological Functions
D-ribose is a penta-sugar precursor of some amino acids like glutamate, histidine, proline, and arginine. This substance is transformed into piruvate, enters Krebs's cycle, and has a crucial role in energetic metabolism; it is also involved in glycogen synthesis. The non-oxidative transketolase PPP reaction can be directly synthesized by transferring a keto group to glyceraldehyde 3-phoshate from fructose 6-phosphate. Both these substrates are intermediate products of glycolysis[1].
Biological Activity
D-ribose is a natural sugar that our bodies produce for a variety of purposes most notably encrgy in the form of ATP(adenosine triphosphate), which powers every cell in our body. Ribose is crucial for the synthesis of energy (ATP) and without it, your cells run out of energy and the health of the cell is compromised. Supplementing with ribose improves cell function by restoring energy.
One of the most vital organs to suffer energy depletion is the heart. That is why so much of the research on D-ribose has focused on the impact of supplement ribose in heart disease. Although ribose is classified as a sugar, when taken orally, it does not have any impact on blood sugar like glucose. Instead, it is used for energy production and energy recovery. Every cell in the body has the capacity to make ribose. But more ribose may be needed than the cell can produce when cells are metabolically stressed, such as with strenuous exercise or disease. When the cells are metabolically stressed they tend to consume more glucose rather than producing more ribose. This can dramatically affect recovery.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Ribose is an aldopentose monosaccharide that is phosphorylated into D-ribose 5-phosphate by ribokinase.
Side Effects
D-ribose is a dietary supplement approved by the US FDA. It is generally considered safe for dosage of ribose is less than 15g/d. However, possible side effects include diarrhea, stomach discomfort, nausea, headache, and low blood sugar.
Purification Methods
Crystallise -D(-)-ribose from aqueous 80% EtOH, dry it under vacuum at 60o over P2O5 and store it in a vacuum desiccator. It exhibits a complex mutarotation with : [] D 10 -23.1o (1.5minutes), -21.3o (5minutes), -19.5o (10minutes), -19.1o (30minutes), -21.2o (60minutes), -23.1o (120minutes), -23.7o (300minutes), (c 4.5, H2O) [Phelps et al. J Am Chem Soc 56 748 1934]. 1H NMR in D2O at 44o shows 17% -pyranose, 59% -pyranose, 9% -furanose and 15% -furanose forms with furanose -H at 5.34ppm (J 3.0Hz) and -H at 5.31 (J 1.7Hz) [Angyal Adv Carbohydr Chem 42 15 1984, Angyal & Pickles Aust J Chem 25 1711 1972]. The phenylhydrazone crystallises from aqueous pyridine in yellow needles, m 163-164o, and the benzylphenylhydrazone has m 127-128o [Snowden J Am Chem Soc 72 808 1950.] [Beilstein 1 IV 4211.]
References
[1] Simonetta Croci. “Potassium bicarbonate and D-ribose effects on A72 canine and HTB-126 human cancer cell line proliferation in vitro.” Cancer Cell International 11 (2011): 30.
Properties of D-Ribose
| Melting point: | 88-92 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 191.65°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | -20.8 º (c=4, H2O) |
| Density | 1.1897 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | -21 ° (C=1, H2O) |
| FEMA | 3793 | D-RIBOSE |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 g/mL, clear, colorless to light yellow |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 12.46±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | White to light beige or slightly yellow |
| PH Range | 7 |
| optical activity | [α]21/D 19.7°, c = 4 in H2O |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. Insoluble in ether. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,8204 |
| BRN | 1723081 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 50-69-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | D-Ribose(50-69-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | D-Ribose (50-69-1) |
Safety information for D-Ribose
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for D-Ribose
| InChIKey | HMFHBZSHGGEWLO-SOOFDHNKSA-N |
D-Ribose manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



![RIBOSE, D-, [1-14C]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/4005-39-4.gif)
You may like
-
 D-Ribose 99%View Details
D-Ribose 99%View Details -
 D-Ribose for tissue culture CAS 50-69-1View Details
D-Ribose for tissue culture CAS 50-69-1View Details
50-69-1 -
 D-Ribose extrapure CAS 50-69-1View Details
D-Ribose extrapure CAS 50-69-1View Details
50-69-1 -
 D-Ribose 98% CAS 50-69-1View Details
D-Ribose 98% CAS 50-69-1View Details
50-69-1 -
 D-Ribose CASView Details
D-Ribose CASView Details -
 D-Ribose (CAS Number: 50-69-1)View Details
D-Ribose (CAS Number: 50-69-1)View Details
50-69-1 -
 D Ribose PowderView Details
D Ribose PowderView Details
50-69-1 -
 D-RiboseView Details
D-RiboseView Details
50-69-1
